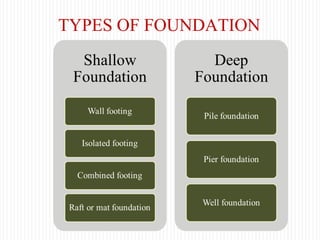
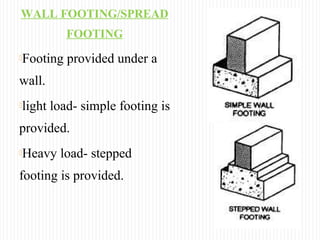
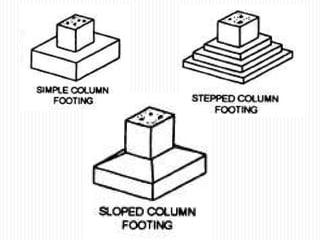
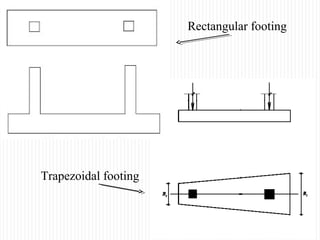
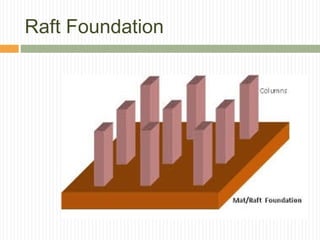
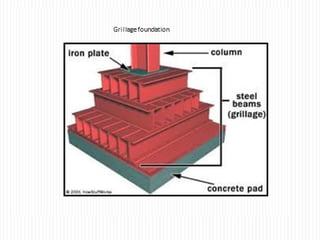
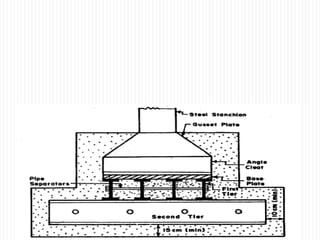
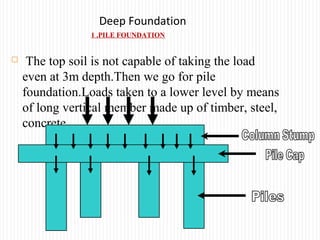
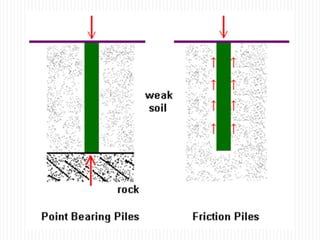
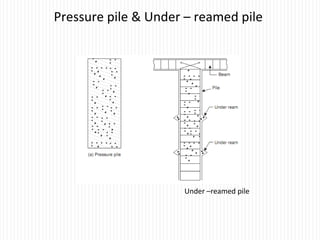
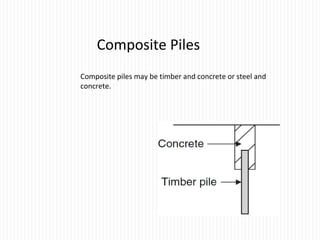
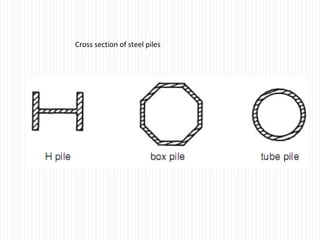
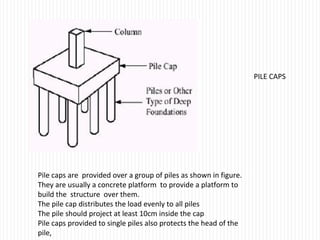
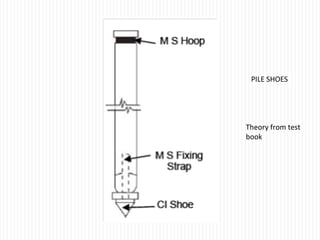
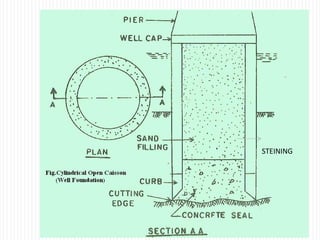
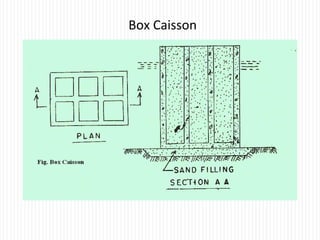
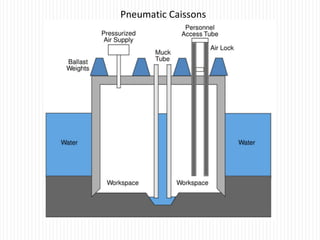
The document discusses different types of foundations used to transmit the load of a building to the underlying soil. It describes shallow foundations such as wall footings, isolated column footings, and combined footings. Deep foundations including pile foundations, well foundations using caissons and cofferdams, are also summarized. Specific foundation types are defined, like mat/raft foundations used for soft soils, and grillage foundations for supporting high-rise steel structures.