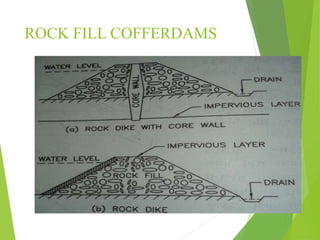
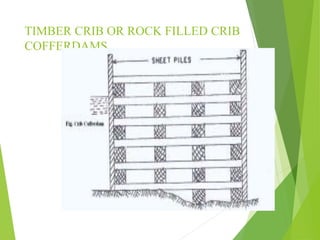
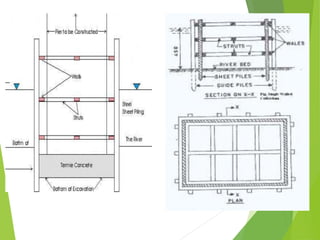
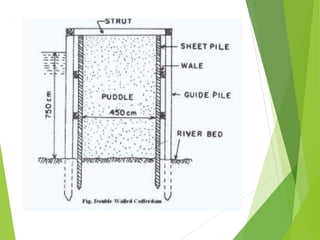
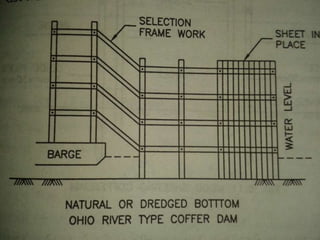
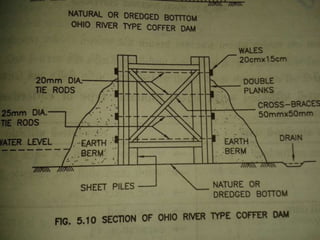
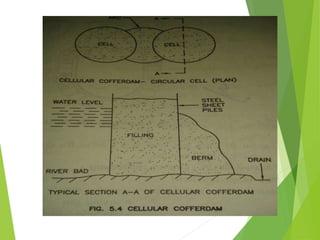
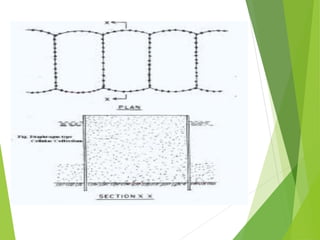
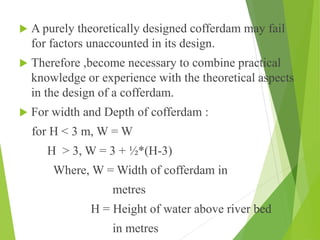
Coffer dams are temporary structures built to retain water and soil in order to create a dry work area for construction projects. There are several types of coffer dams suited to different conditions, including earth-filled, sheet pile, and cellular designs. Key considerations in selecting a coffer dam include water depth, area size, soil/river bed conditions, and potential for erosion or flooding. Proper design is needed to withstand hydrostatic pressures and ensure structural integrity until the permanent structure is complete.