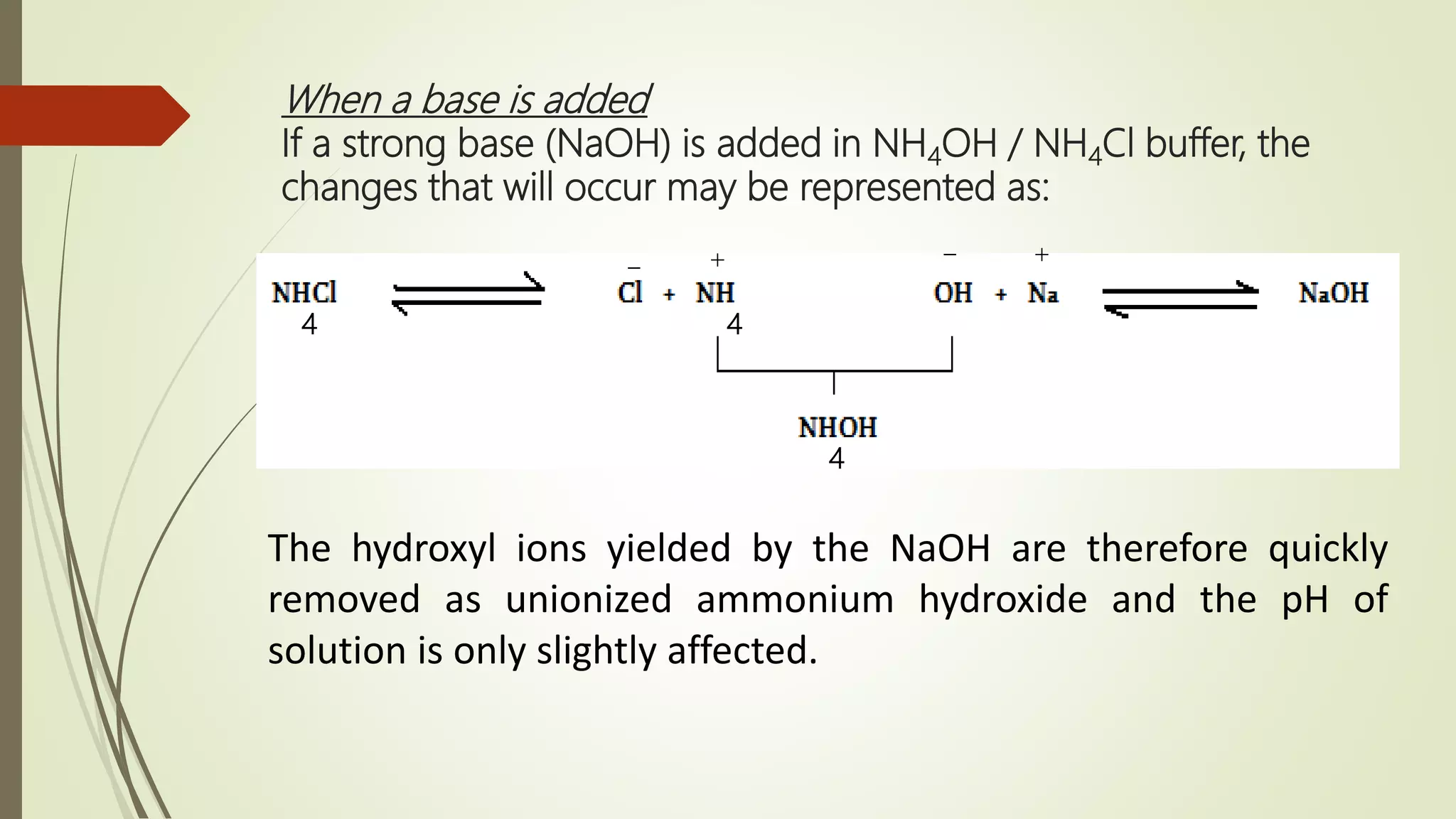
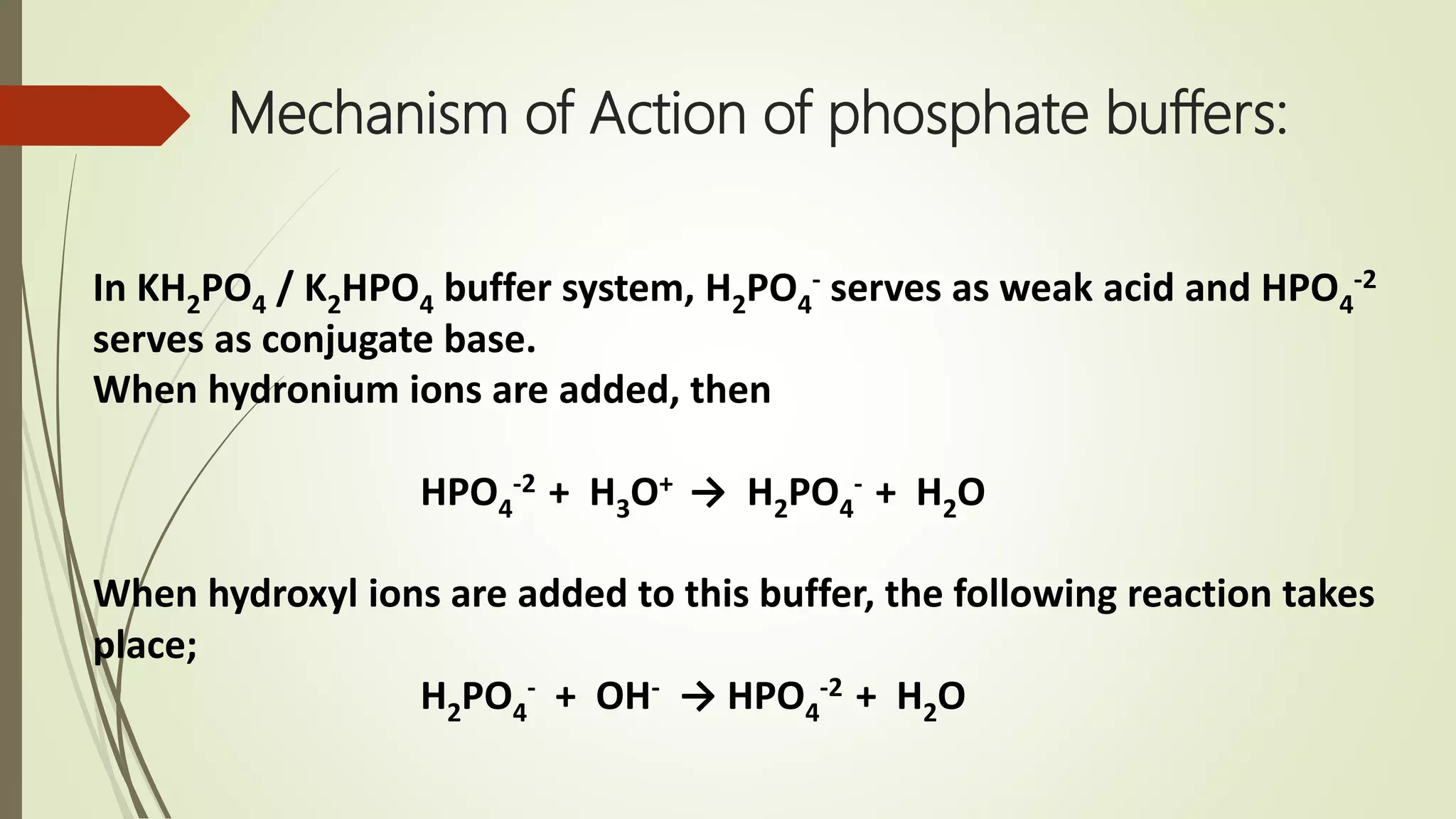
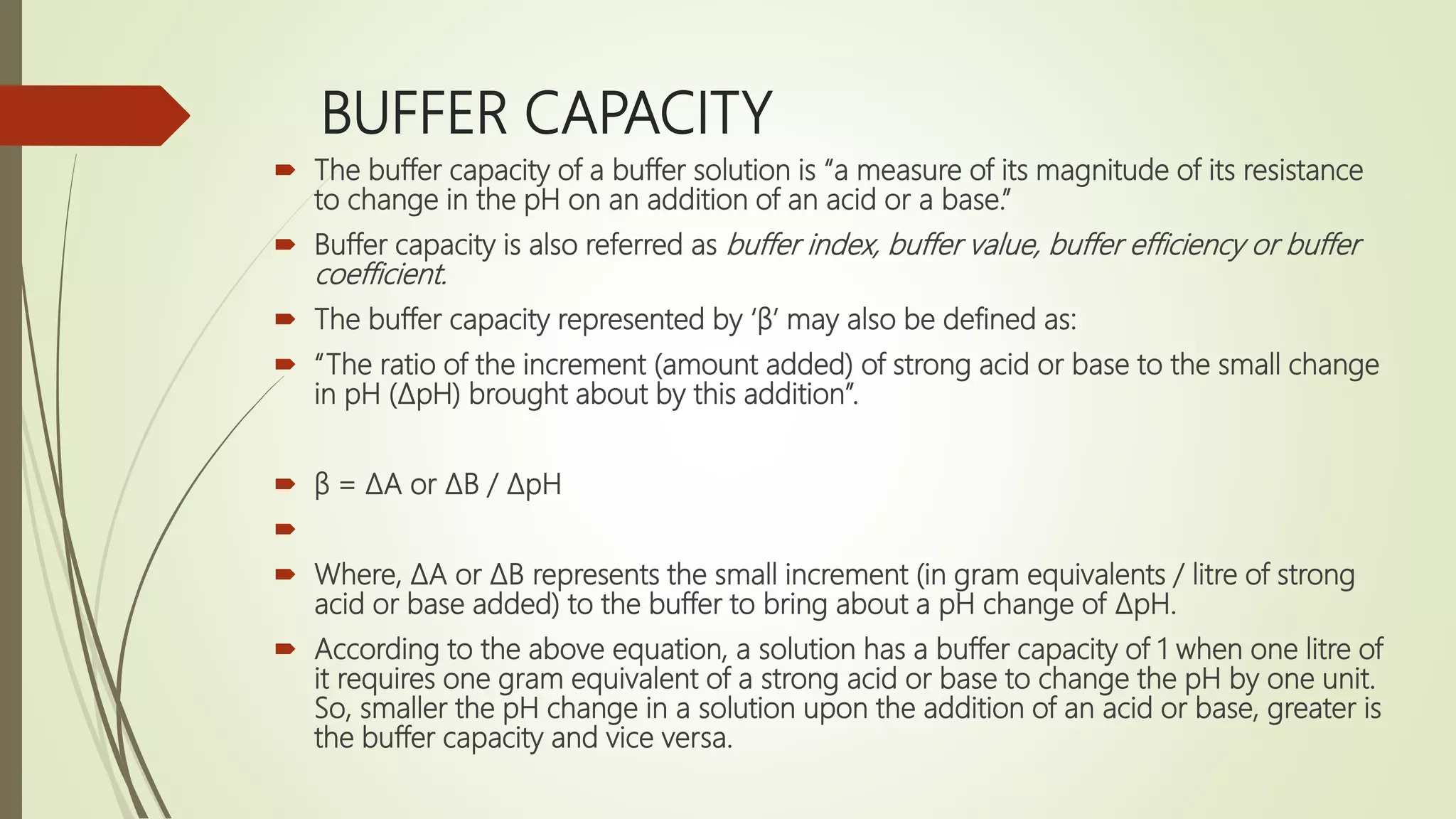
Buffers resist changes in pH upon the addition of small amounts of acid or base. They work by neutralizing added acid or base through chemical reactions. There are two main types of buffers - acidic buffers which use a weak acid and its salt, and basic buffers which use a weak base and its salt. The pH of buffer solutions can be calculated using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. Buffer capacity is a measure of a buffer's ability to resist pH changes and depends on the buffer components and their concentrations. Buffers have many important applications, including maintaining the pH of blood and pharmaceutical products.









