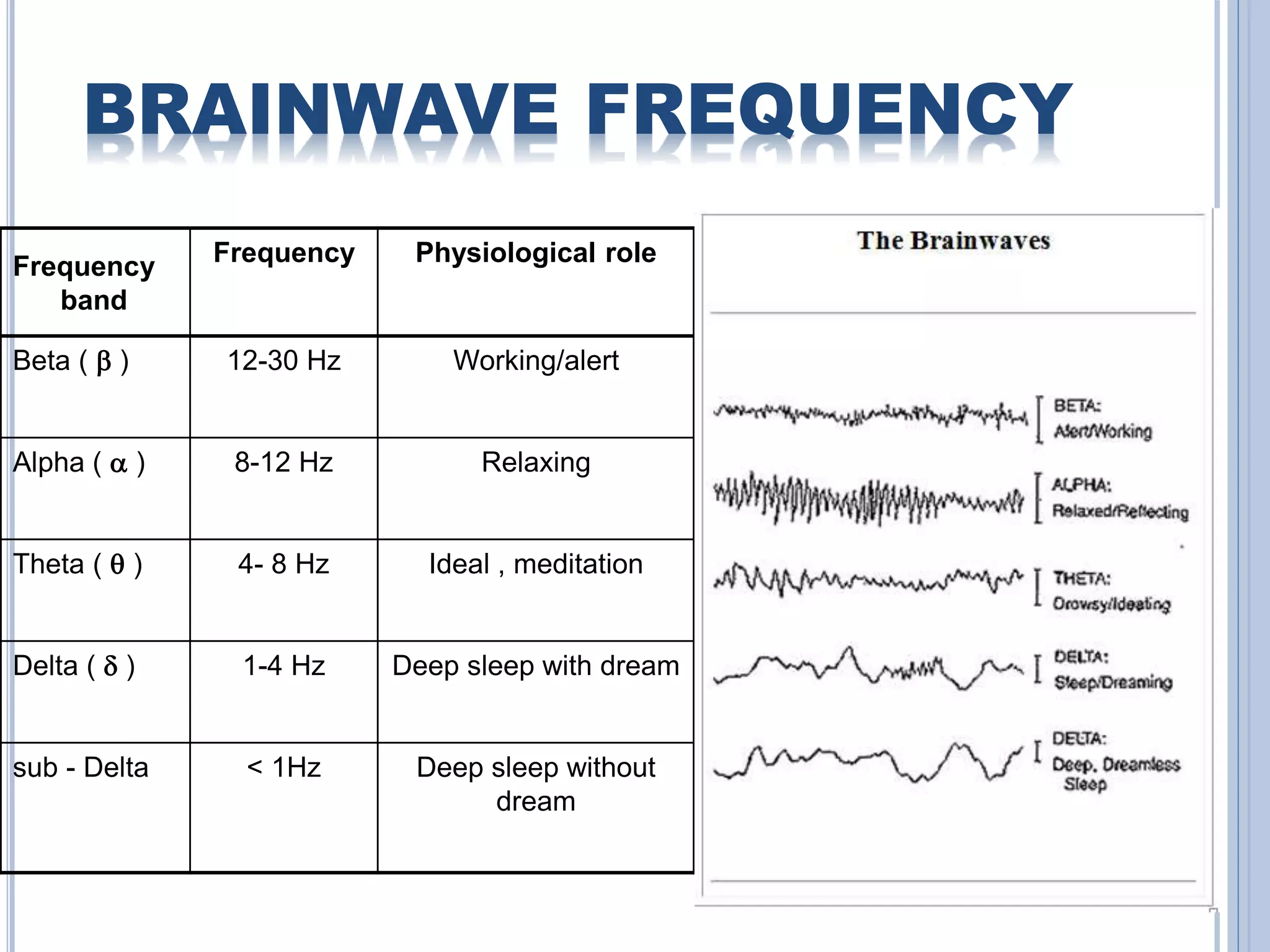
