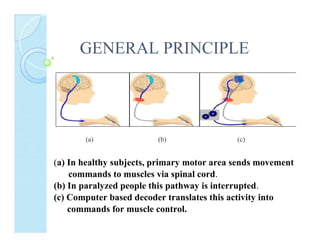
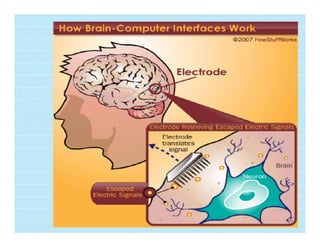
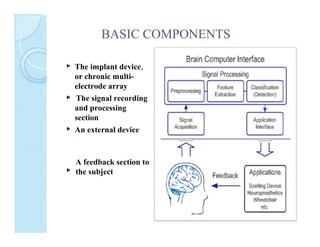
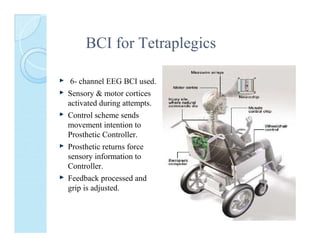
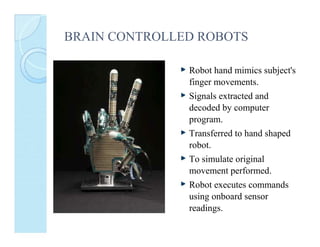
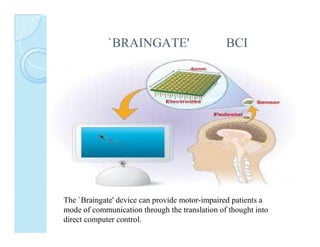
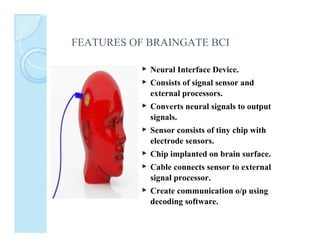
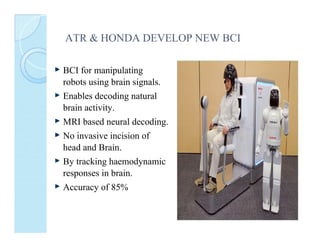
A brain-computer interface (BCI) enables direct communication between the brain and mechanical devices, allowing motor-impaired patients to control them through thought. Key developments have included the 'Braingate' device, which converts neural signals into computer commands, as well as research into BCIs for robotic manipulation. While BCIs show promise in medical and military applications, challenges remain, including signal weakness and equipment bulkiness.