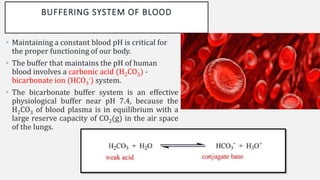
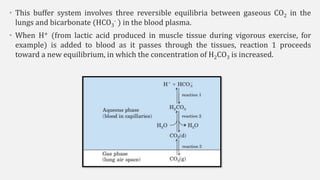
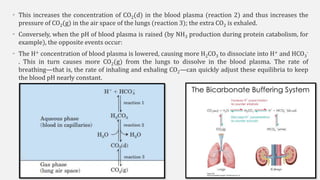
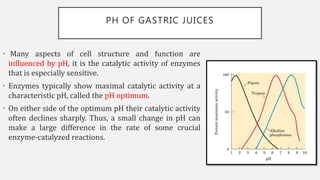
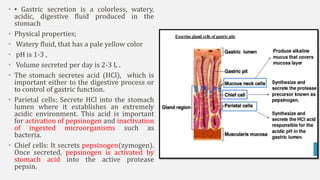
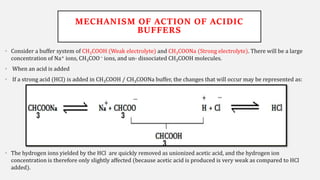
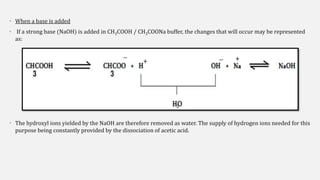
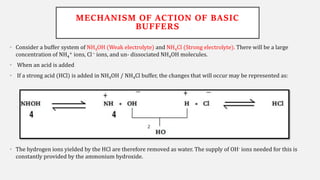
The document discusses pH, buffers, and their importance in maintaining blood pH homeostasis and gastric juice pH. It defines pH as a measure of hydrogen ion concentration and describes the pH scale. It explains how buffers work by achieving resistance to pH change through an equilibrium between a weak acid and its conjugate base. Important buffers mentioned are the bicarbonate buffer system, which maintains blood pH, and the acidic gastric juices, with a pH of 1-3 maintained by secreted hydrochloric acid.

![PH EQUATION
• The equation for calculating pH was proposed in 1909 by Danish
biochemist Søren Peter Lauritz Sørensen:
pH = -log[H+]
• Where log is the base-10 logarithm and [H+] stands for the hydrogen
ion concentration in units of moles per liter solution. The term "pH"
comes from the German word "potenz," which means "power,"
combined with H, the element symbol for hydrogen, so pH is an
abbreviation for "power of hydrogen."](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarphbuffers-220108163020/85/ph-and-buffers-3-320.jpg)




![PREPARING BUFFER SOLUTIONS
HANDERSON HASSELBALCH EQUATION
• Determines the exact amount of acid and
conjugate base needed to make a buffer of
a certain pH, using the Henderson-Hassel
Bach equation:
pH= pKa + log (
[A−]
[HA]
)
where pH is the concentration of [H+], pKa is
the acid dissociation constant, and [ log{A-}]
and [ log{HA}] are concentrations of the
conjugate base and starting acid.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarphbuffers-220108163020/85/ph-and-buffers-13-320.jpg)