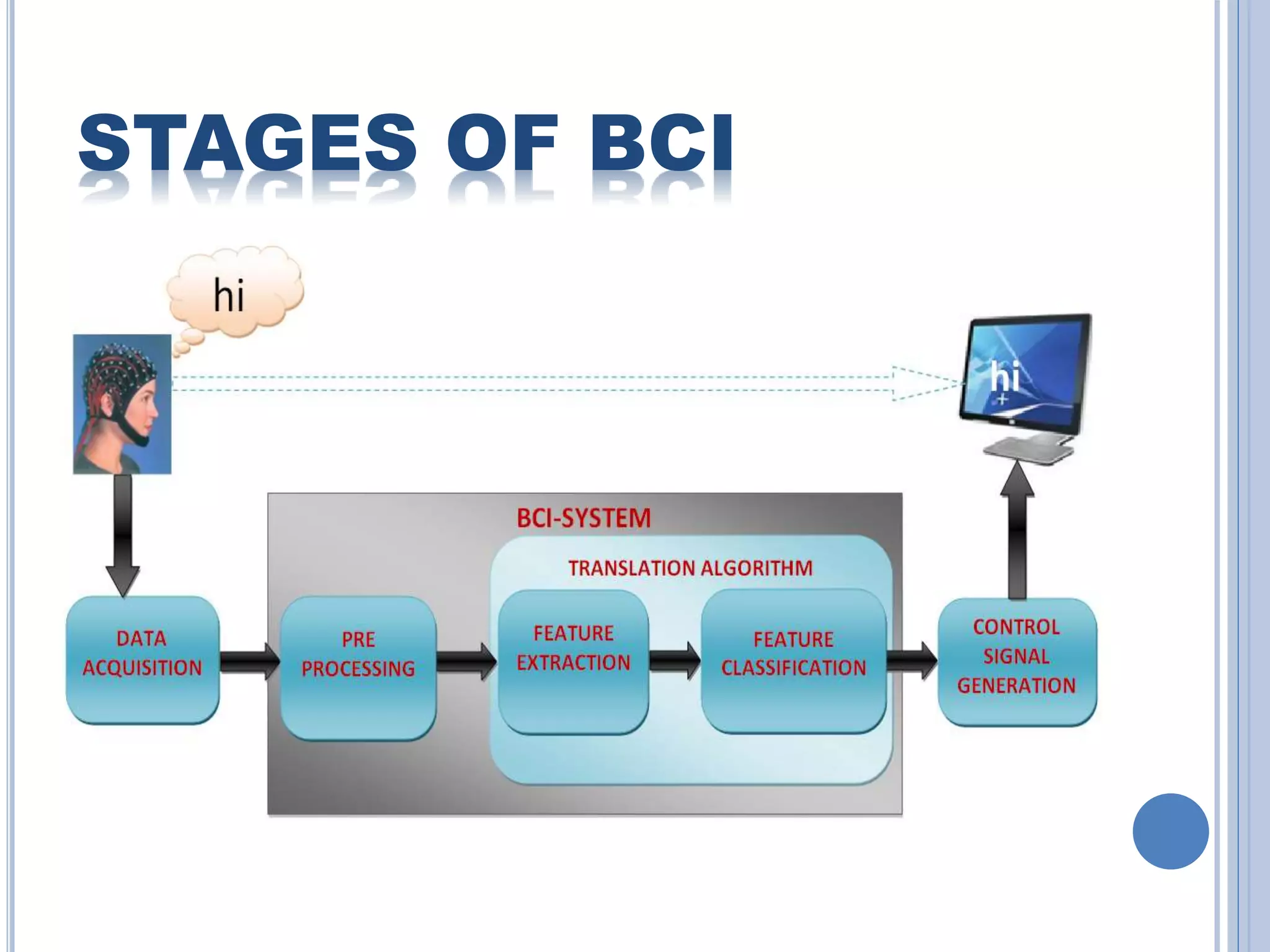
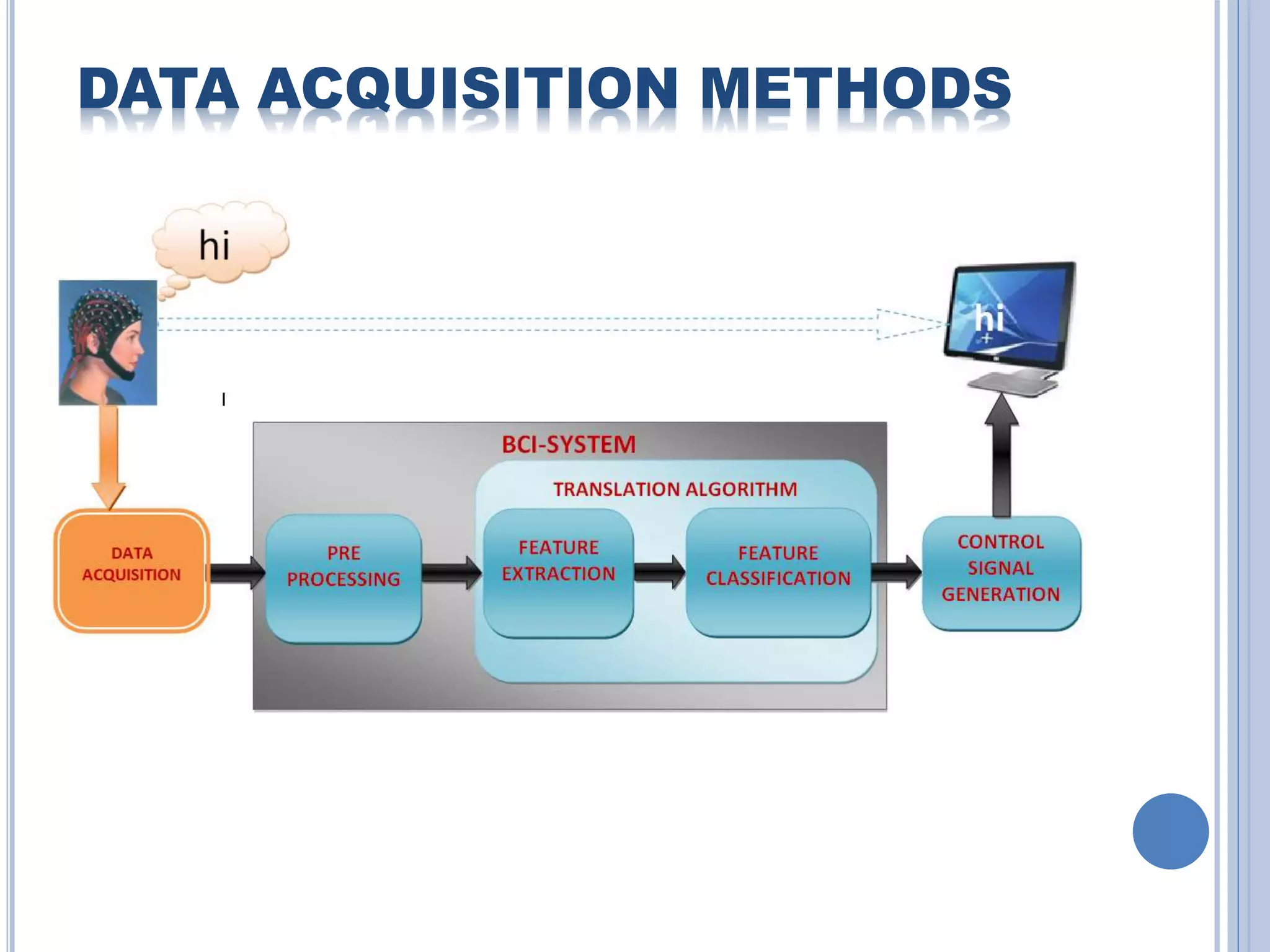
