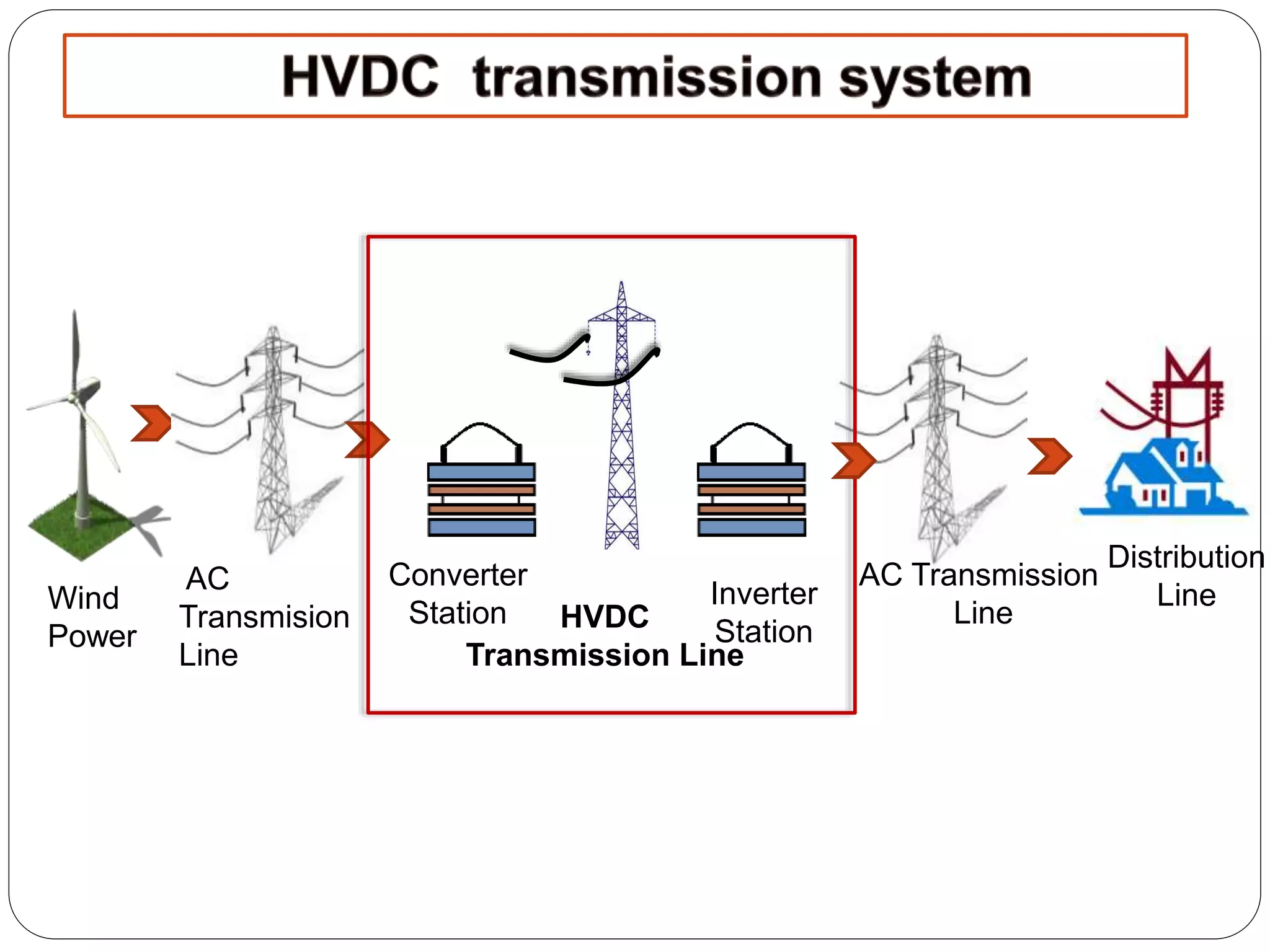
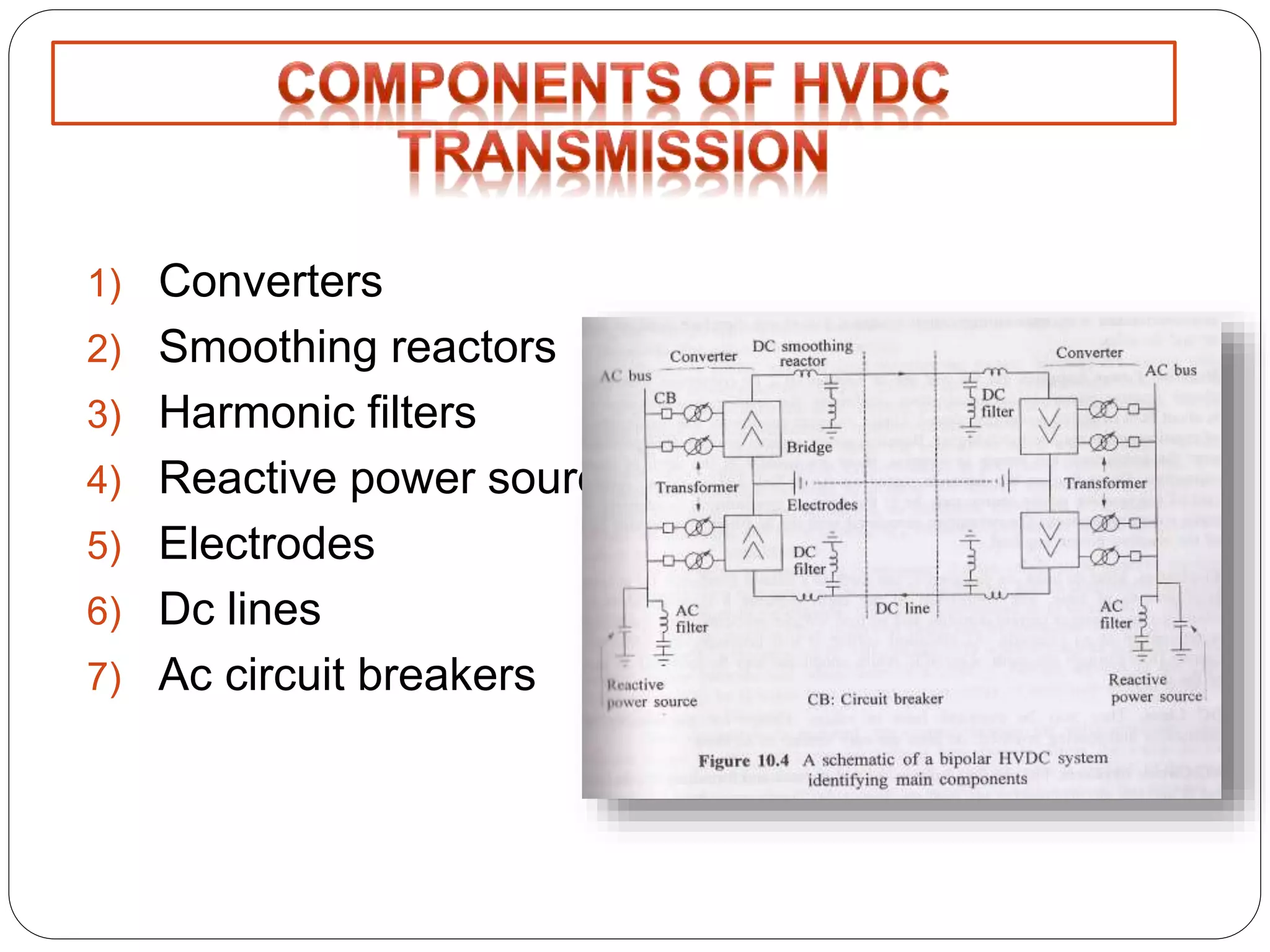
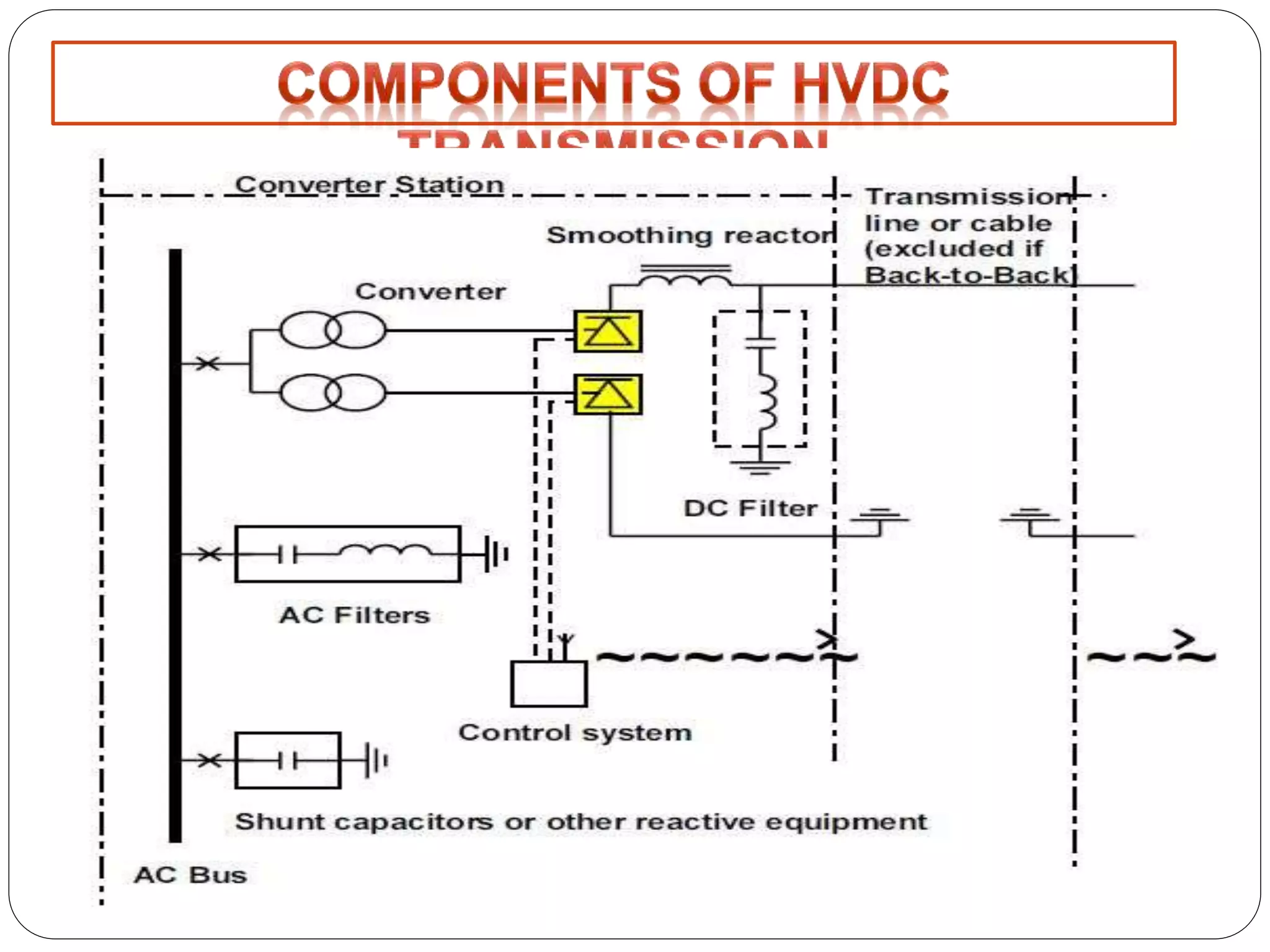
