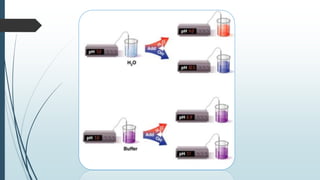
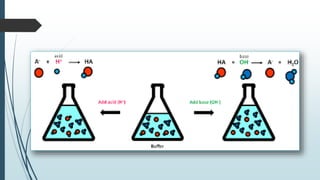
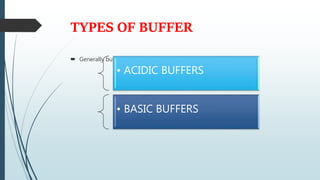
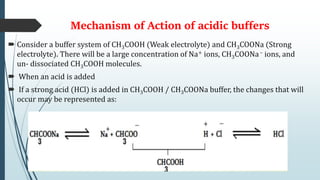
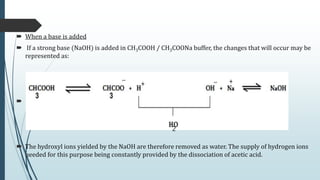
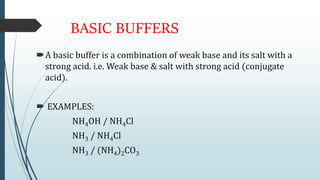
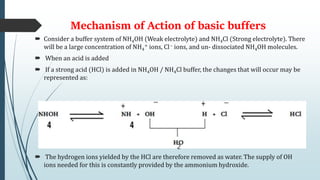
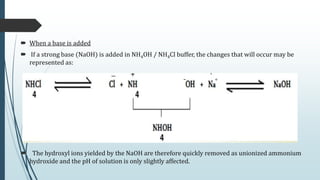
Buffer solutions are aqueous solutions that resist changes in pH upon the addition of small amounts of acid or base. They work by having both a weak acid and its conjugate base present in solution. Common examples include acetate, phosphate, and bicarbonate buffers. Buffers are important in biological systems like blood to regulate pH, and are also used in pharmaceuticals, biochemical assays, food, and other applications where constant pH is necessary. Their ability to neutralize added acid or base comes from the equilibrium between the weak acid and its conjugate base that can absorb added H+ or OH- ions.






![Preparing a Buffer Solution
In the first method, prepare a solution with an acid and its conjugate base by
dissolving the acid form of the buffer in about 60% of the volume of water required
to obtain the final solution volume. Once the pH is correct, dilute the solution to the
final desired volume.
Alternatively, you can prepare solutions of both the acid form and base form of the
solution. Both solutions must contain the same buffer concentration as the
concentration of the buffer in the final solution. To get the final buffer, add one
solution to the other while monitoring the pH.
In a third method, you can determine the exact amount of acid and conjugate base
needed to make a buffer of a certain pH, using the Henderson-Hassel Bach equation:
pH=pKa+log([A−]/[HA])
where pH is the concentration of [H+], pKa is the acid dissociation constant, and [
log{A-}] and [ log{HA}] are concentrations of the conjugate base and starting acid.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bufferrdtpp-200819093051/85/Buffers-15-320.jpg)








![Carbonate Buffer In Nature
In natural systems, there are many buffers. One that is
important in surface waters is the carbonic acid/bicarbonate
buffer.
Calcium carbonate, [Ca][CO3] is a very common mineral.
Limestone is one familiar form of calcium carbonate. Acids in
acid rain promote the dissolution of calcium carbonate by
reacting with the carbonate anion.
This produces a solution of bicarbonate. Because surface
waters are in equilibrium with atmospheric carbon dioxide
there is a constant concentration of carbonic acid, H2CO3, in
the water.
The presence of limestone and other calcium carbonate rock
in lakes and streams helps to maintain a constant pH because
the minerals react with the excess acid.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bufferrdtpp-200819093051/85/Buffers-27-320.jpg)