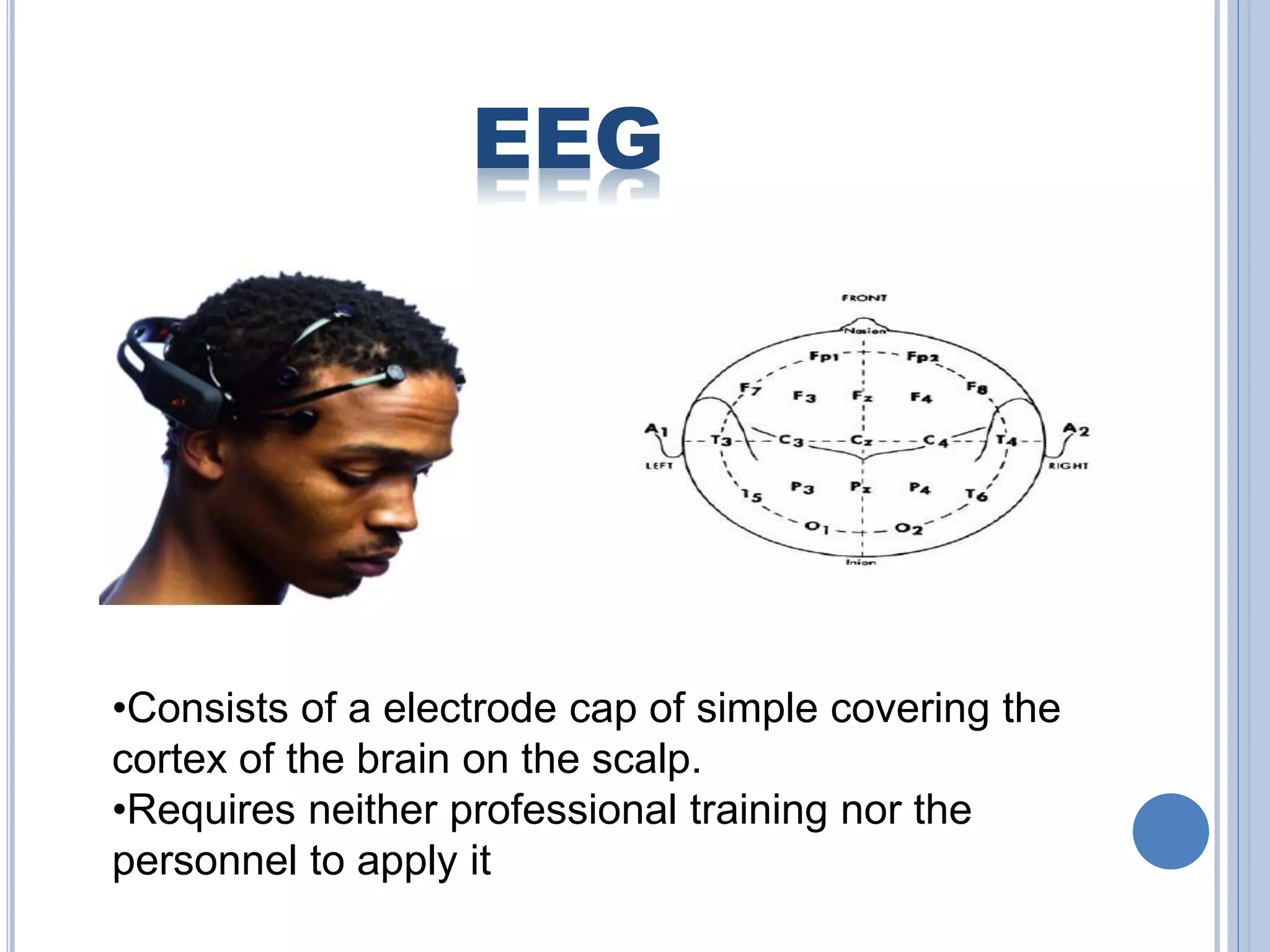
