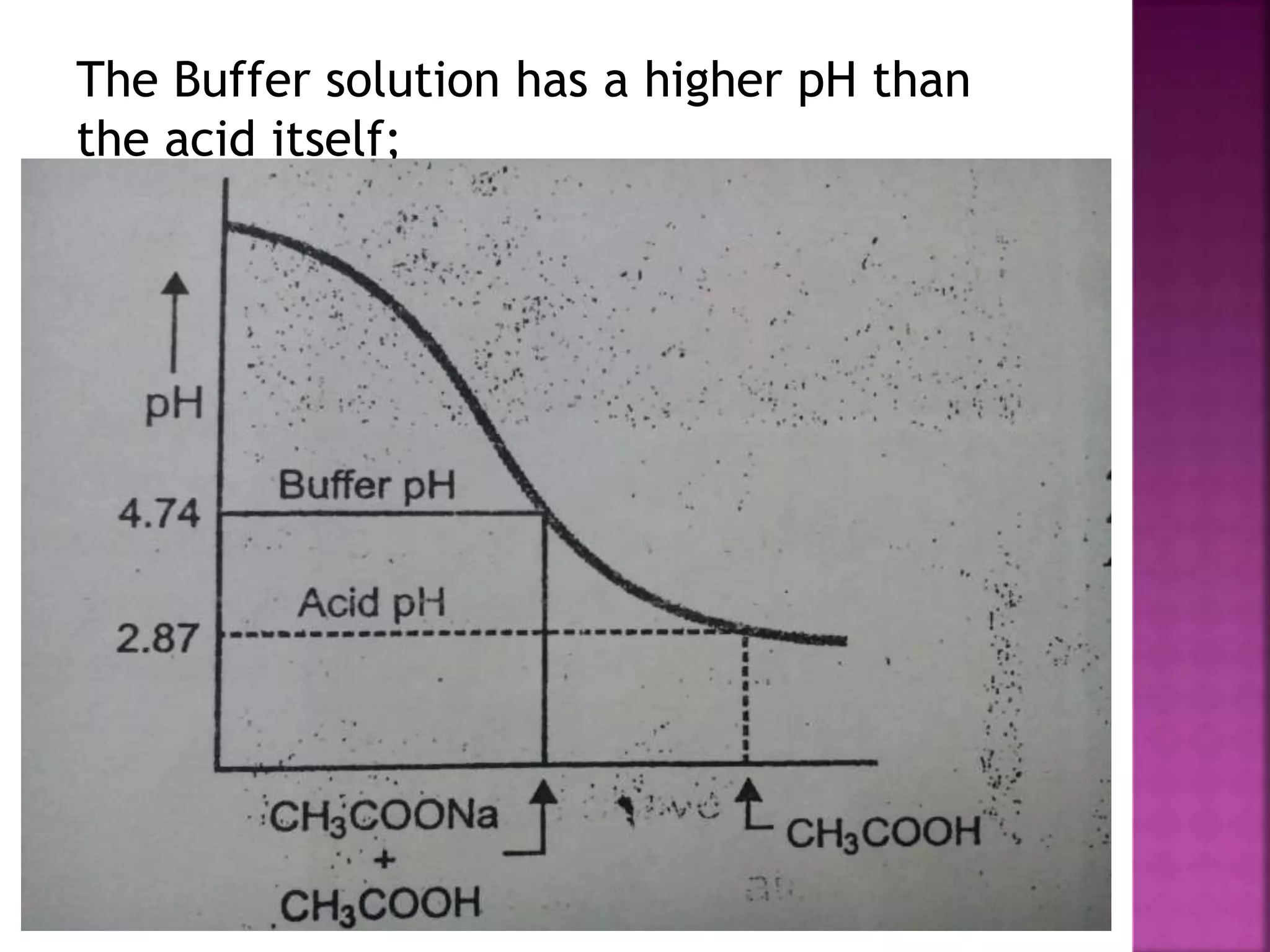
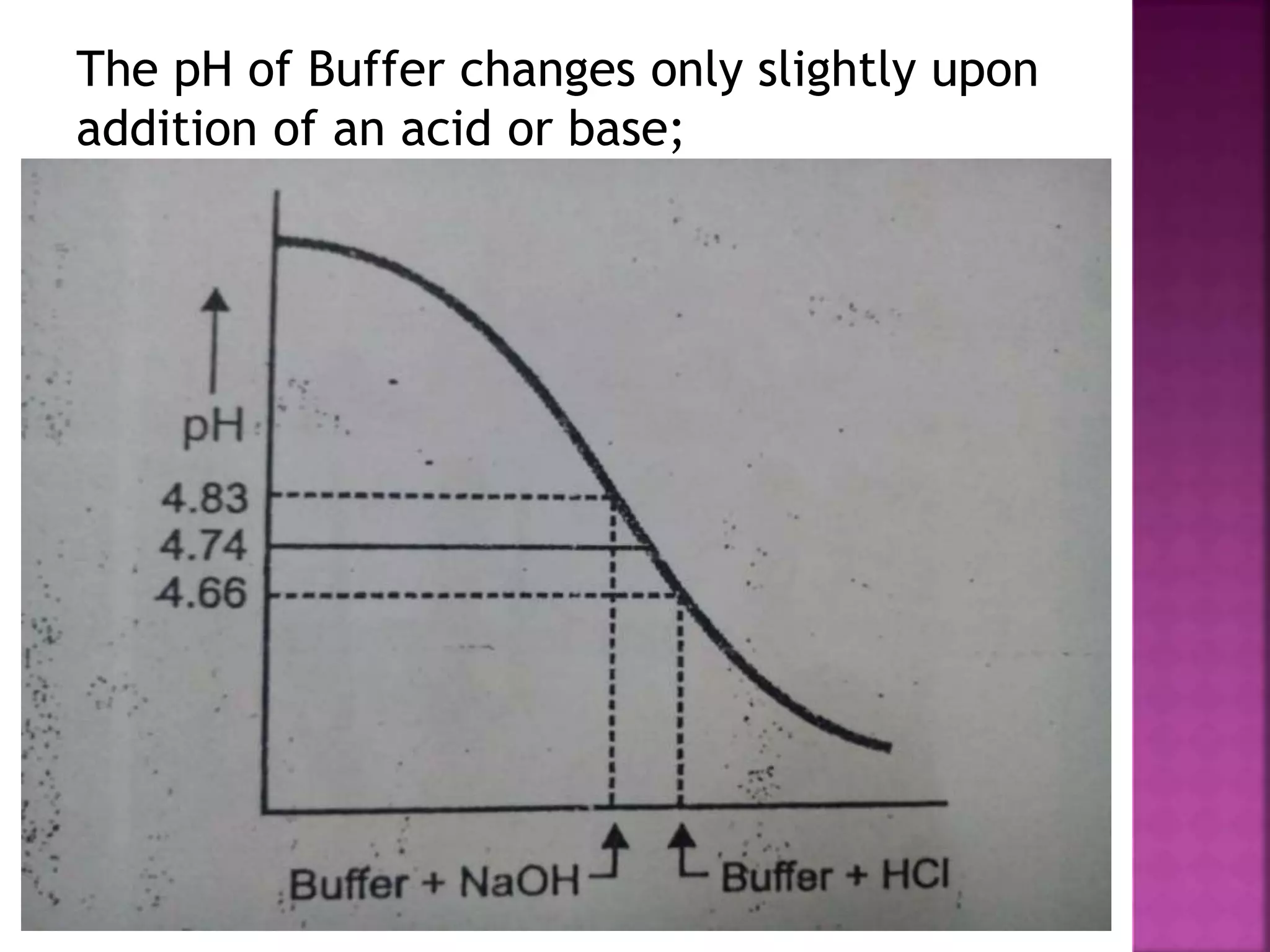
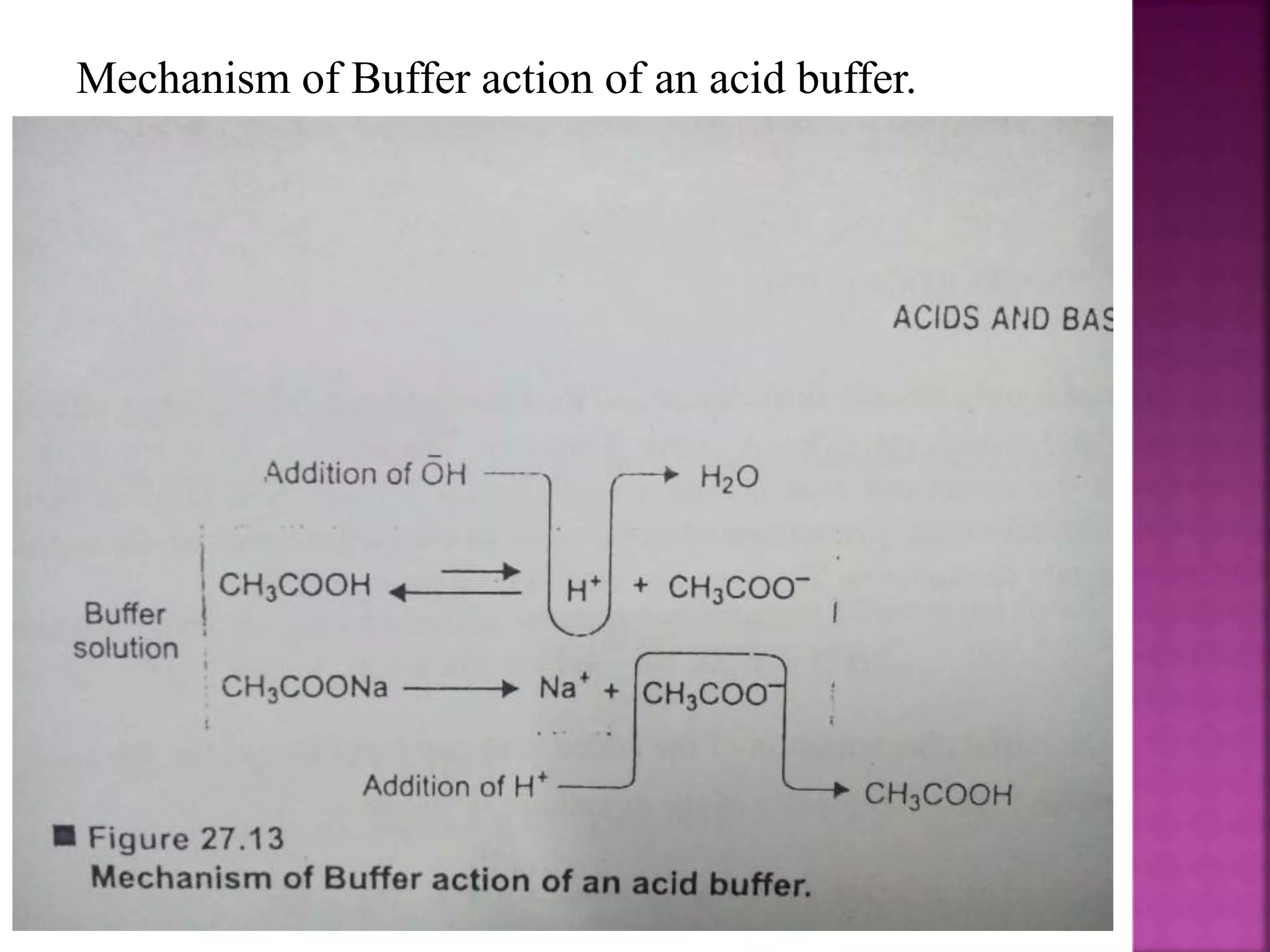
