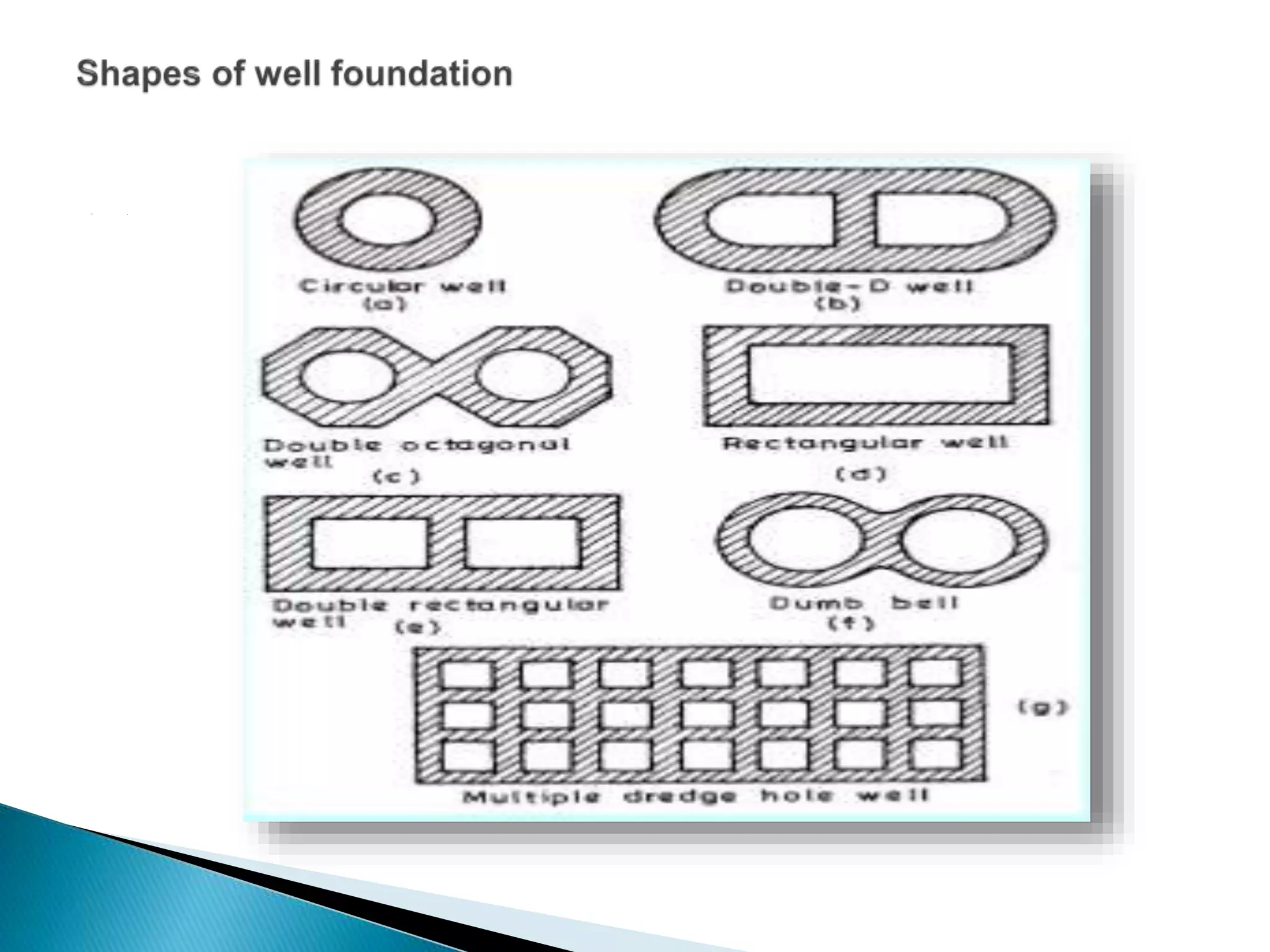
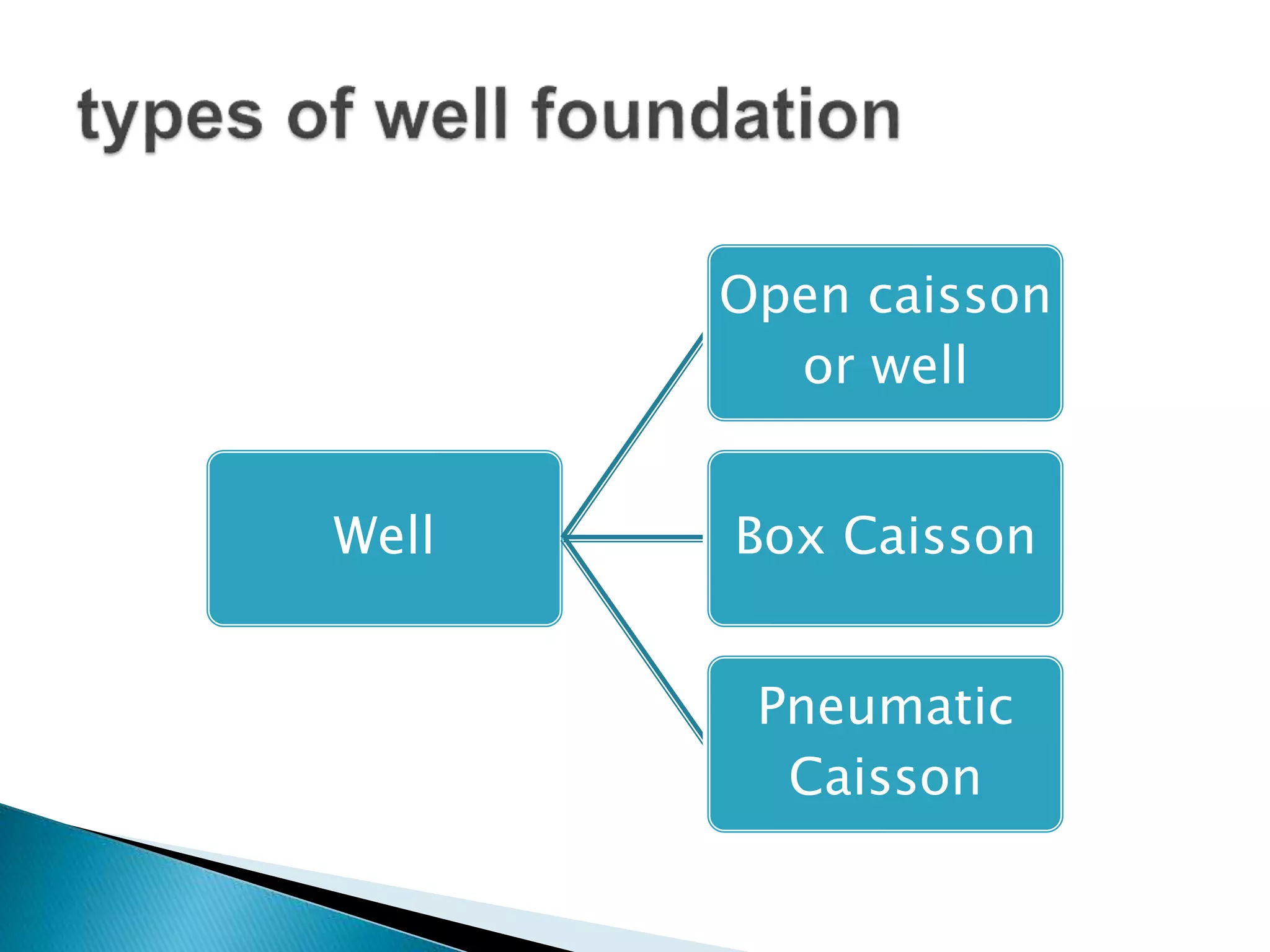
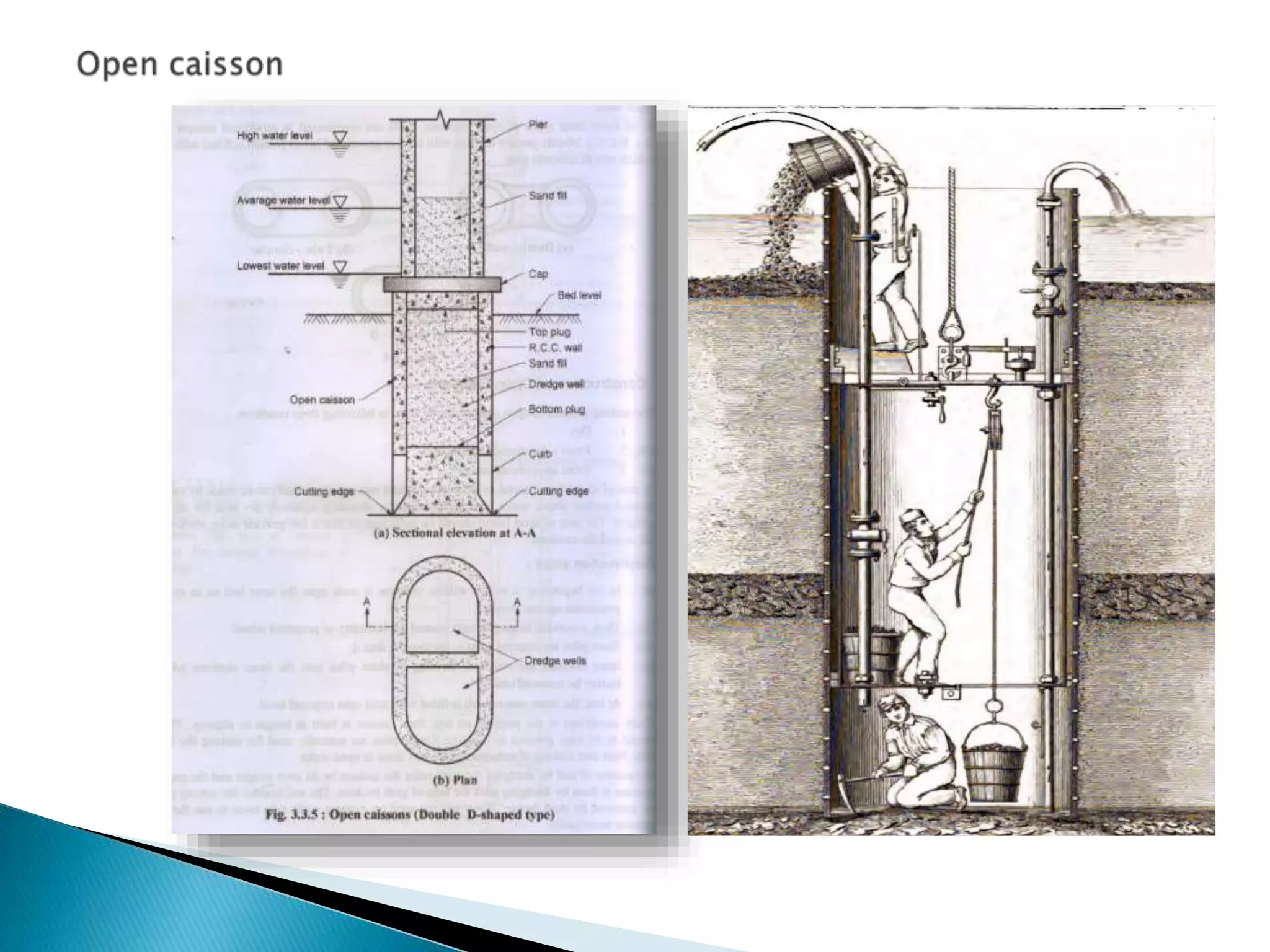
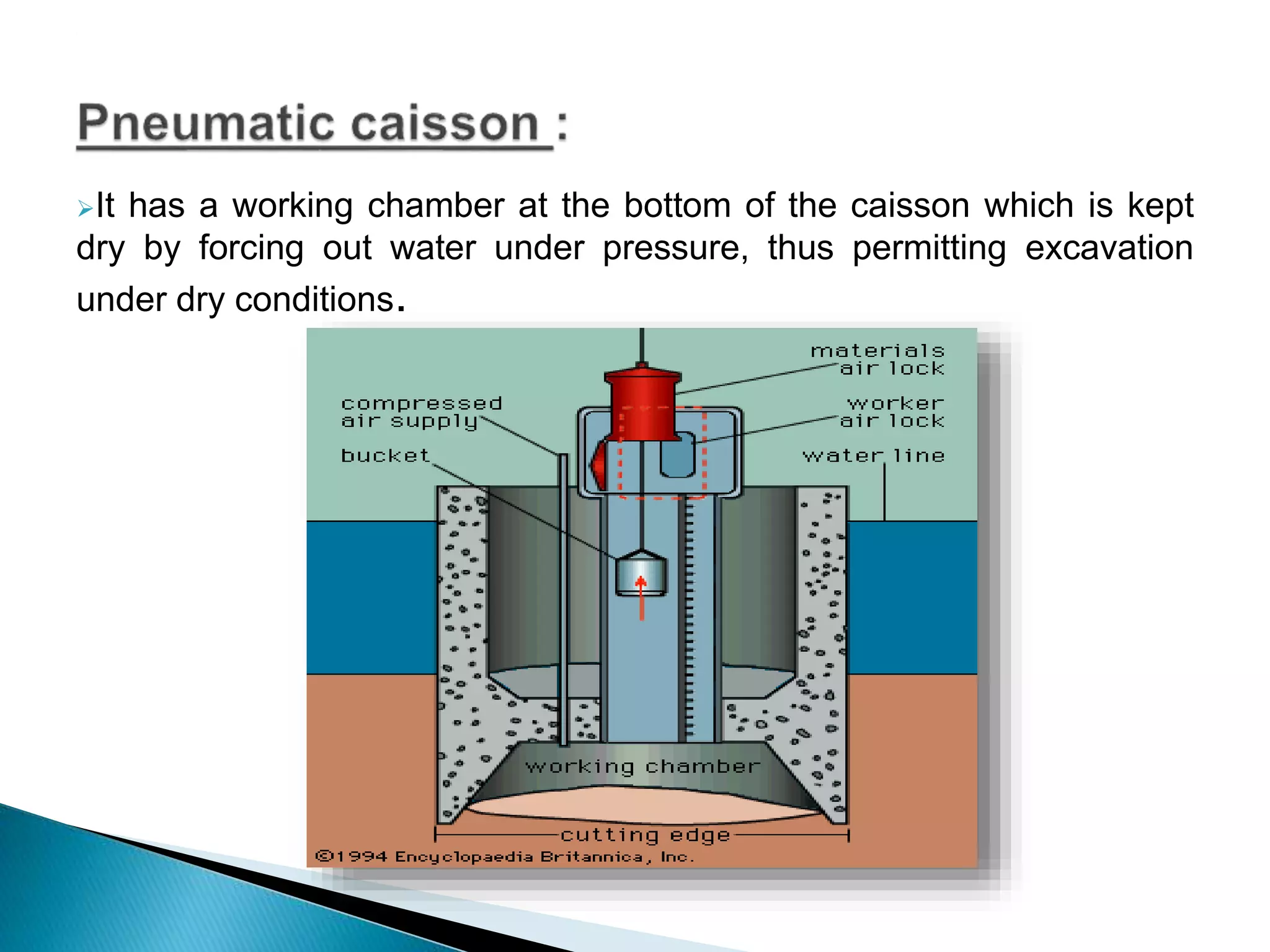
