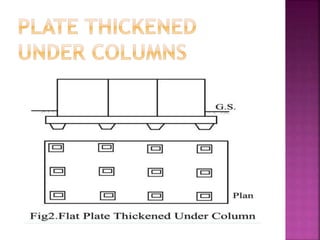
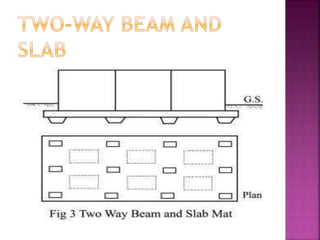
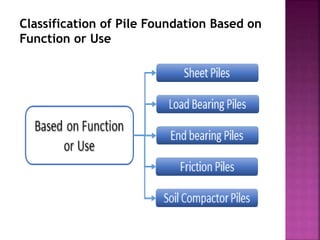
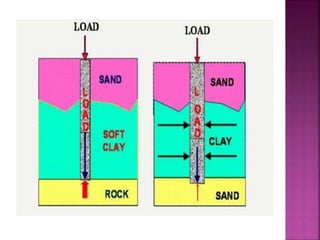
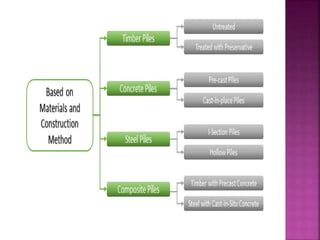
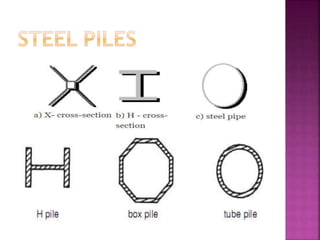
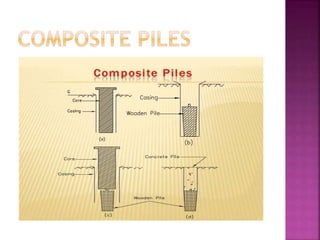
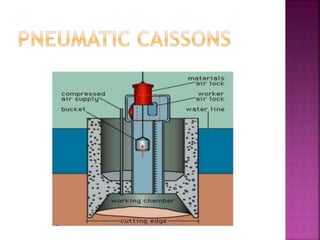
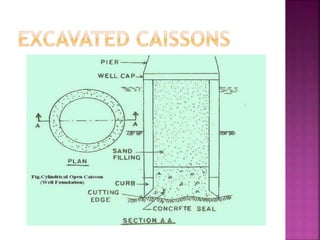
The document discusses the significance of foundations in construction, explaining their role in providing stability and load distribution for structures. It categorizes foundations into shallow (e.g., isolated spread footings, raft foundations) and deep (e.g., pile, pier, and caisson foundations), detailing the various types and their specific functions. Additionally, it outlines the principles of load transfer and the unique advantages of each foundation type in different soil conditions and structural requirements.