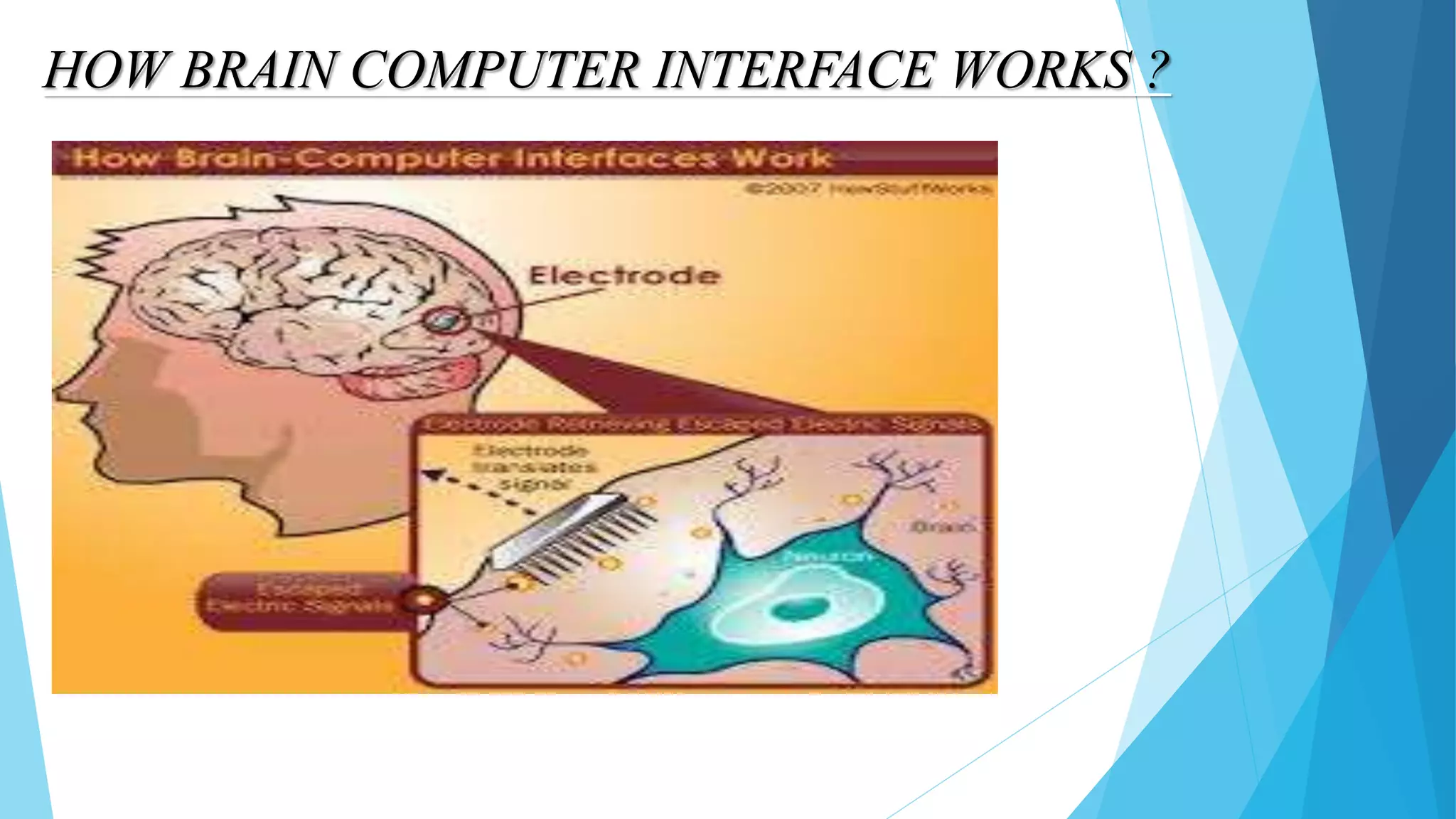
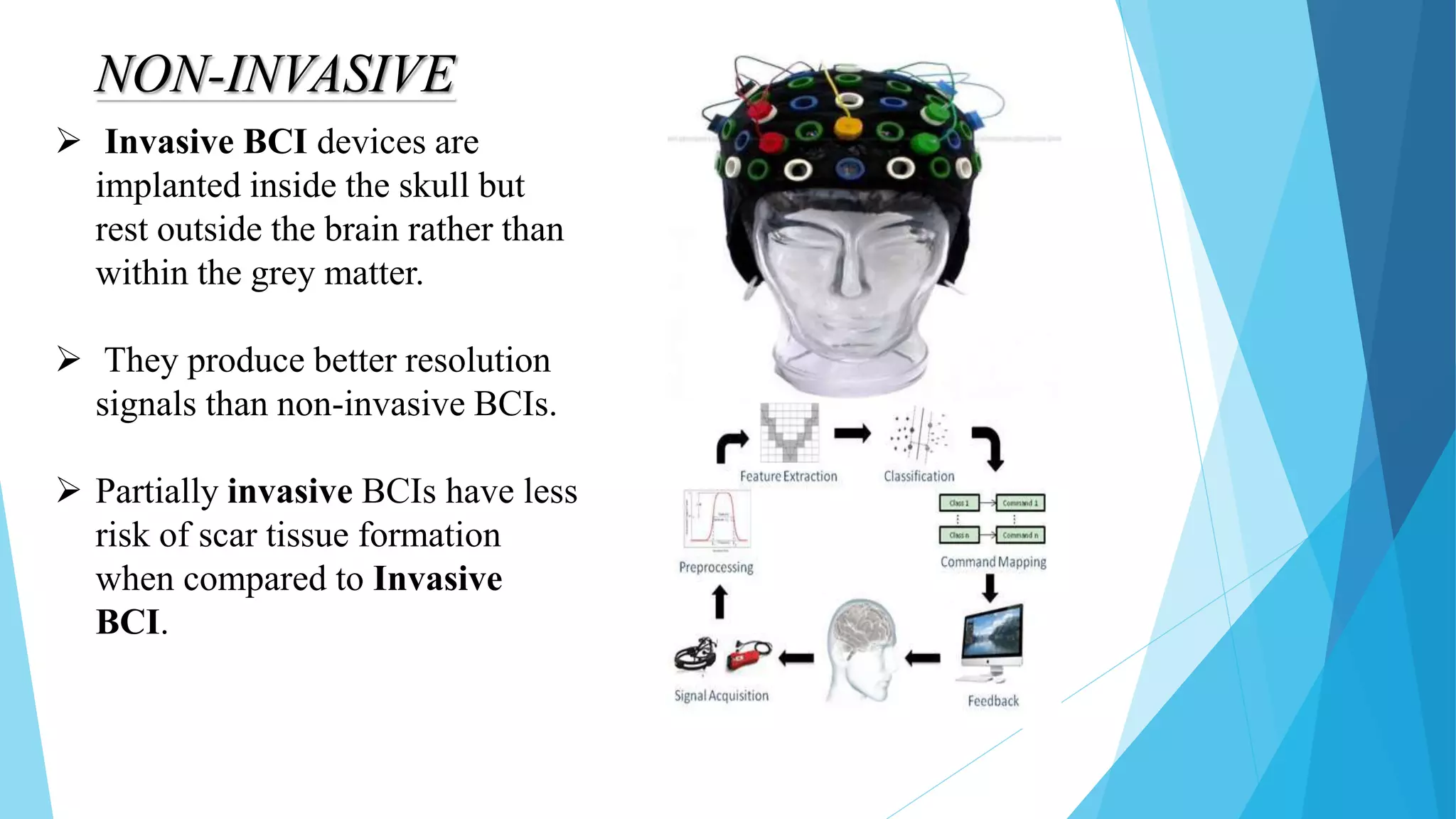
This document provides an overview of brain-computer interfaces (BCI). It begins with an introduction defining BCI as a direct communication pathway between the brain and an external device. It then discusses the history of BCI research from the 1920s to present day. The document explains how BCI systems work through signal acquisition, preprocessing, feature extraction and classification. It describes invasive and non-invasive BCI types and some of their applications in fields like medicine, education and games. The advantages of BCI are its precision and potential benefits to quality of life. However, current BCI technology also has disadvantages like inaccuracy and ethical issues regarding reading thoughts.