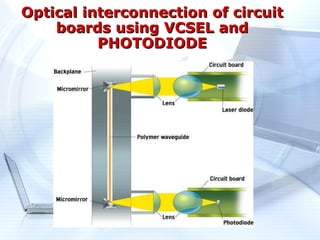
Optical computing uses light instead of electricity to perform computations. It offers several advantages like speed, easy manipulation of light, and parallelization. There are two approaches - building electro-optical hybrid computers or all-optical computers. Optical computing can solve miniaturization problems and allow parallel processing. Key components include VCSELs, smart pixel technology, WDM, and SLMs. Advantages include higher speed and performance while drawbacks are needing high power and imperfections causing interference. Future trends involve developing new materials and algorithms that leverage optics.