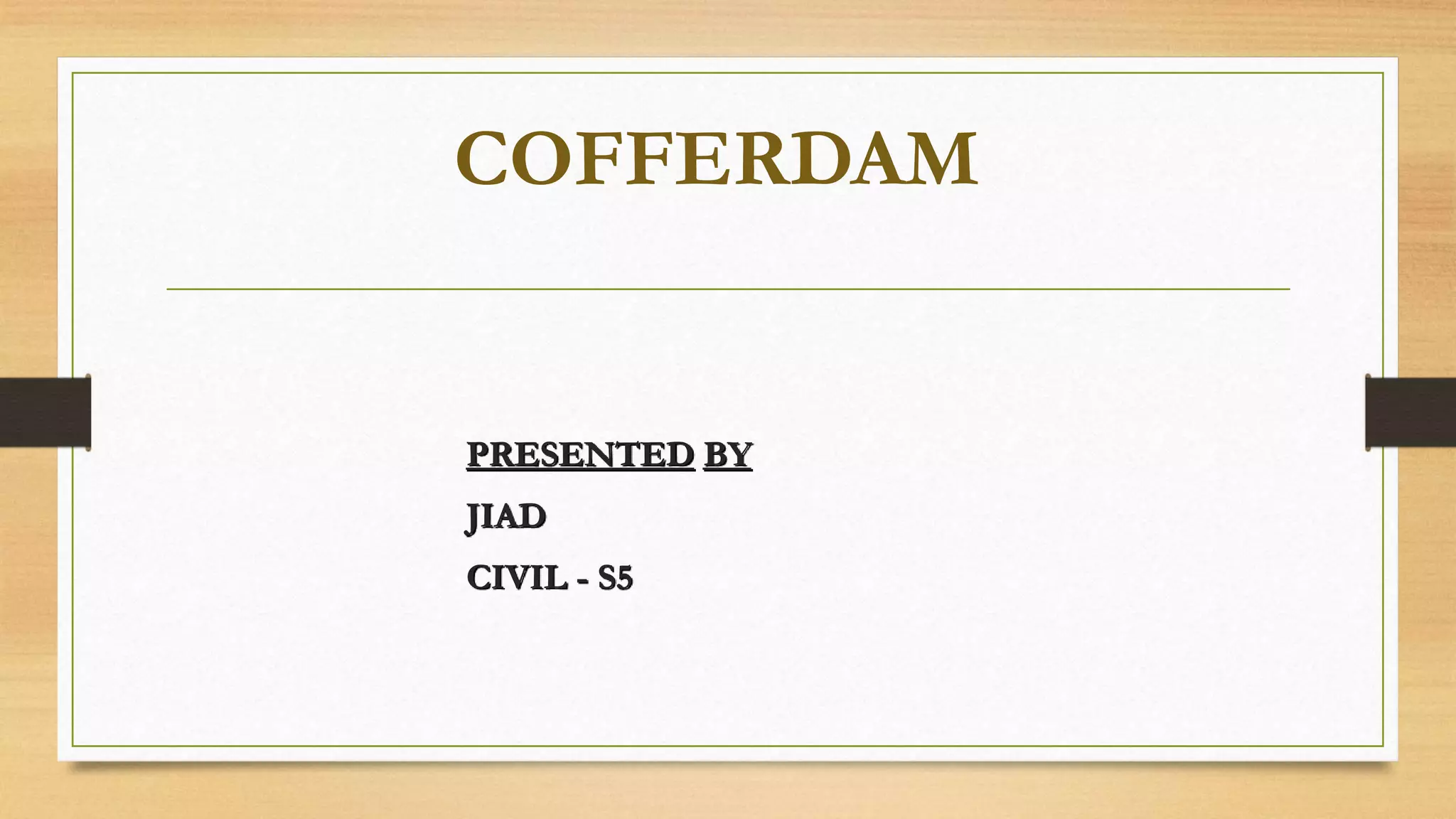
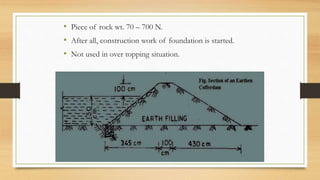
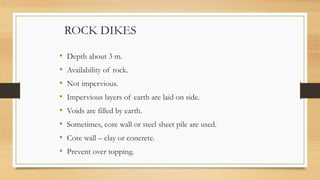
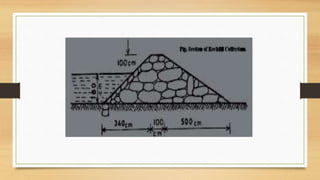
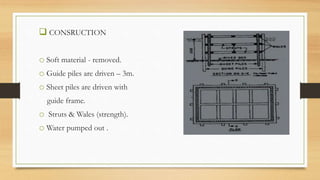
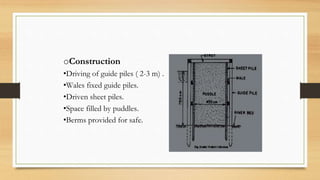
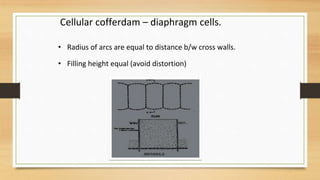
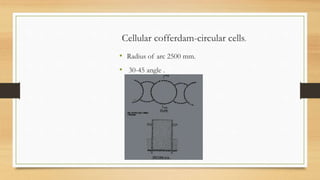
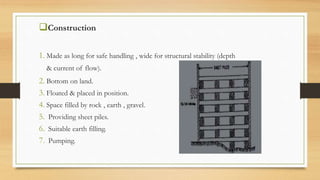
A cofferdam is a temporary structure used to keep water or soil out of an excavation for construction. It must be watertight but does not require absolute water tightness, and various materials like earth, timber, steel, and concrete can be used depending on factors such as depth and soil condition. Different types of cofferdams include dikes, single wall, double wall, cellular, rock-filled crib, and concrete, each having unique construction methods and applications.