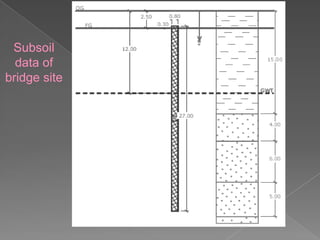
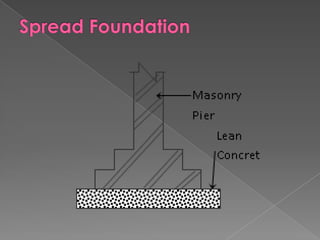
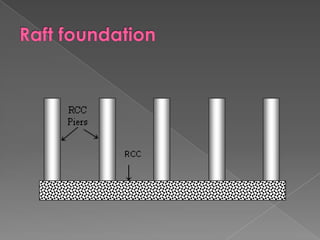
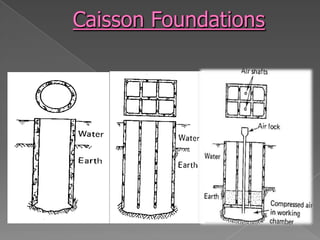
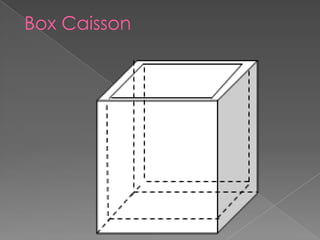
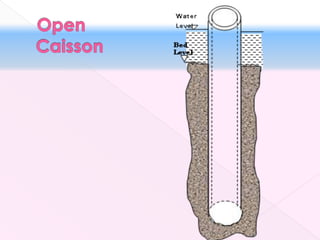
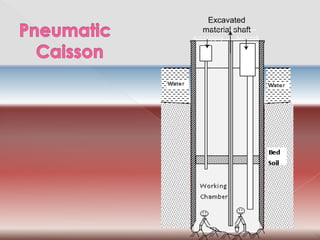
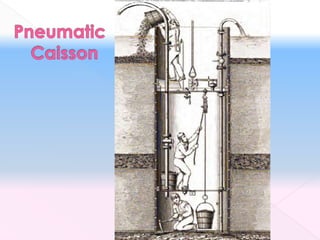
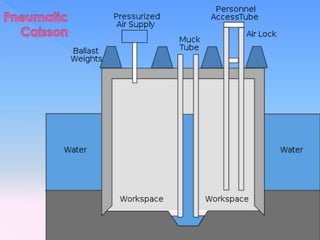
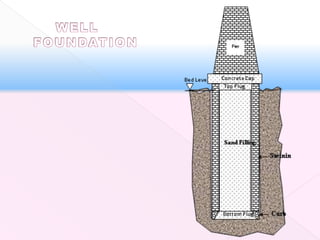
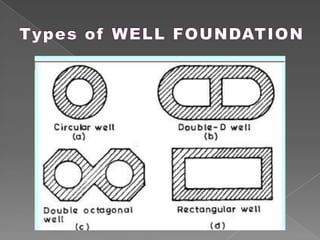
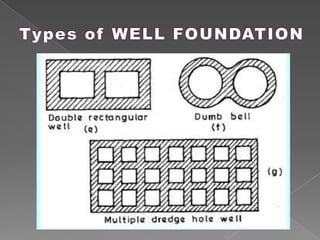
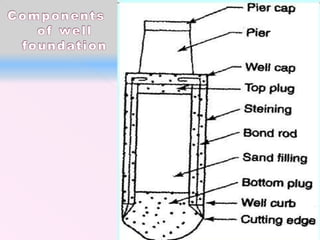
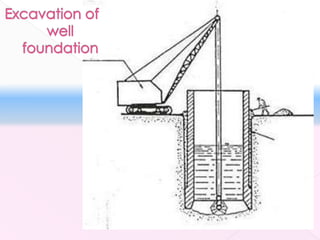
The document discusses different types of bridge foundations. Shallow foundations include spread foundations and raft foundations, which are suitable for small bridges on soil with good bearing capacity. Deep foundations are needed when the bearing soil is deep below ground or water levels are high. Common deep foundation types are pile foundations, caisson foundations, and well foundations. Caisson foundations involve sinking large, reinforced concrete boxes into the ground under water. Well foundations involve constructing circular brick or stone structures that are filled with compacted soil. The type of foundation chosen depends on the subsoil conditions and hydraulic requirements at the bridge site.