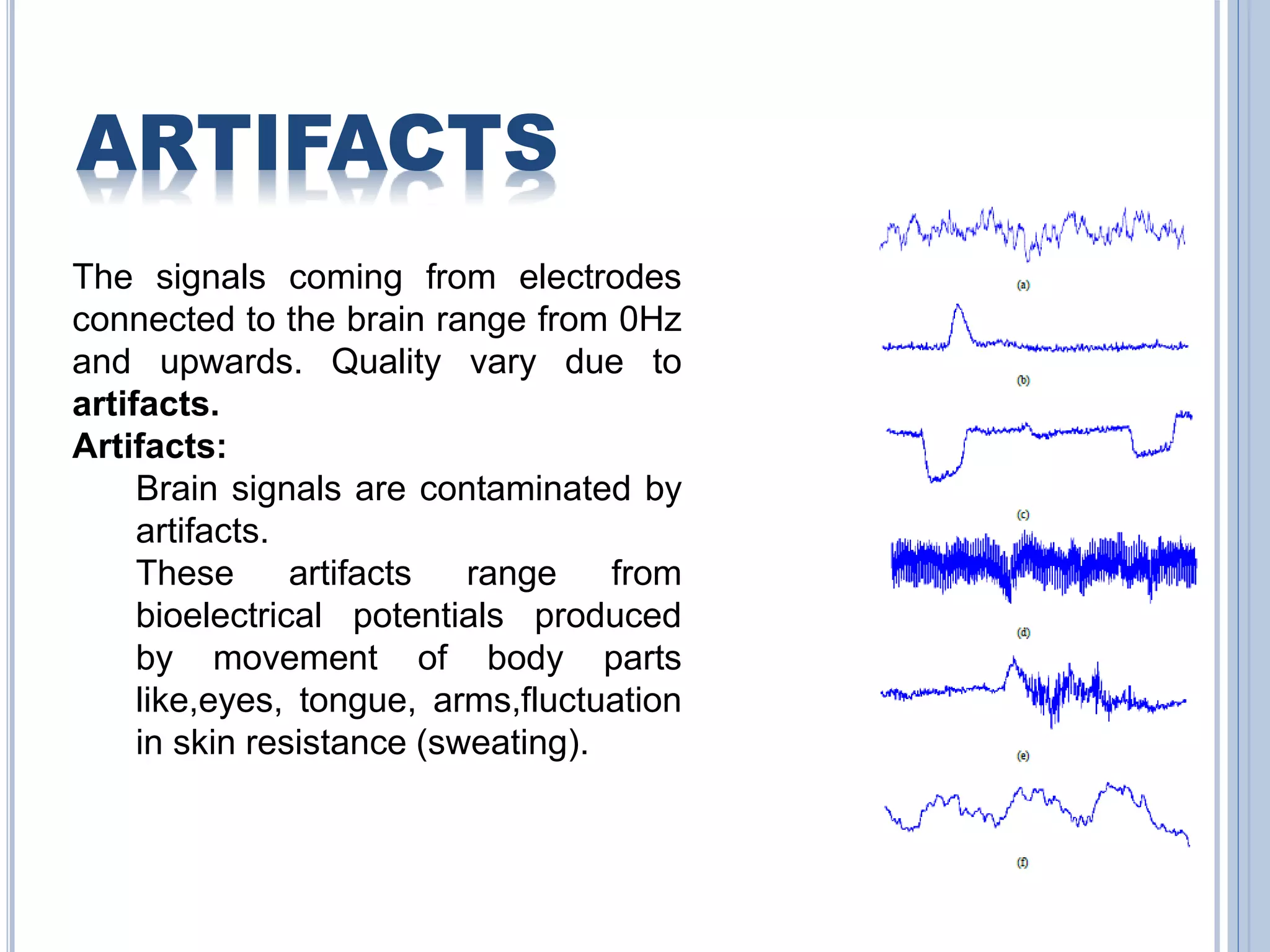
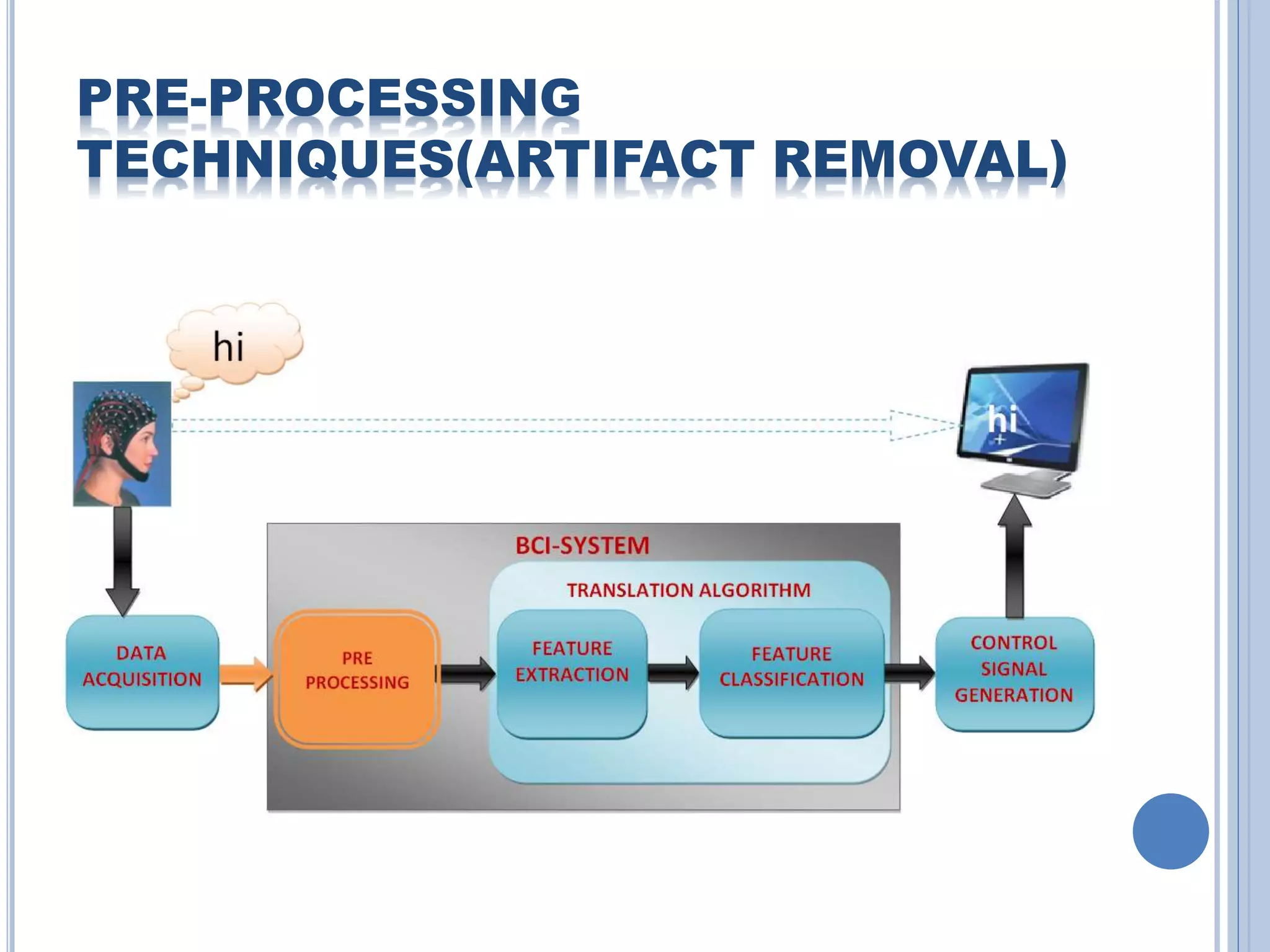
