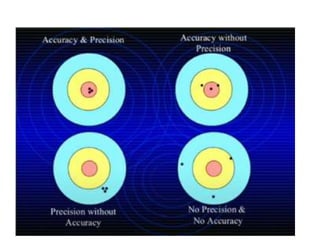
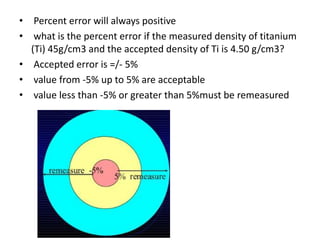
Methods of minimizing errors in chemical analysis involve careful calibration of apparatus, running blanks to account for impurities, using control determinations with standard substances, employing independent analytical methods for comparison, and performing parallel or duplicate determinations. Accuracy refers to how close a measurement is to the true value, while precision describes the agreement between repeated measurements of the same quantity. Significant figures indicate the certainty of measured values and help to properly calculate and report results.