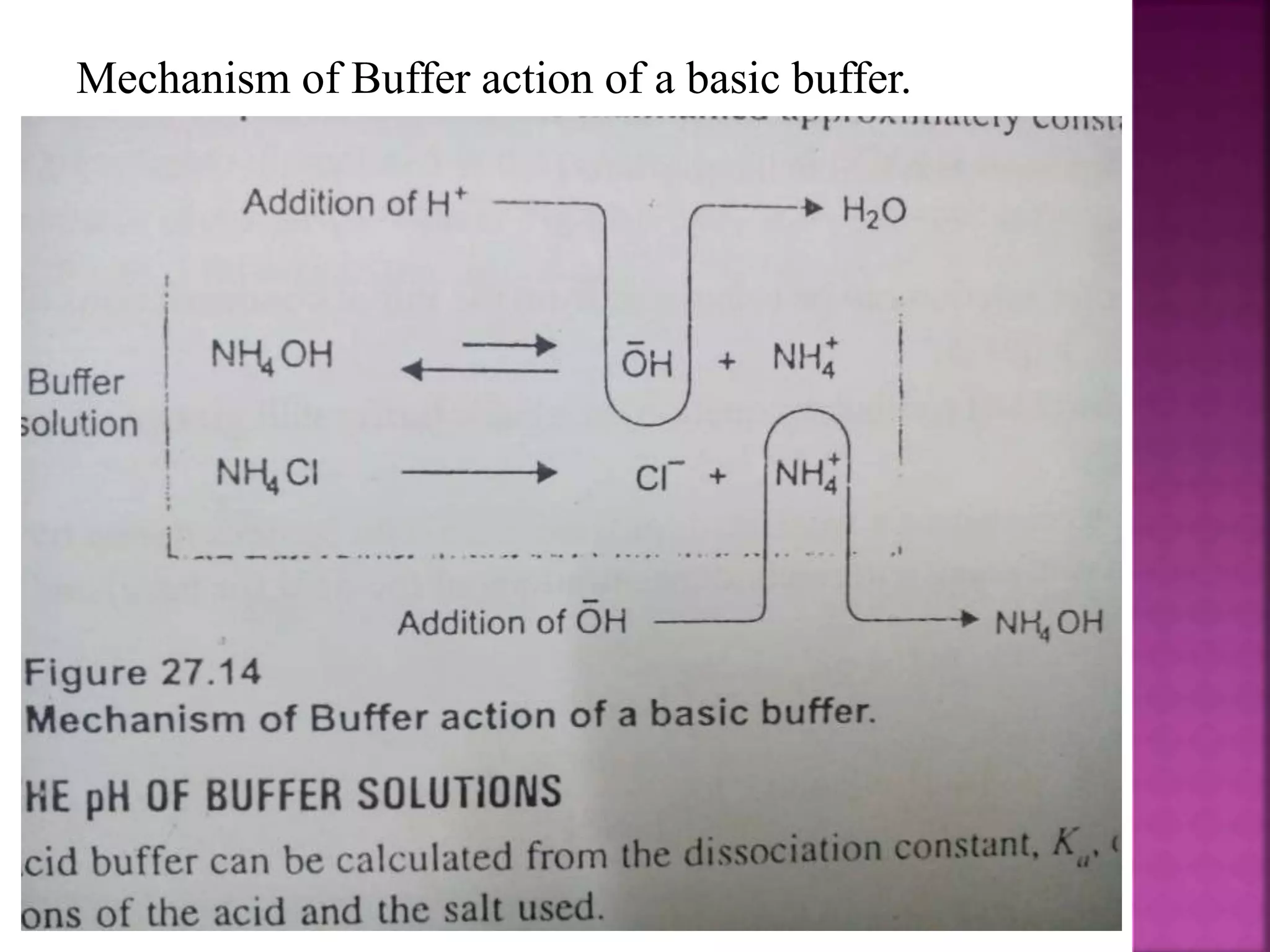
1. A buffer solution maintains a fairly constant pH upon the addition of small amounts of acid or base. There are two types: acidic buffers containing a weak acid and salt of that acid, and basic buffers containing a weak base and salt of that base.
