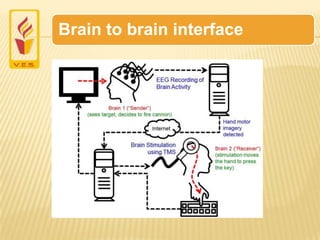
A brain-computer interface is a direct communication pathway between the brain and an external device. BCIs can be invasive, implanted inside the brain, or non-invasive, using external sensors like EEG to read brain signals. The brain's neurons communicate via electric signals that an EEG can detect on the scalp. Researchers have used EEG-based BCIs to allow communication between two human brains. While BCIs could help treat disabilities and allow new forms of control, challenges remain in interpreting complex brain signals and developing portable, non-invasive devices.