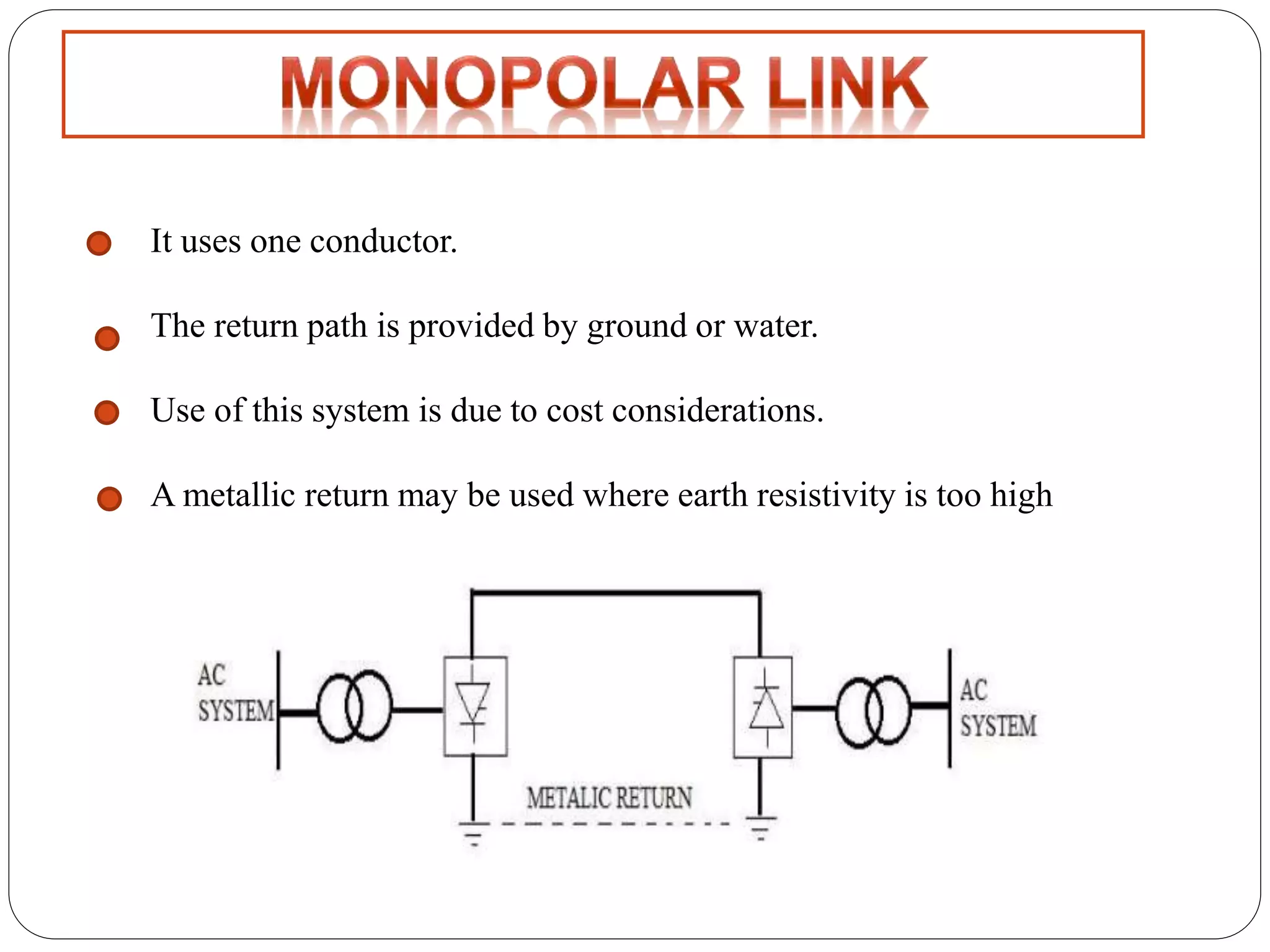
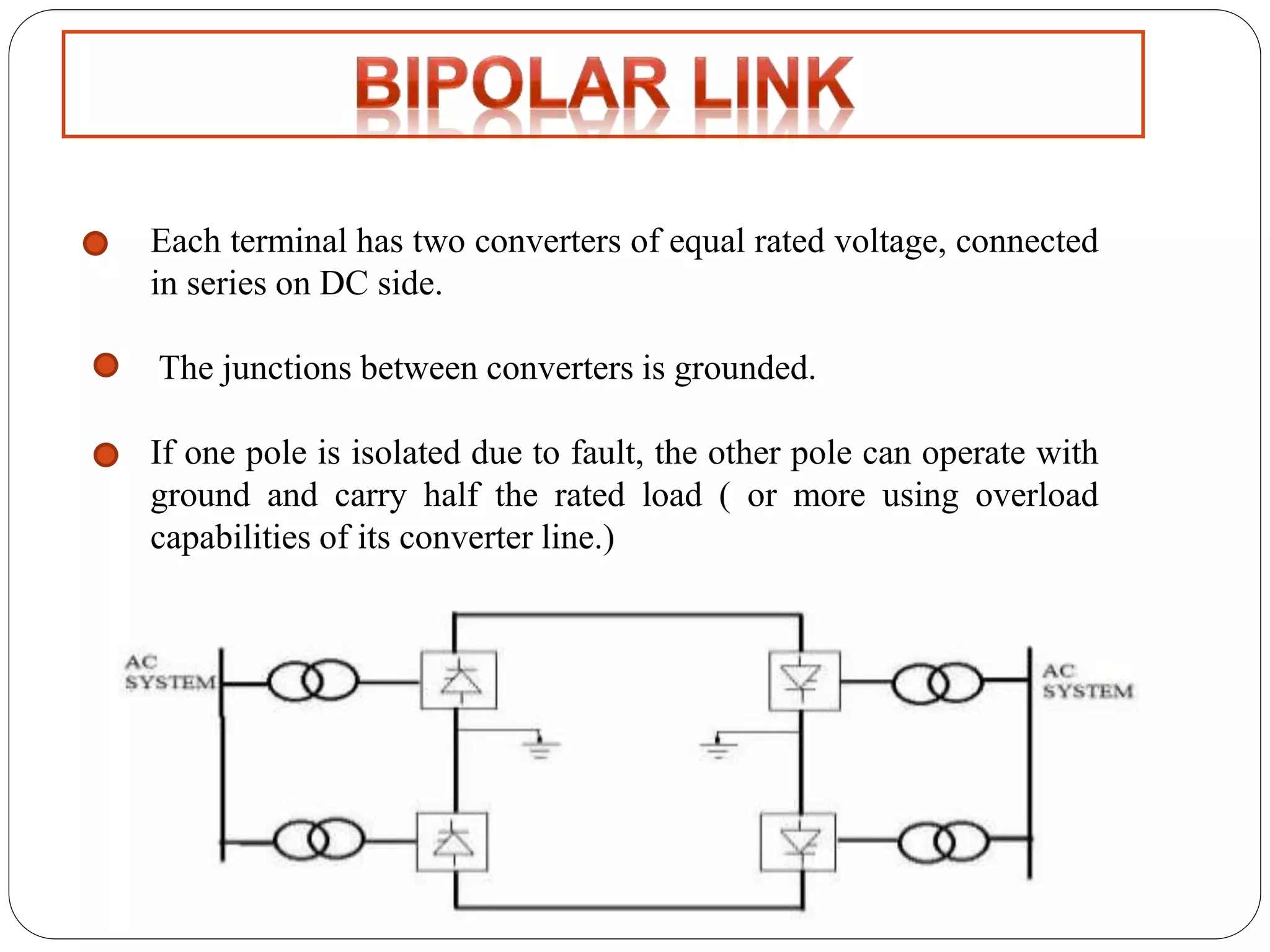
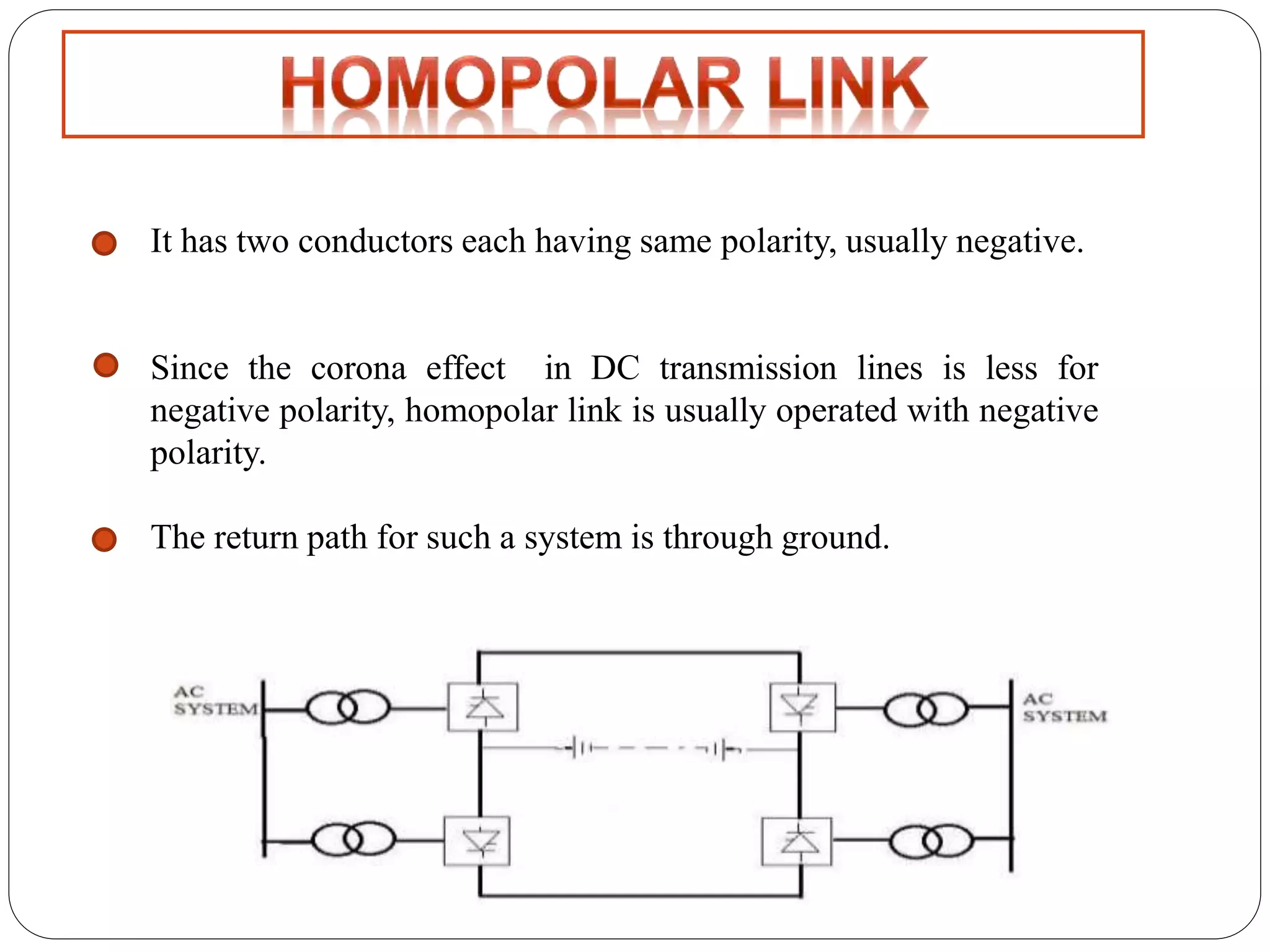
