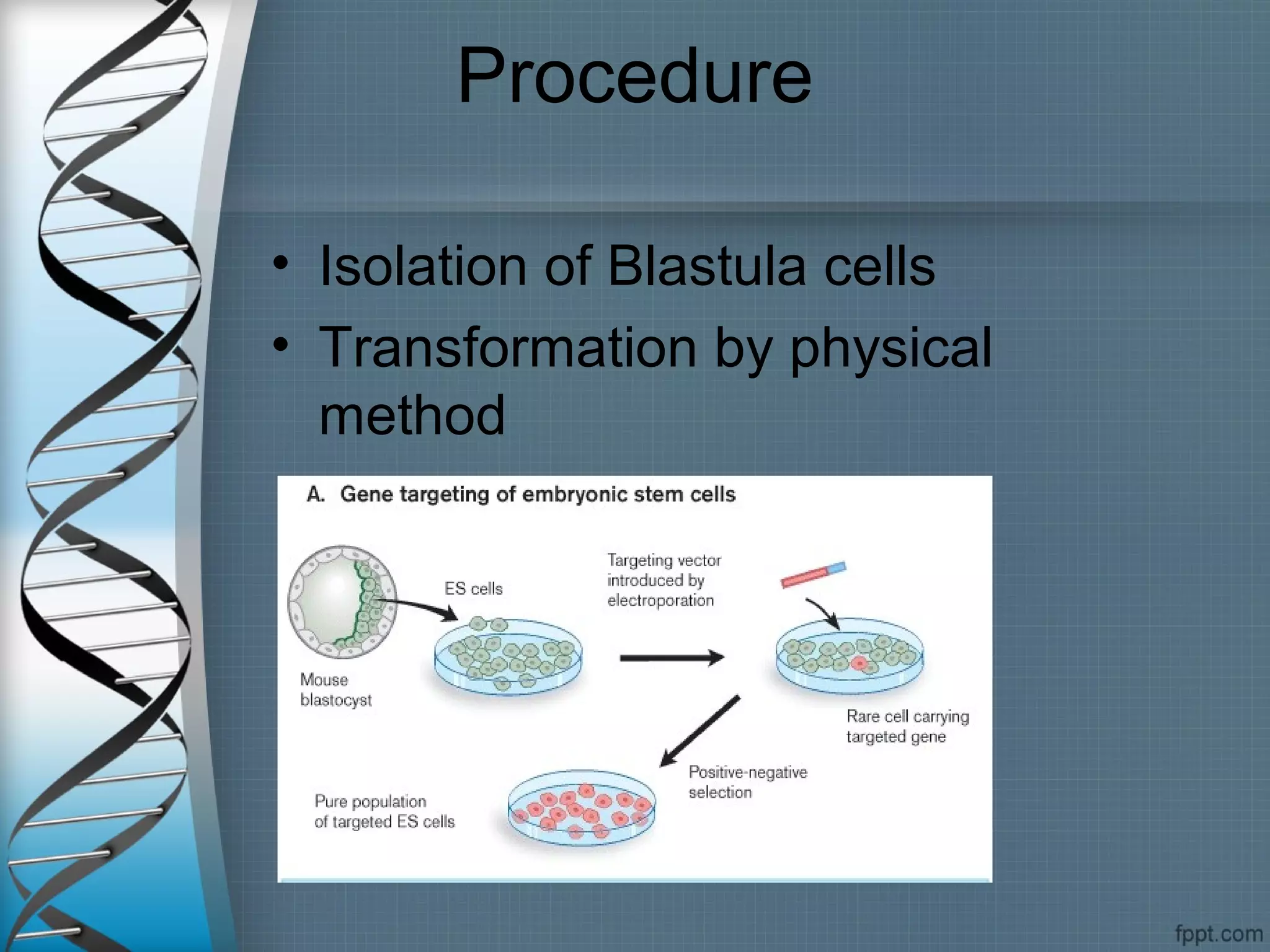
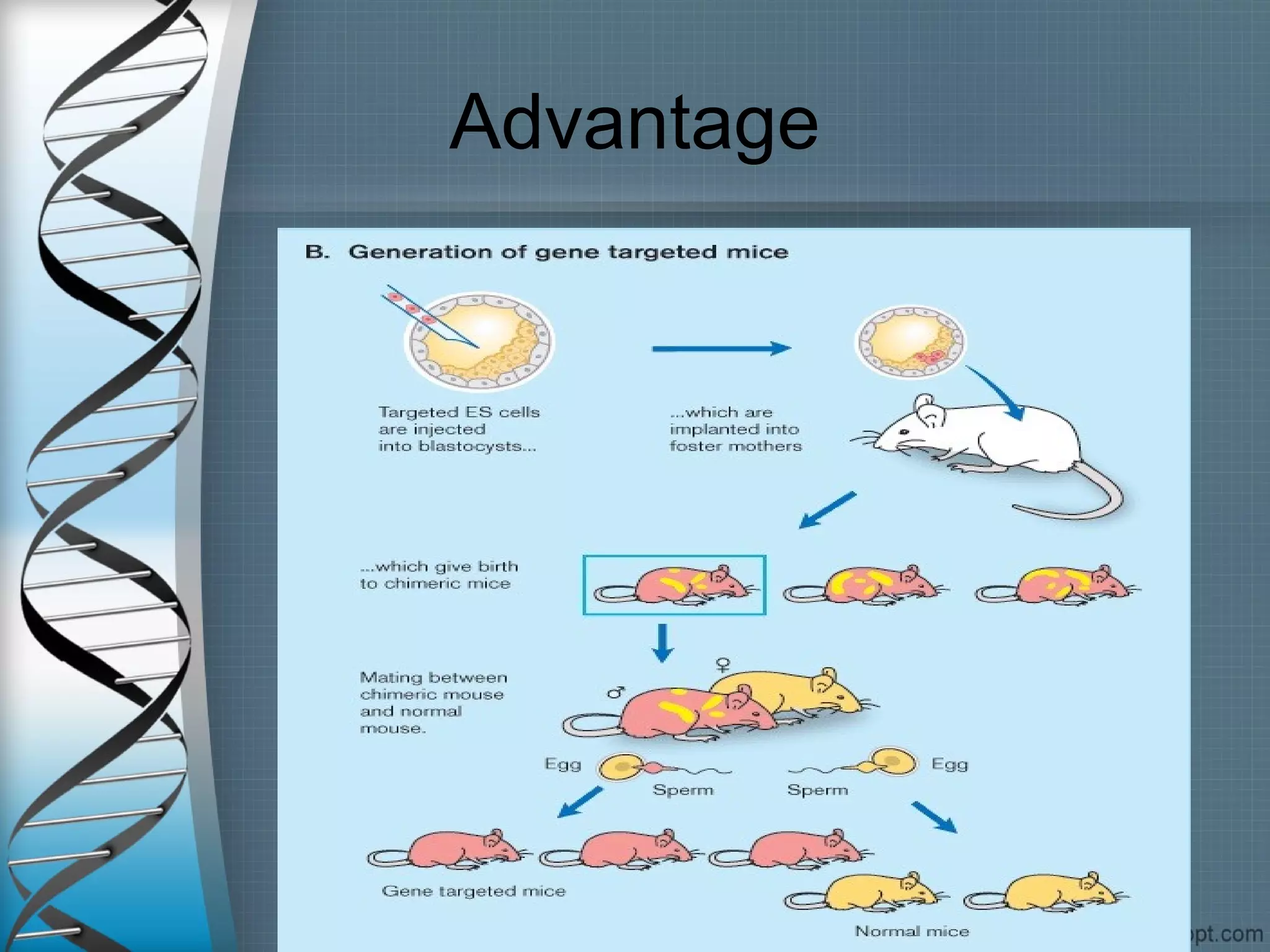
This document discusses various techniques for gene transformation, which is the process of altering or modifying genes. It begins by introducing the topic and describing early discoveries in bacterial genetic transformation in the 1920s. It then describes three main categories of gene transformation techniques: biological, physical, and chemical means. For each category, it provides examples of specific techniques and describes their mechanisms and applications. The physical means discussed include gene guns, microinjection, electroporation, and ultrasound. The document emphasizes that physical techniques allow for direct transformation without the use of carriers. It concludes by mentioning some applications of gene transfer techniques, such as for transgenic animals, crops, and gene therapy.







































![• . Bibliography
The given facts and figure are sort out from different sources which are given
below accordingly
• GENETIC ENGINEERING principles, procedure and consequences
Author: Gurbachan S.Migalani , published by Narosa
• Genetic Transformation of Plants
Edited by J.F.Jackson and H.F.Linksens by Springer (chapter 2)
• Gene Transfer techniques by Hongbao Ma, Guozhong Chen
[Nature and Science. 2005;3(1):25-31]
• URL:
https://www.google.com.pk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=19&](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/genetransformationtechniques-171001070220/75/Gene-transformation-techniques-46-2048.jpg)

