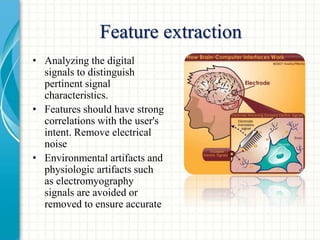
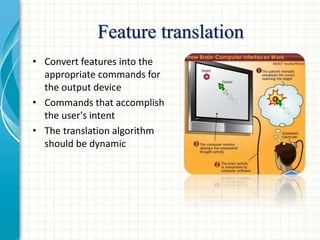
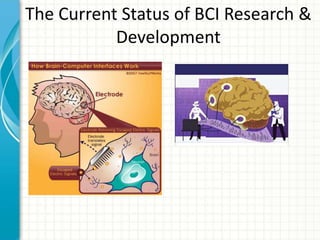
The document discusses brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) and their components, including signal acquisition, feature extraction, and device output. It categorizes BCIs into three types: invasive, partially invasive, and non-invasive, highlighting their signal quality and application differences. The document also mentions the current research status and mentions EEG as a significant non-invasive interface due to its advantages.