![For Acid Buffers:
The pH of acid buffer can be calculated from the dissociation
constant, Ka of the weak acid and the concentrations of the acid and
salt used.
The dissociation expression of the weak acid can be represented
as:
HA ↔ H+ + A-
Ka = [H+] [A-] / [HA]
Or
[H+] = Ka [HA] / [A-] ------------- (1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffers-210223181424/75/Buffers-16-2048.jpg)

![ [H+] = Ka. [Acid] / [Salt] --------- (2)
Taking log on both sides, we get:
log[H+] = logKa + log [Acid] / [Salt]
multiplying both sides by –ve sign,
-log[H+] = -logKa - log [Acid] / [Salt]
As -log[H+] = pH & -logKa = pka
pH = pka - log[Acid] / [Salt] OR
pH = pka + log[Salt] / [Acid] ---------- (3)
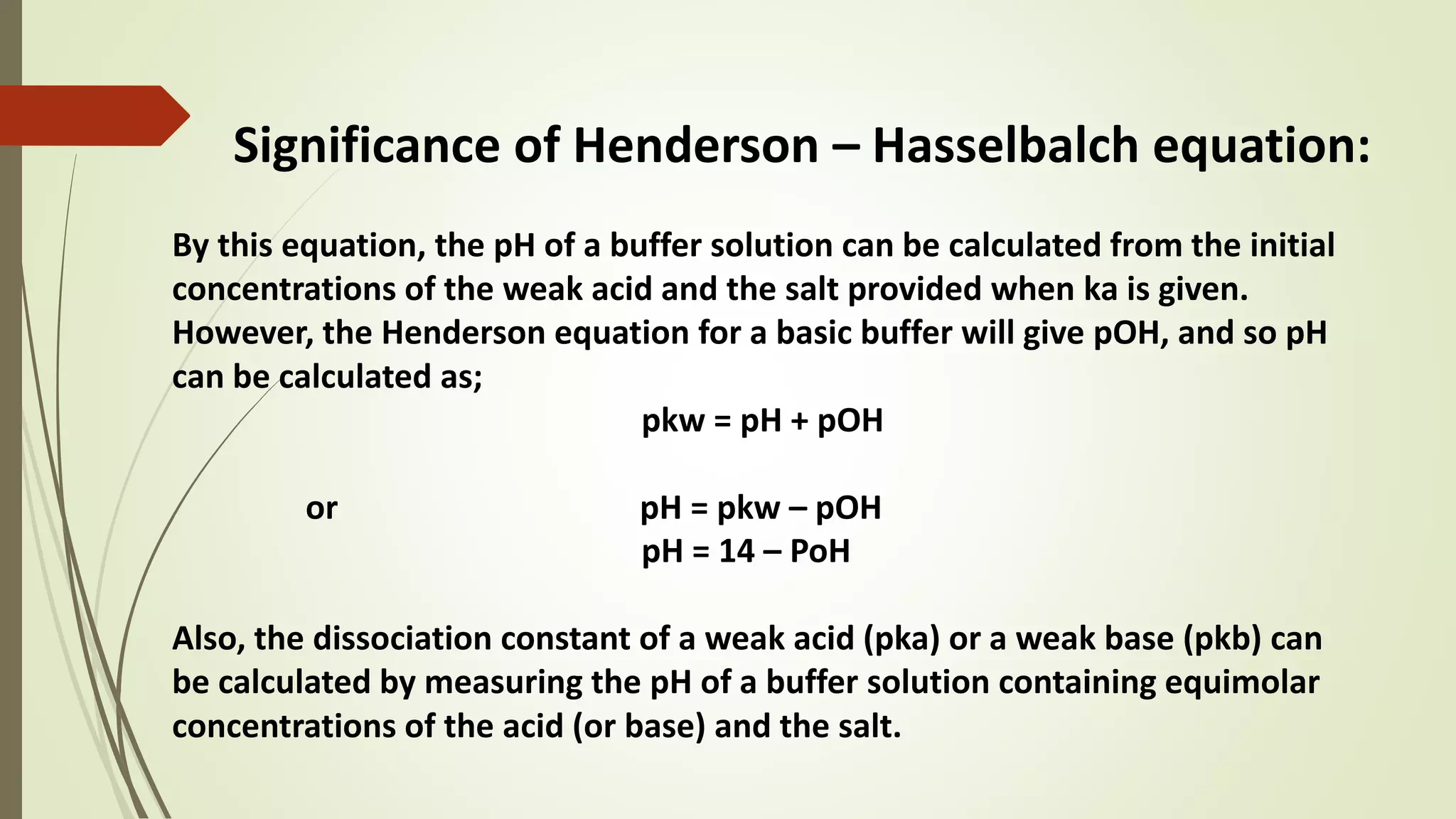
Eq. (3) is called as Henderson – Hasselbalch equation.