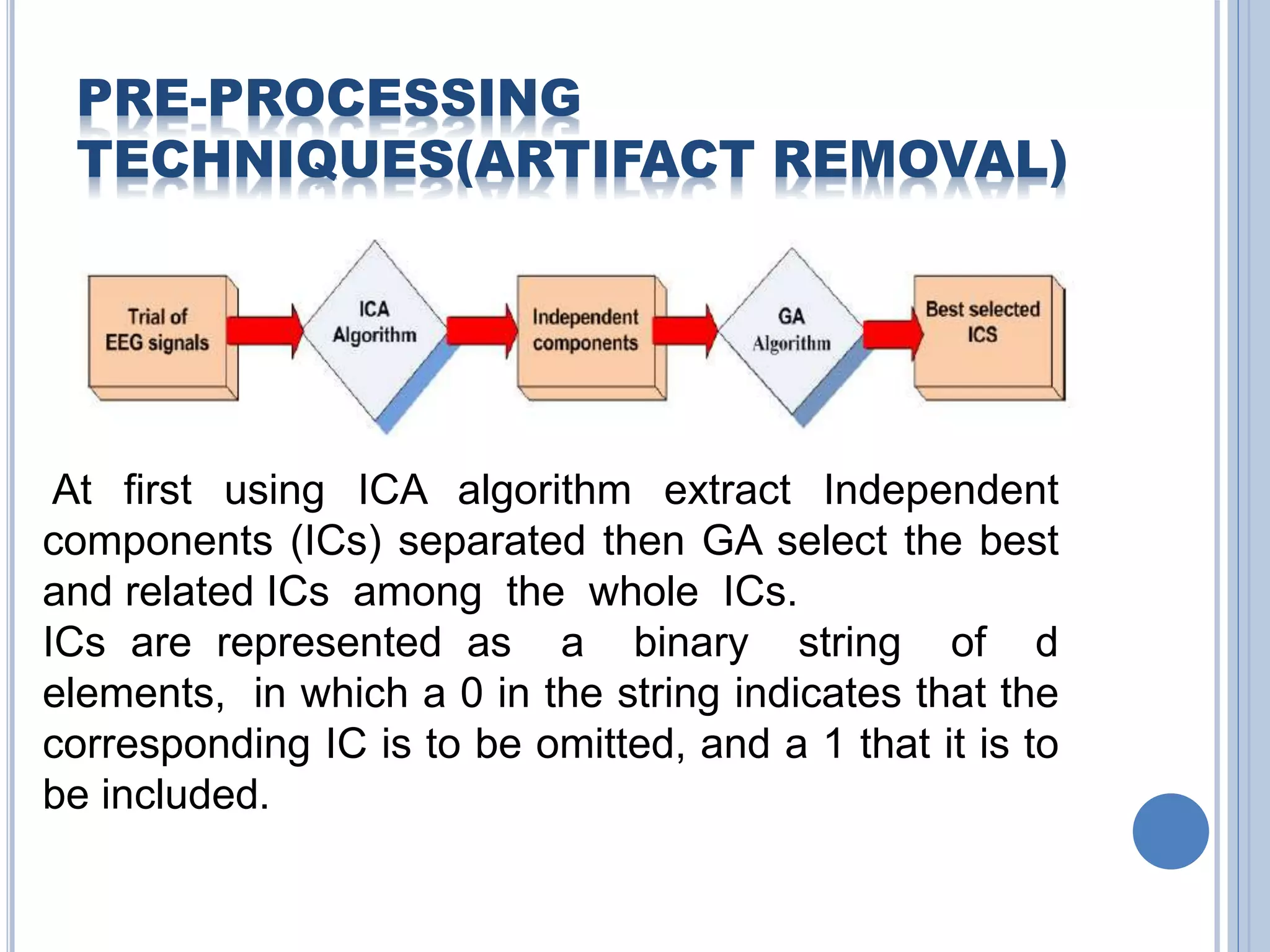