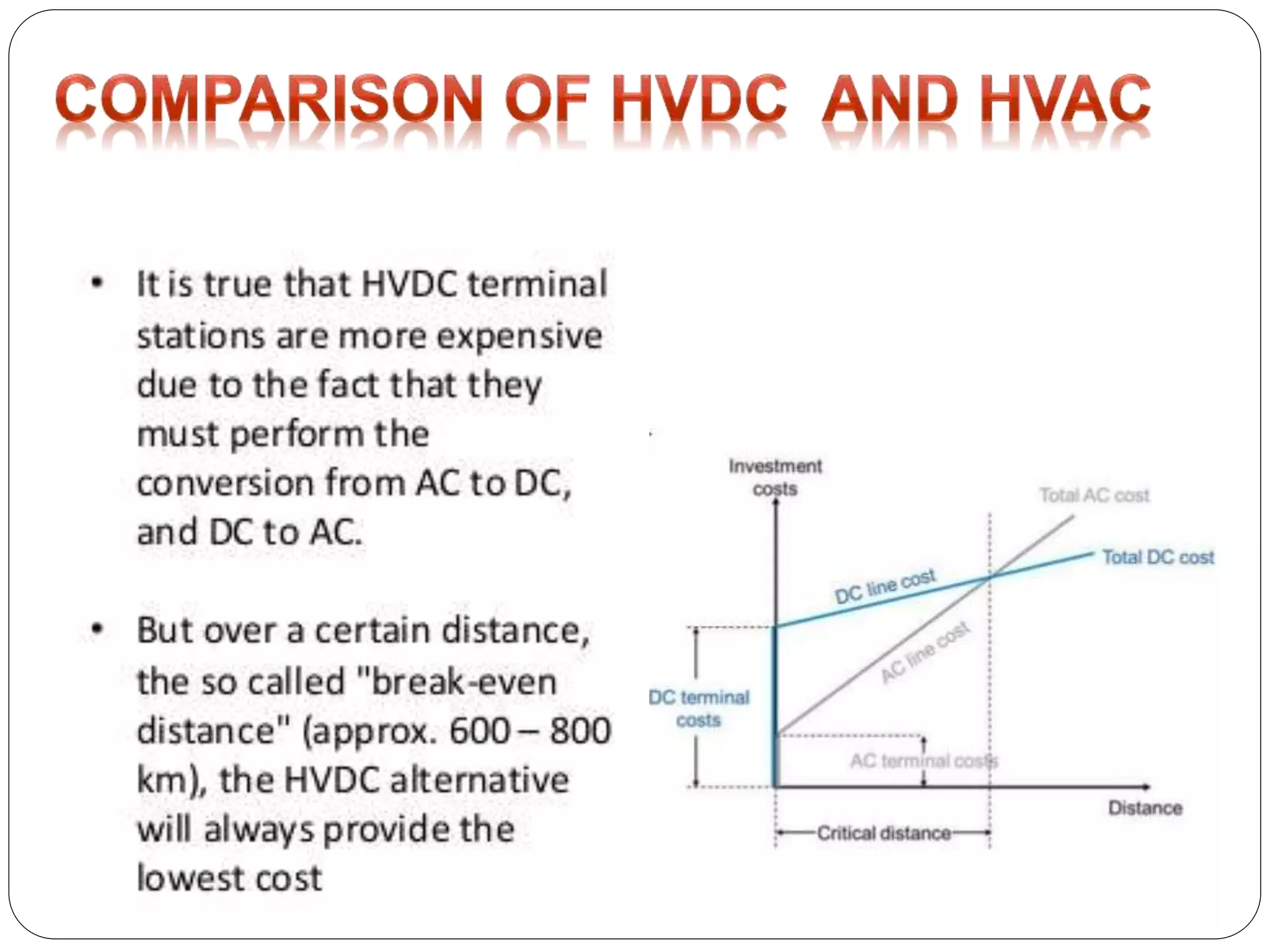
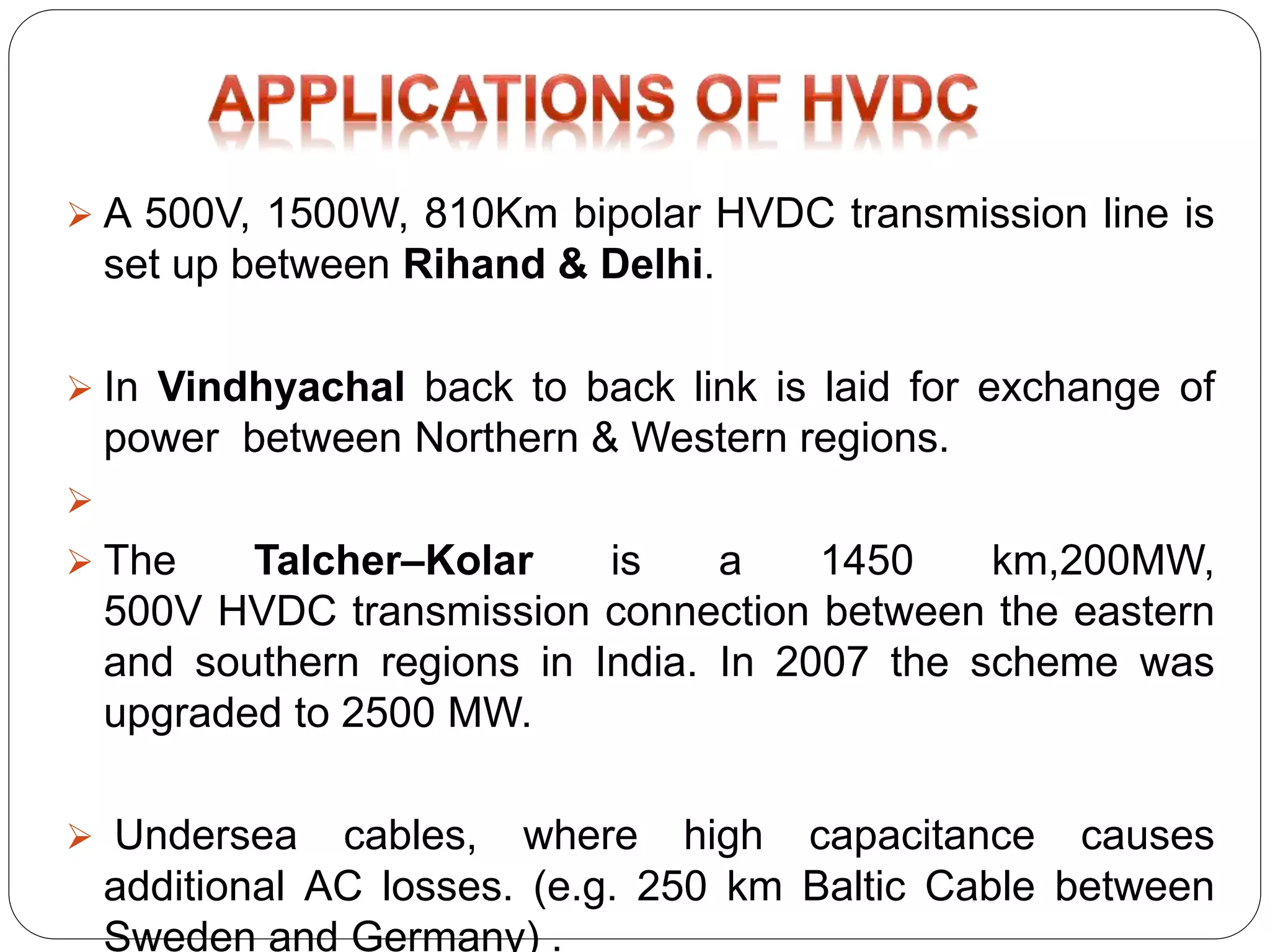
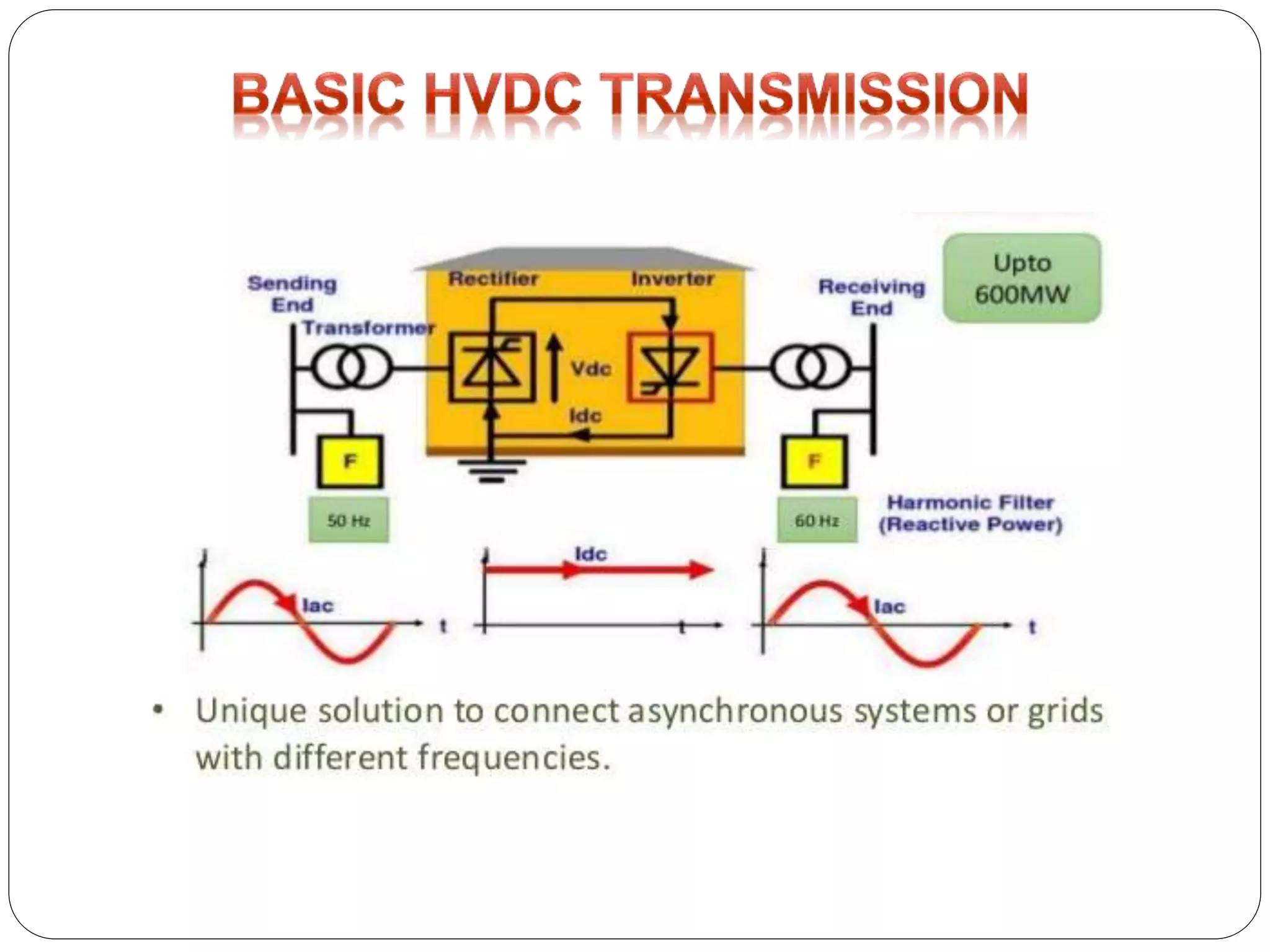
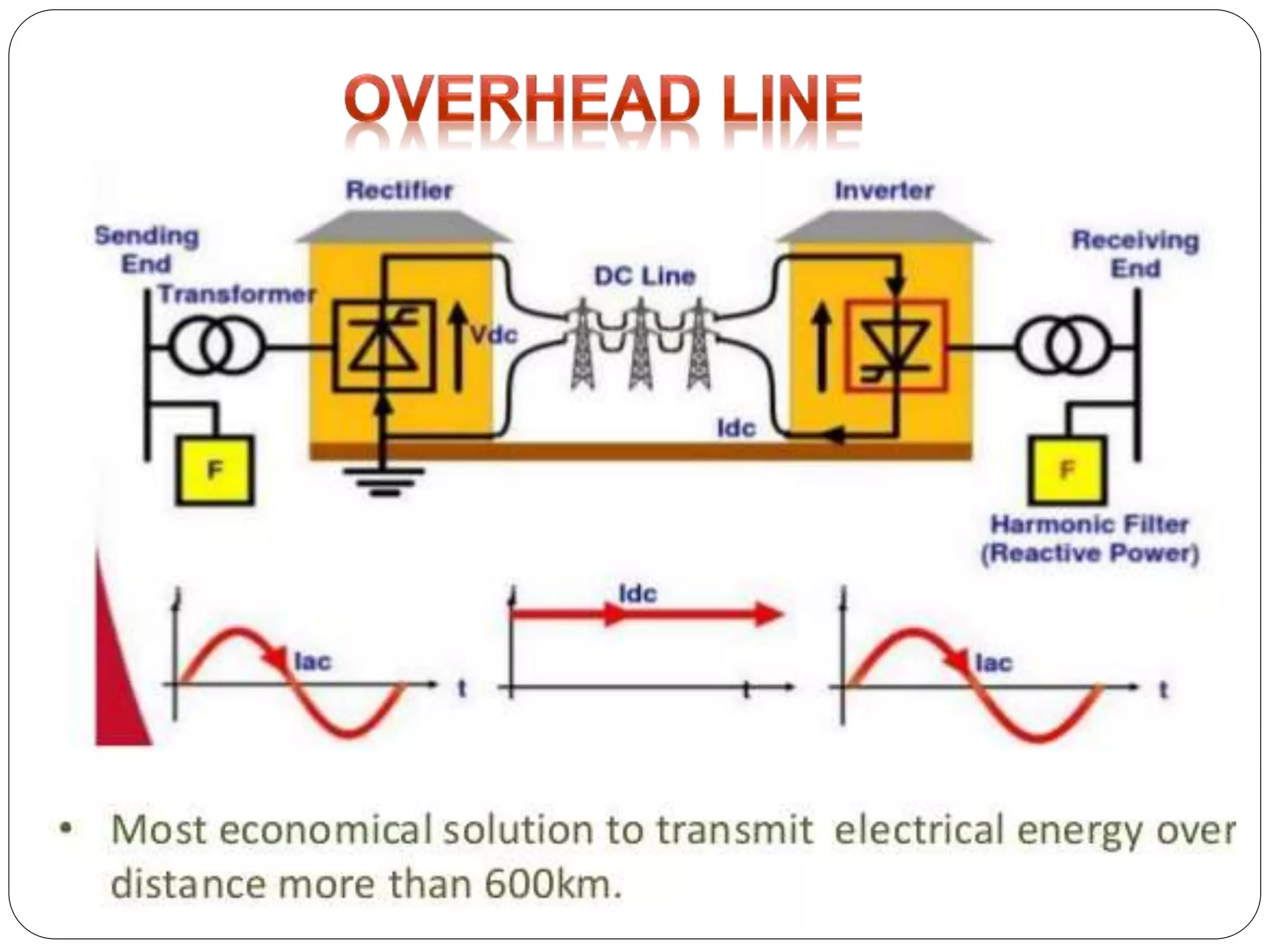
