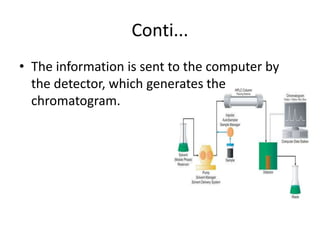
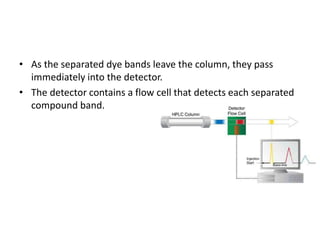
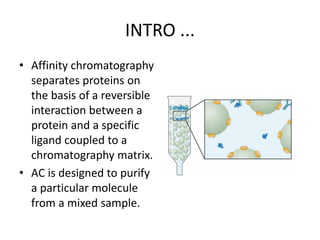
Paper chromatography is a simple type of chromatography that separates colored chemicals or substances based on their partitioning between a stationary phase, such as paper, and a mobile phase, such as a solvent. It works on the principles of partition chromatography, where the paper acts as an absorbent stationary phase, and adsorption chromatography, where moisture in the paper acts as the stationary phase. Compounds are separated based on how strongly they interact with and bind to the stationary phase, with less strongly bound compounds moving faster and farther up the paper. Paper chromatography is useful for identifying unknown mixtures of compounds.