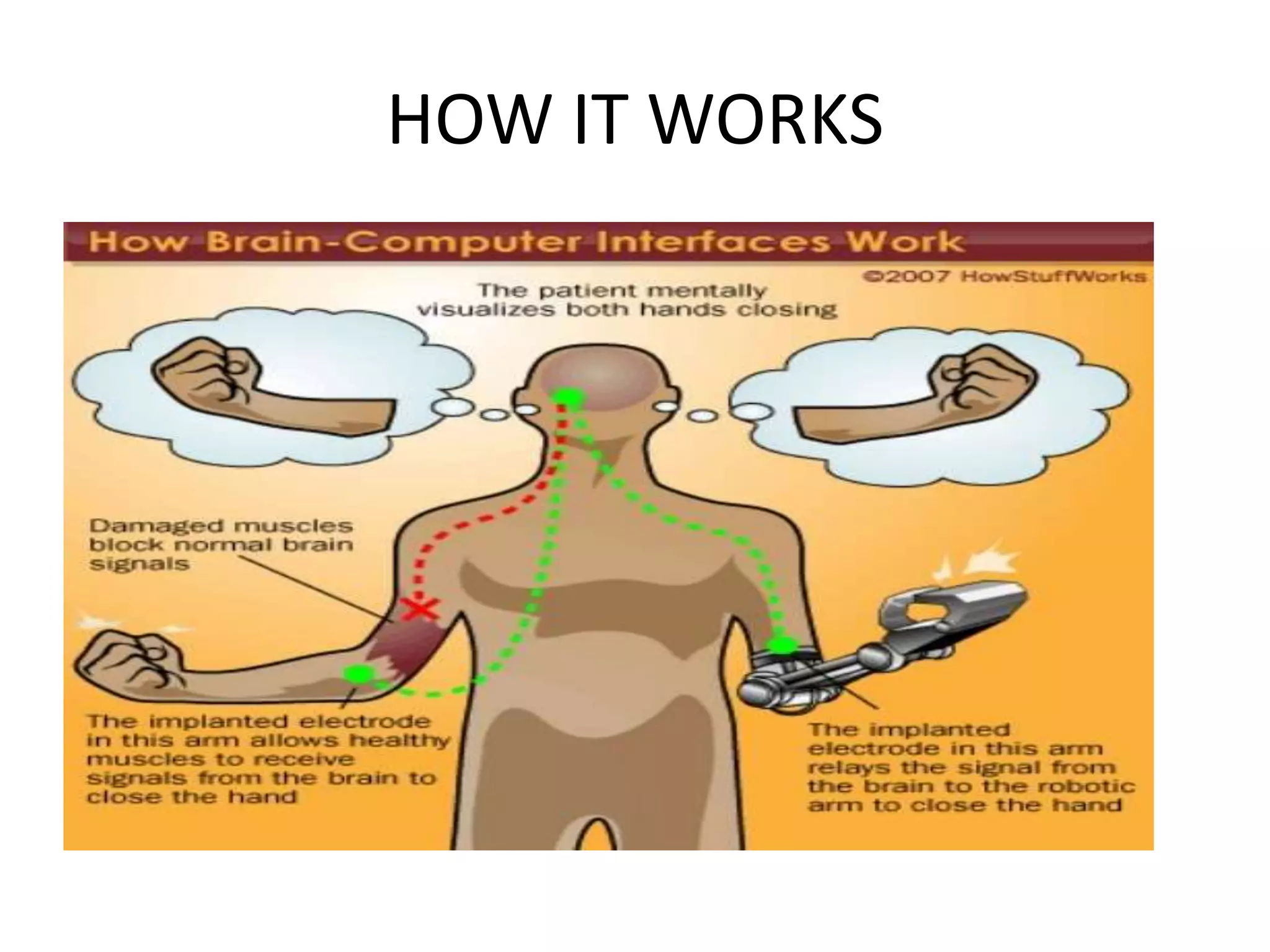
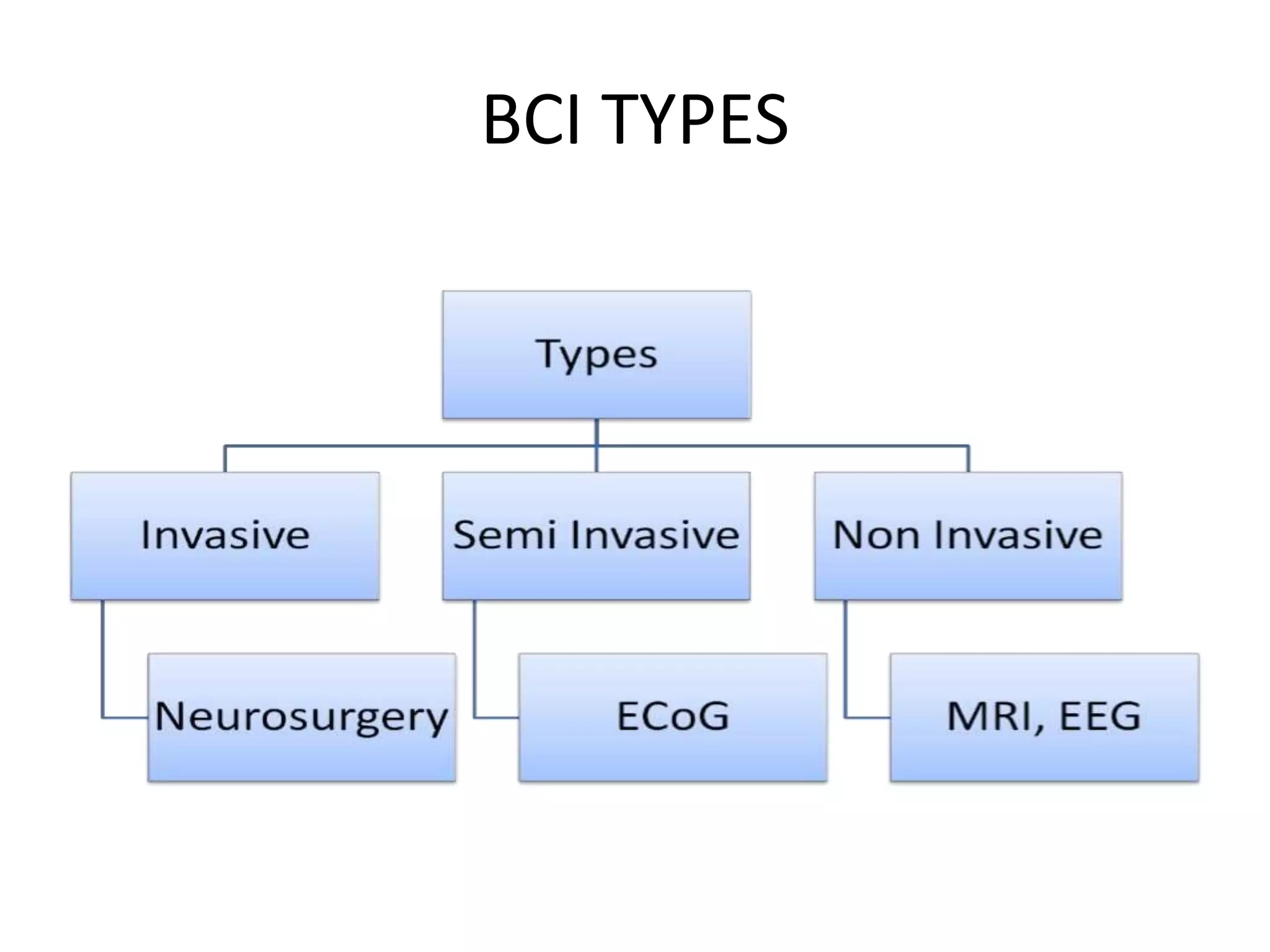
The document discusses brain-computer interfaces (BCI), including a brief history starting with Hans Berger's discovery of EEG in 1924. It describes invasive, semi-invasive, and non-invasive BCI types, with invasive having higher accuracy but risks from surgery, and non-invasive using EEG, MRI, or other external measures. Potential applications include assisting paralyzed patients, memory functions, and direct brain-to-brain communication. BCI is presented as an advancing technology with applications in machine control, human enhancement, and more.