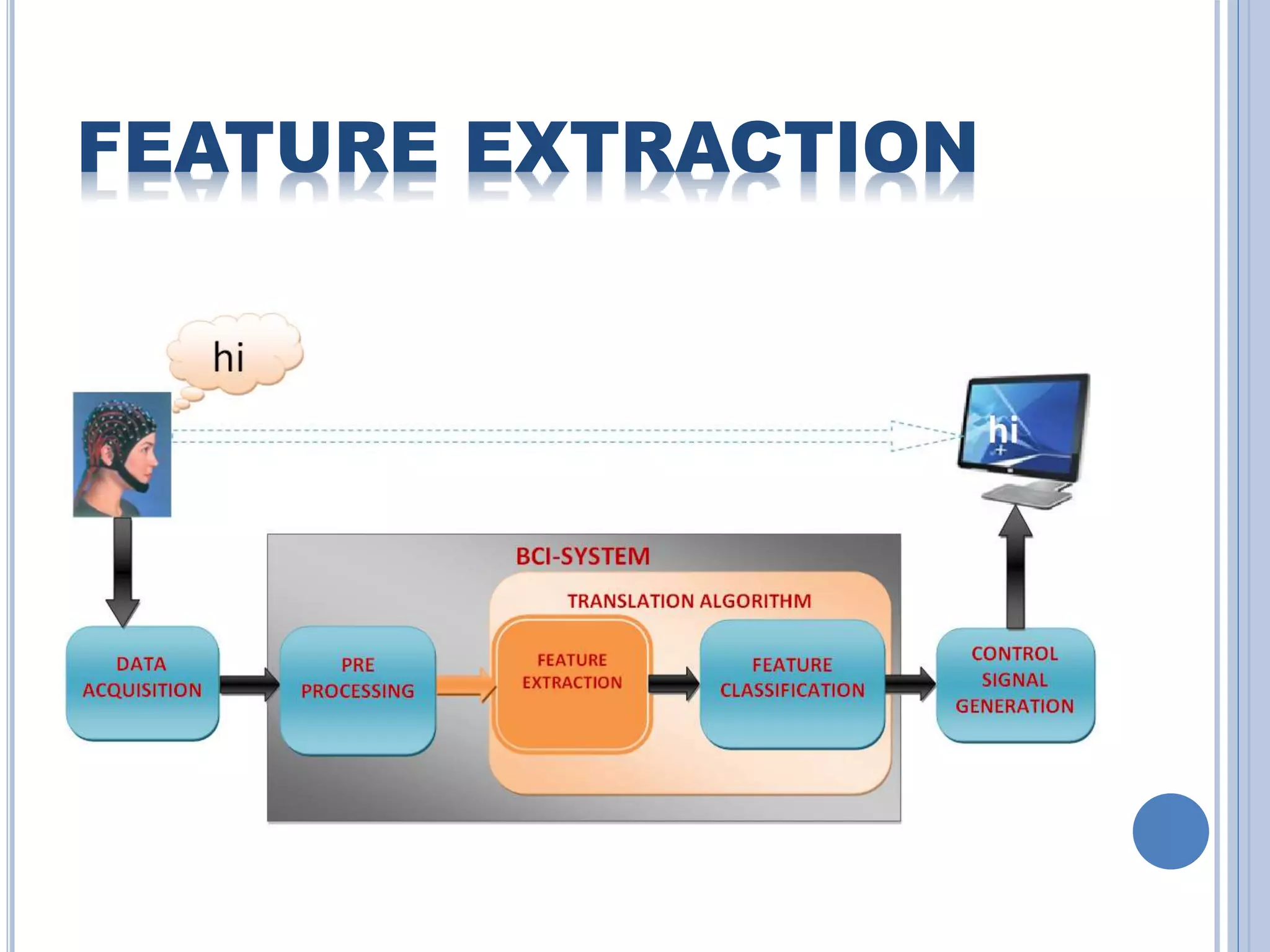