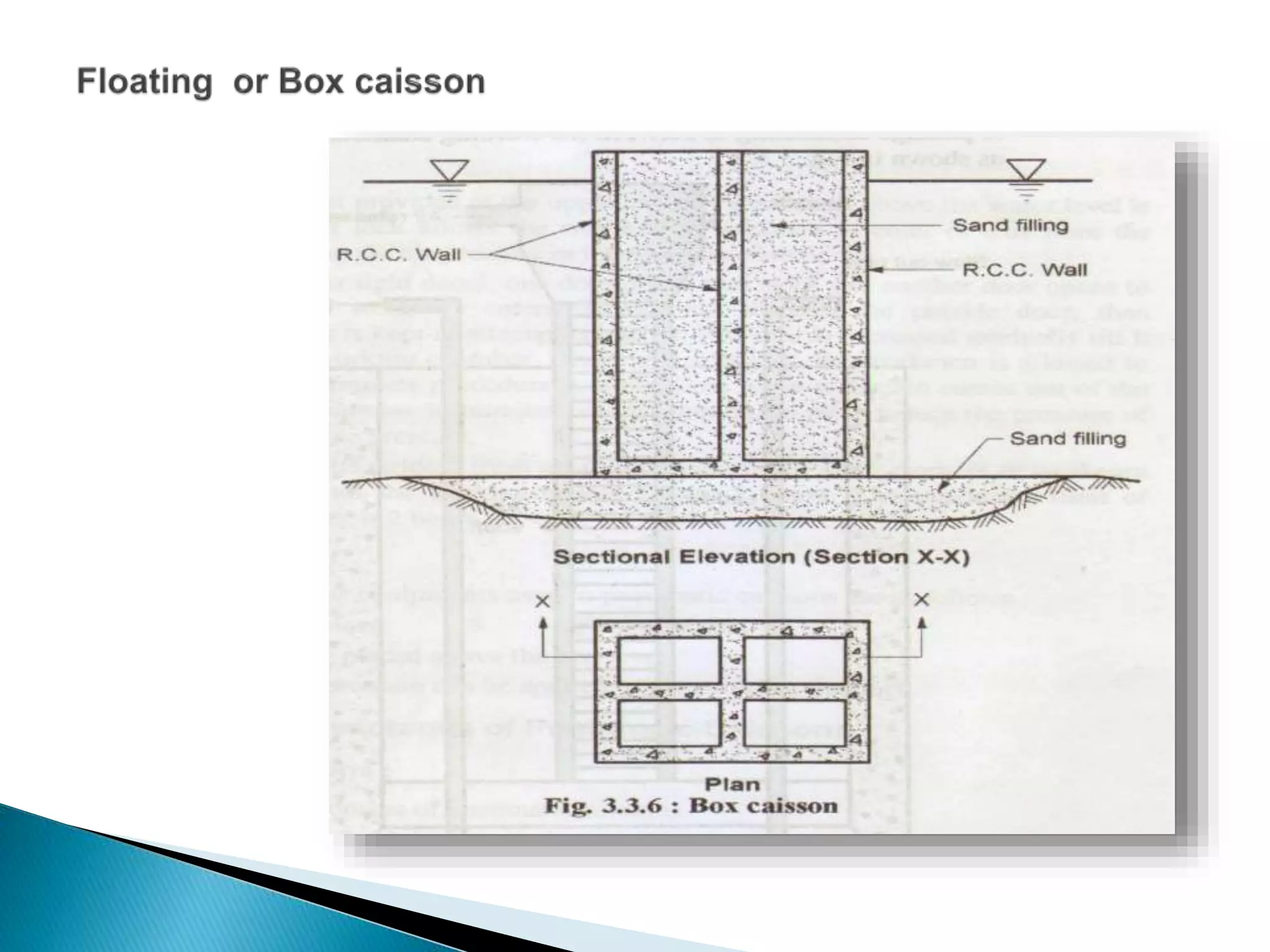
This document discusses different types of well foundations used in India for major bridges. Well foundations are commonly used in India and have been for centuries, with a notable example being the foundations of the Taj Mahal. The document outlines different shapes of well foundations, including circular, double D, twin circular, double octagonal, and rectangular wells. It also discusses open caisson foundations, box caisson foundations, and pneumatic caisson foundations, providing details on their construction methods and advantages and disadvantages.