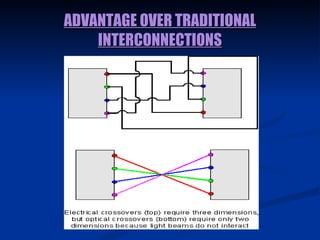
Optical computing uses optics and related technologies to improve computing. It can provide terabit network speeds beyond what is possible with electronic circuits alone. There are several types of optical computers including analog, optoelectronic, and parallel digital computers. Optical computers use photonic circuits and can exploit the speed of light for parallel processing. While promising, optical computing still faces challenges in dense organization and optoelectronic conversion delays.