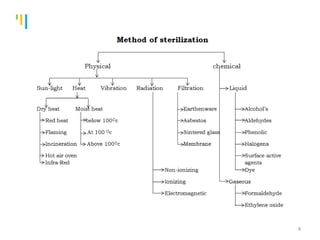
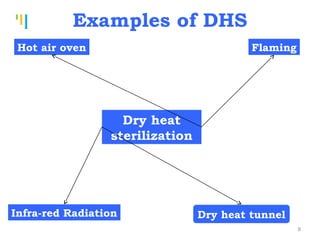
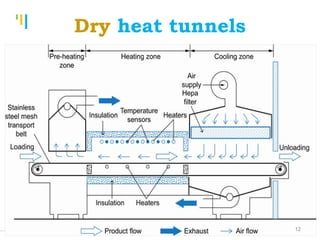
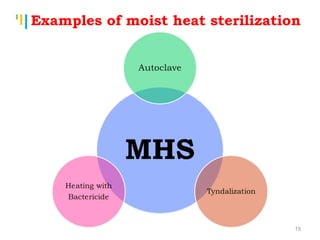
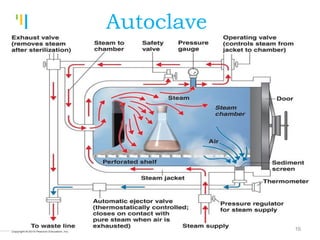
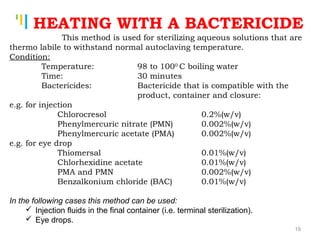
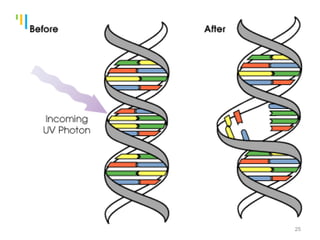
The document summarizes various sterilization methods used for parenterals including dry heat, moist heat, filtration, radiation, and gas sterilization. Dry heat is used to sterilize glassware and some metals by heating to temperatures between 160-180°C. Moist heat sterilization with steam under pressure is commonly used for liquids and porous materials in an autoclave. Filtration through sterile membranes can sterilize heat-labile solutions. Radiation methods include UV, gamma rays, and electrons. Gaseous methods use ethylene oxide or formaldehyde gas.























![Tankertanker Design
Tankertanker Design
Tankertanker Design
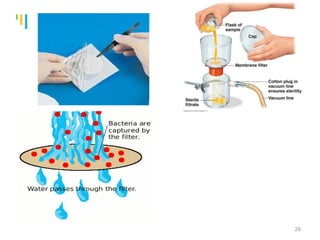
SEITZ FILTER
They are made of asbestos pad.
[For further details see Cooper & Gunn Dispensing pp. 582]
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sterilizationmethodsofparenterals-151124041956-lva1-app6891/85/Sterilization-methods-of-parenterals-34-320.jpg)