It helps in calculating the pH value of buffer solution,
if the concentrations of acid as well as that of the salt are known.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffers-210223181424/75/Buffers-18-2048.jpg)
![For Basic Buffers:
Buffer equation for basic buffer can be calculated in same way as that
for acidic buffers.
Consider a basic buffer composed of a mixture of weak base (BOH)
and its salt (BA). The dissociation constant for base can be written as,
BOH ↔ B+ + OH-
Kb = [B+] [OH-] / [BOH]
OR
[OH-] = Kb [BOH] / [B+] ------------- (1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffers-210223181424/75/Buffers-19-2048.jpg)

![[OH-] = Kb. [Base] / [Salt] --------- (2)
Taking log on both sides, we get:
log[OH-] = logKb + log [Base] / [Salt]
multiplying both sides by –ve sign,
-log[OH-] = -logKb - log [Base] / [Salt]
As -log[OH-] = pOH & -logKb = pkb
pOH = pkb – log [Base] / [Salt]
Or
pOH = pkb + log[Salt] / [Base] ---------- (3)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffers-210223181424/75/Buffers-21-2048.jpg)
![EXAMPLE:
Calculate the pH of a buffer solution containing 0.03 moles/litre of acetic acid and
0.1 moles/litre of sodium acetate. pka for CH3COOH is 4.57.
Solution:
Conc. Of acid = 0.03 M
Conc. Of salt = 0.1 M
So,
pH = pka + log [salt] / [acid]
= 4.57 + log 0.1 / 0.03
= 4.57 + 0.52
= 5.09
Result →The pH of the buffer solution containing 0.03 M of acetic acid and 0.1 M
of sodium acetate is 5.09.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffers-210223181424/75/Buffers-23-2048.jpg)
![ EXAMPLE:
Calculate the pH of a buffer solution containing 0.25 moles / litre of formic
acid (HCOOH) and 0.10 moles / litre of sodium formate (HCOONa). Ka for
formic acid is 1.8 × 10 -4.
Solution:
Conc. Of acid = 0.25 M
Conc. Of salt = 0.10 M
Ka = 1.8 × 10 -4
& pka is
pka = -log ka = -log 1.8 × 10 -4
= - (log 1.8 × 10 -4) = - (log 1.8 + log 10 -4) = - [0.25 + (-4)] = - (- 3.75) = 3.75
So,
pH = pka + log [salt] / [acid]
= 3.75 + log 0.10 / 0.25 = 3.75 – 0.397 = 3.34
Result → The pH of a buffer solution containing 0.25 M of formic acid and
0.10 M of sodium formate is 3.34.
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffers-210223181424/75/Buffers-24-2048.jpg)
![Prepare a buffer solution of pH 5 from acetic acid
CH3COOH & CH3COONa. pka of CH3COOH is 4.7.
Required pH = 5
pka = 4.7
Molar concentration of acid required = 1M, Molar concentration of base required = x M = ?
So, by putting above information in equation, we get:
pH = pka + log[Salt] / [Acid]
5 = 4.7 + log [x] / [1]
5 – 4.7 = log x – log 1
as log 1 = 0,
0.3 = log x
x = log- 0.3 (log- means anti-log)
x = 2
Result → in order to prepare buffer solution of pH 5, acetic acid CH3COOH & sodium acetate CH3COON
must be mixed in a ratio of 1M : 2M](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buffers-210223181424/75/Buffers-26-2048.jpg)



