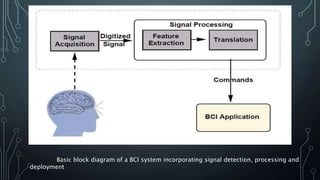
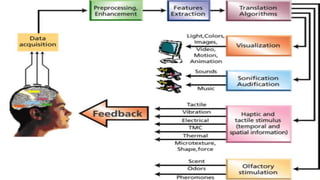
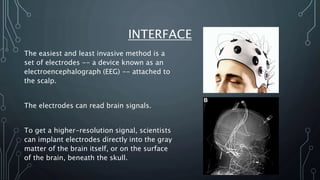
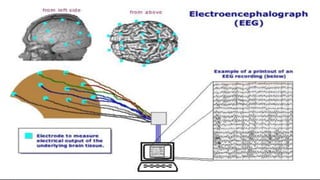
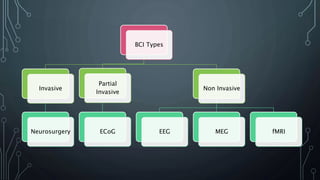
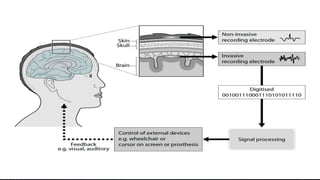
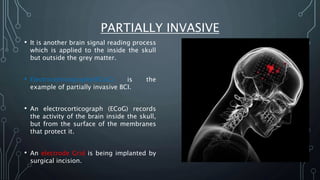
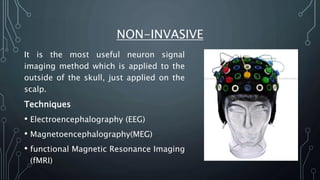
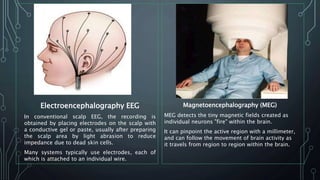
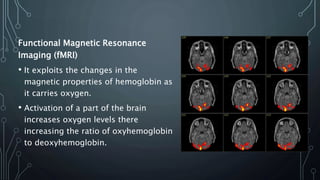
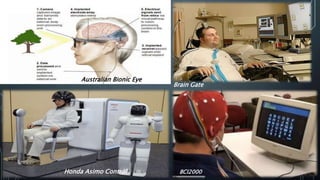
The document discusses brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), which allow humans to control electronic devices using thought by detecting brain signals through electrodes. It outlines the history of BCI development, various types including invasive and non-invasive methods, and applications such as aiding disabled individuals, enhancing gaming experiences, and potential future uses in prosthetics. The document also addresses the advantages and disadvantages of BCI technology, emphasizing ongoing research challenges and ethical considerations.