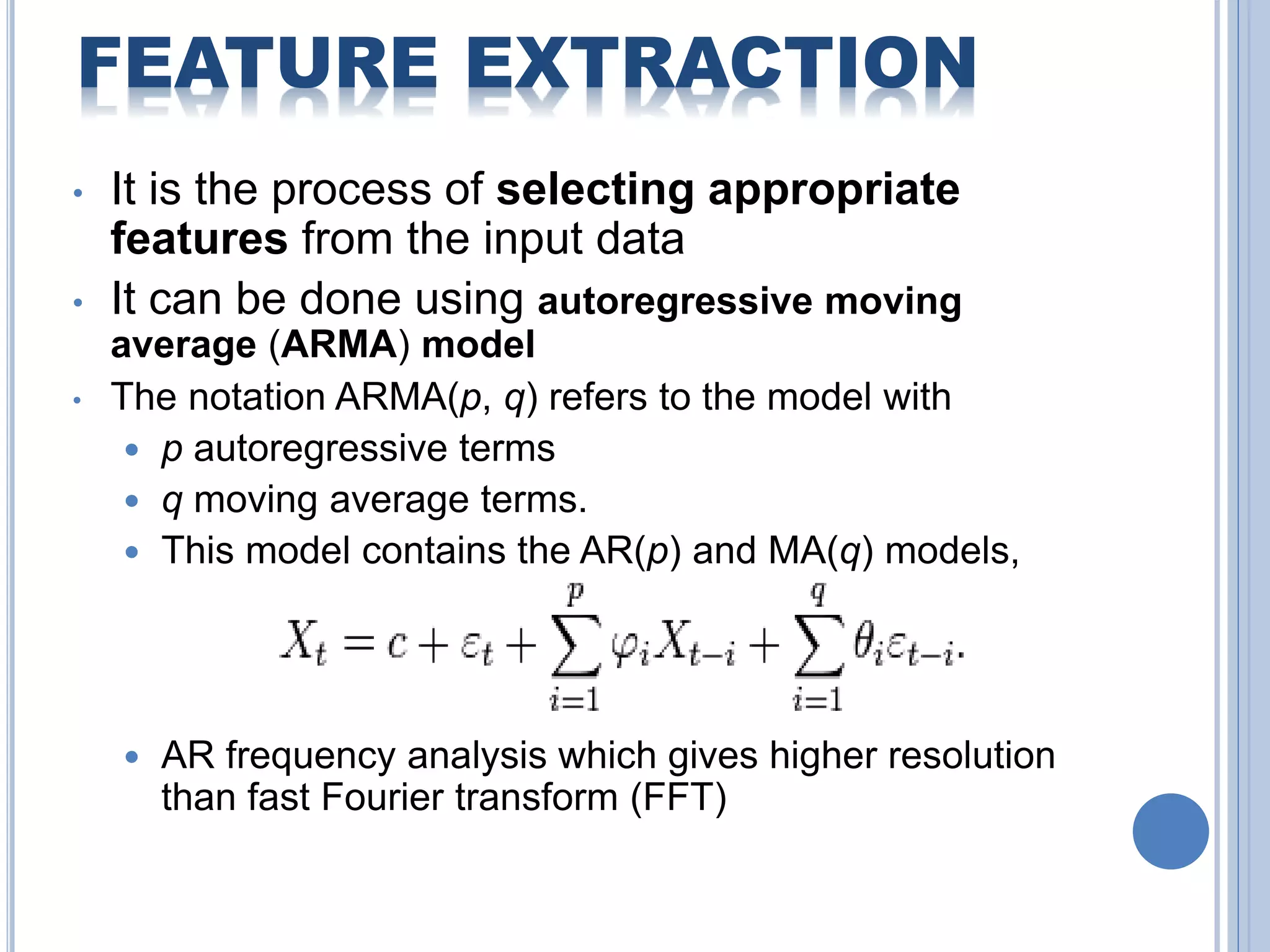
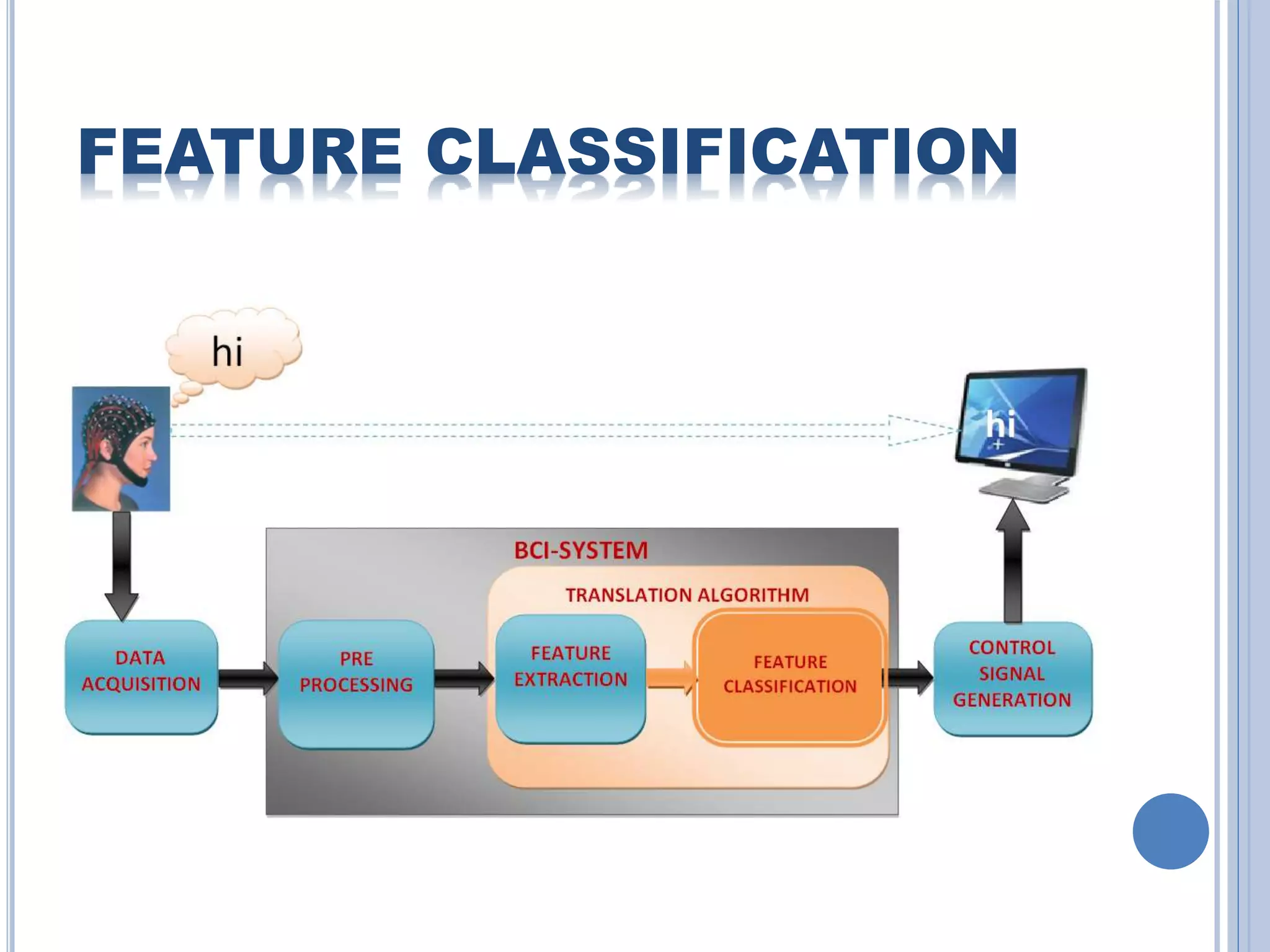