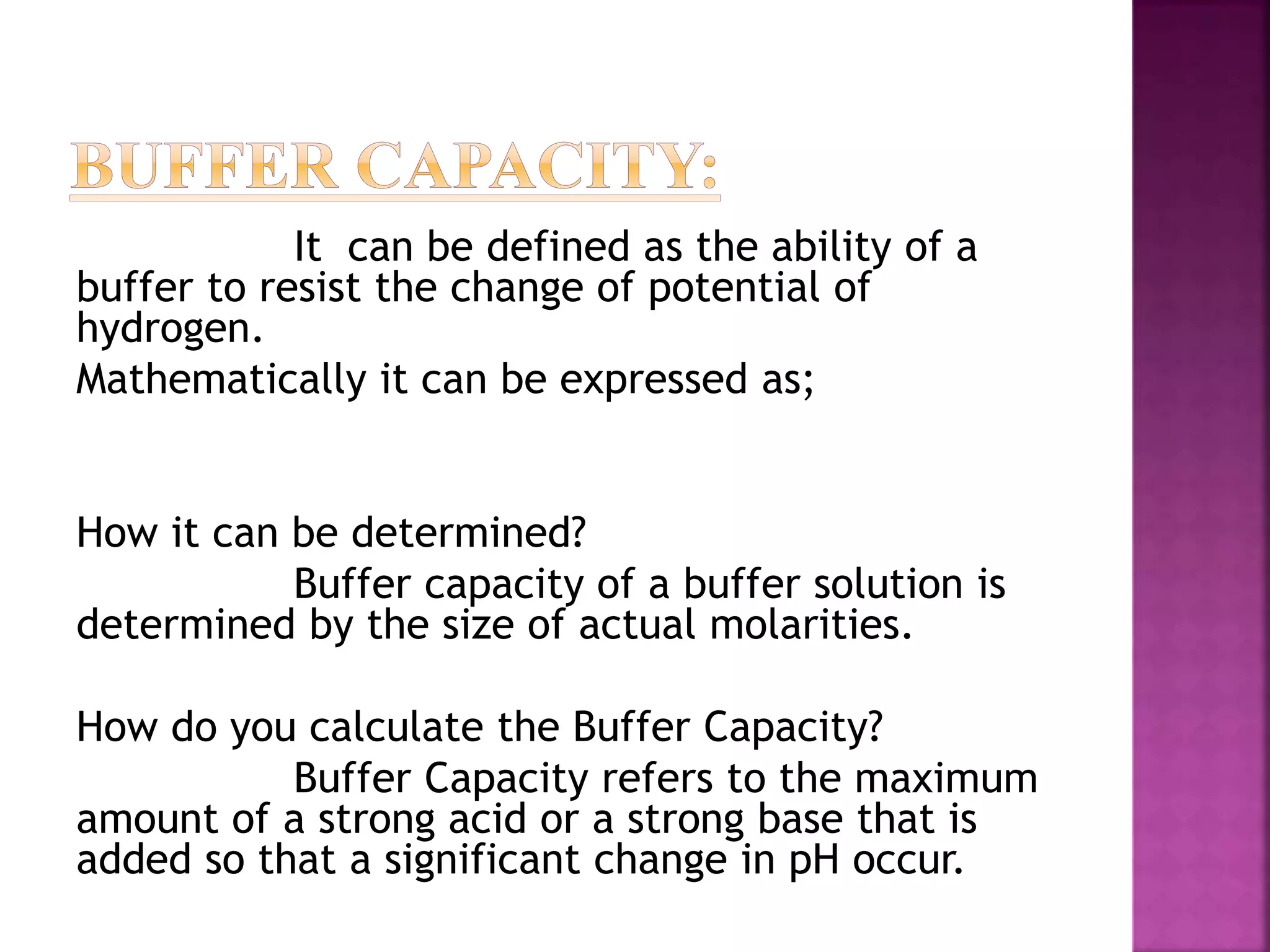
2. Buffer solutions resist changes in pH when acids or bases are added. The buffer capacity depends on the concentrations of the buffer components and how close the pKa is to the solution's pH.
3. Common acid-base indicators like phenolphthalein and methyl orange change color over a specific pH range, signaling the endpoint in acid-base titrations.