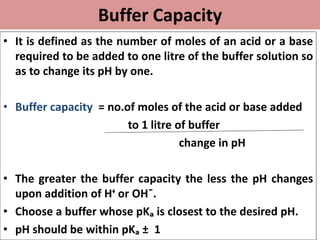
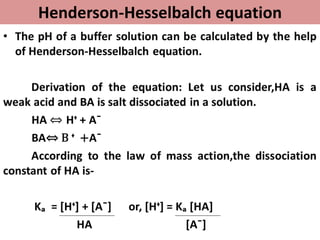
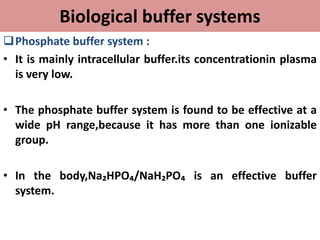
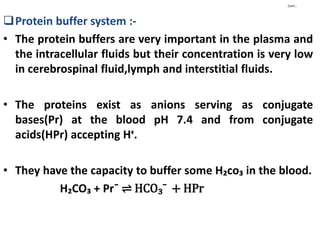
This document discusses pH, buffers, and biological buffer systems. It defines pH as the negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration and describes the pH scale from 0 to 14. Buffers help maintain pH and consist of weak acids/bases and their salts. Important biological buffers include the phosphate buffer system found intracellularly and protein buffers in blood plasma which help buffer carbonic acid. The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation relates pH and the chemical equilibrium of buffers.

![Cont…
• The concept of pH was first introduced by the danish
chemist sorenson in 1909.
• P means “puissance d” and H mean “Hydrogen”.it is the
french word,which means strength/power of hydrogen.
• Defination :-The formal defination of pH is the
negative logarithm of the hydrogen
ion activity.
pH = ¯log [Hᶧ]
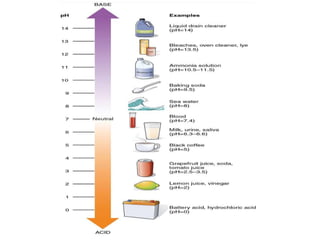
• pH is a unit of measure which describes the degree of
acidity or alkalinity(basic) of a solution.
• It is measured on a scale of 0 to14.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phandbuffers-180810165941/85/p-H-and-buffers-4-320.jpg)

![Cont…
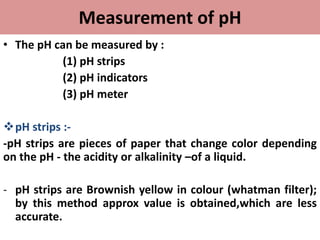
• pH meter :-
-The pH meter is a laboratory equipment which used to
measure acidity or alkalinity of a solution.
-The pH meter measures
The concentration of
Hydrogen ions [Hᶧ] using
An ion-sensitive electrode .
-It is the most reliable and
Convenient method for
Measuring ph.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phandbuffers-180810165941/85/p-H-and-buffers-10-320.jpg)

![How buffers work :-
• Equilibrium between acid and base.
• Example : ACETATE BUFFER
CH₃COOH ↔ CH₃COO¯ + Hᶧ
• If more Hᶧ is added to this solution,it simply shifts
the equilibrium to the left,absorbing Hᶧ,so the [Hᶧ]
remains unchanged.
• If Hᶧ is removed (e.g. by adding OH¯)then the
equilibrium shifts to the right,releasing Hᶧ to keep
the pH constant.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phandbuffers-180810165941/85/p-H-and-buffers-13-320.jpg)