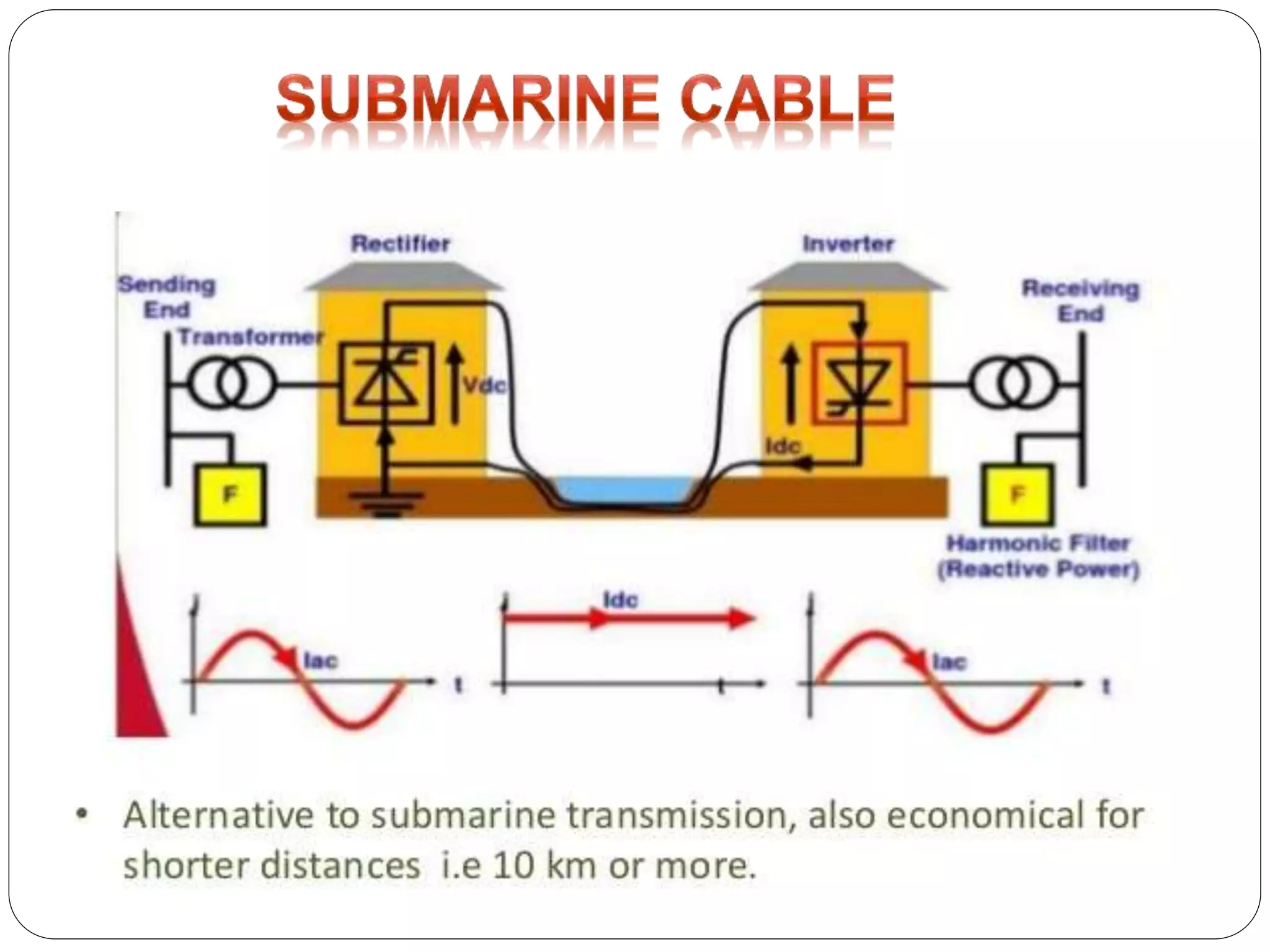
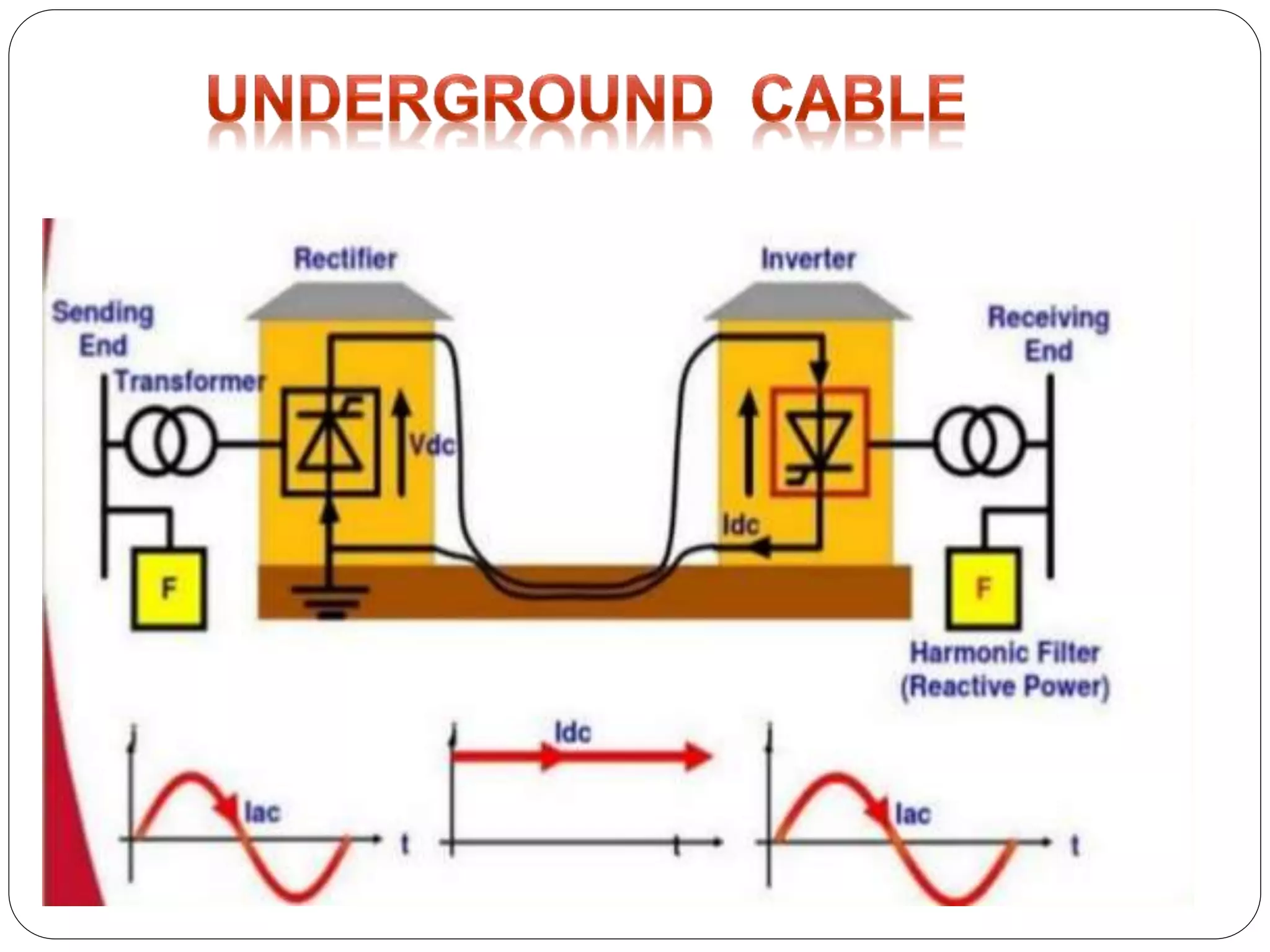
HVDC transmission involves converting AC power to DC, transmitting it through DC lines, and converting it back to AC. It has technical advantages over AC like lower transmission losses and asynchronous operation. Economically, DC lines and cables are cheaper to build than AC, and losses during transmission are lower. HVDC is used in long distance bulk power transmission and for undersea power cables due to its advantages over high voltage AC for these applications. Major HVDC projects in India transmit power between different regions of the country.