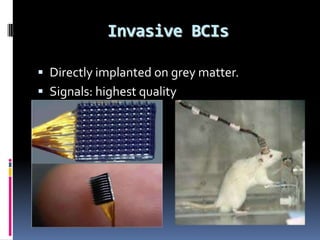
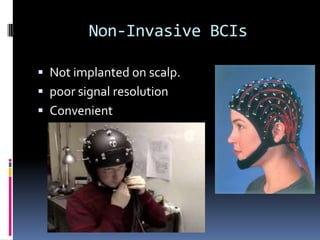
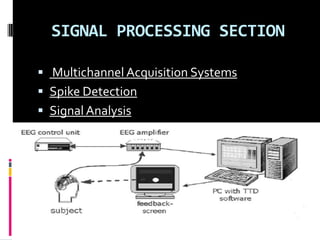
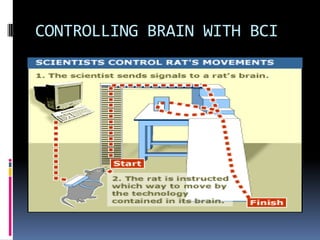
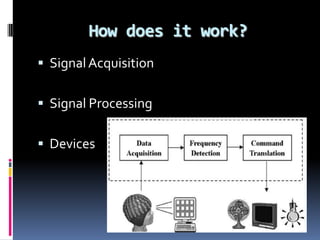
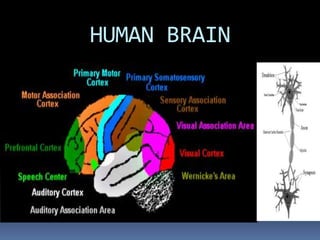
This document discusses brain-computer interfaces (BCI), which allow direct communication between the brain and external devices. It describes how BCIs work by acquiring brain signals through non-invasive or invasive methods, processing the signals to extract features, and using those features to control external devices. The document outlines different types of brain waves and BCI applications, as well as disadvantages like potential brain damage from invasive methods.



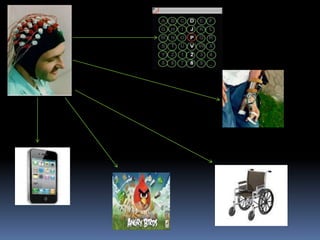


![SIGNAL ACQUISITION
EEG(ELECTROENCHEPHALOGRAPHY)
Measurements of electrical activity of the brain .
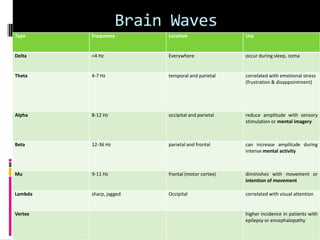
The basic frequency of the EEG range is classified into five bands for
purposes of EEG analysis called brain rhythms.
Band Frequency [Hz]
Delta 0.5- 4
Theta 4- 8
Alpha 8- 13
Beta 13- 22
Gamma 22-30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/braincomputerinterface-140522035444-phpapp02/85/Brain-computer-interface-10-320.jpg)