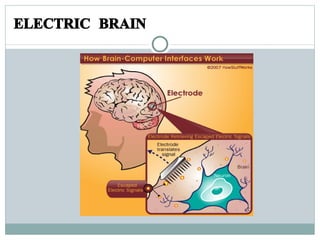
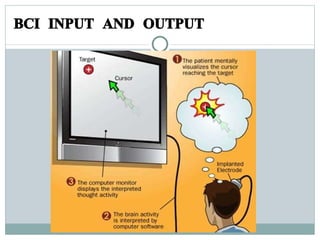
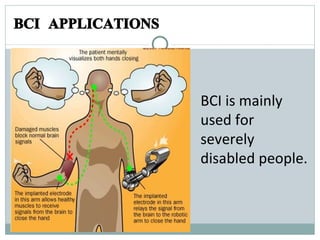
A brain-computer interface (BCI) allows direct communication between the brain and an external device. There are invasive, partially invasive, and non-invasive types of BCI. A BCI works by measuring electric signals in the brain through electrodes and transmitting them to a computer which interprets the signals. BCI applications include helping disabled people through neuroprosthetics and being used in medicine, the military, gaming, and more.