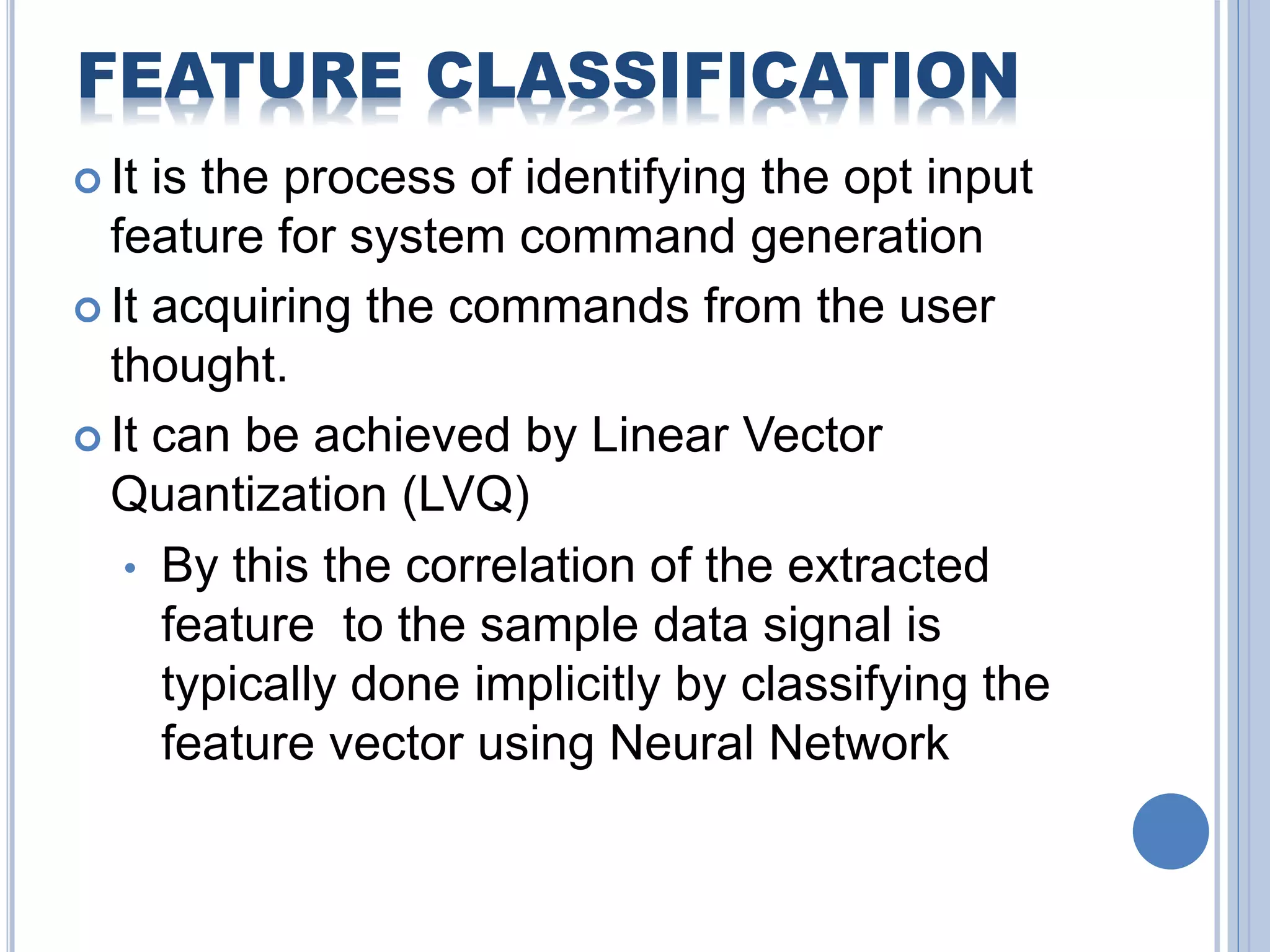
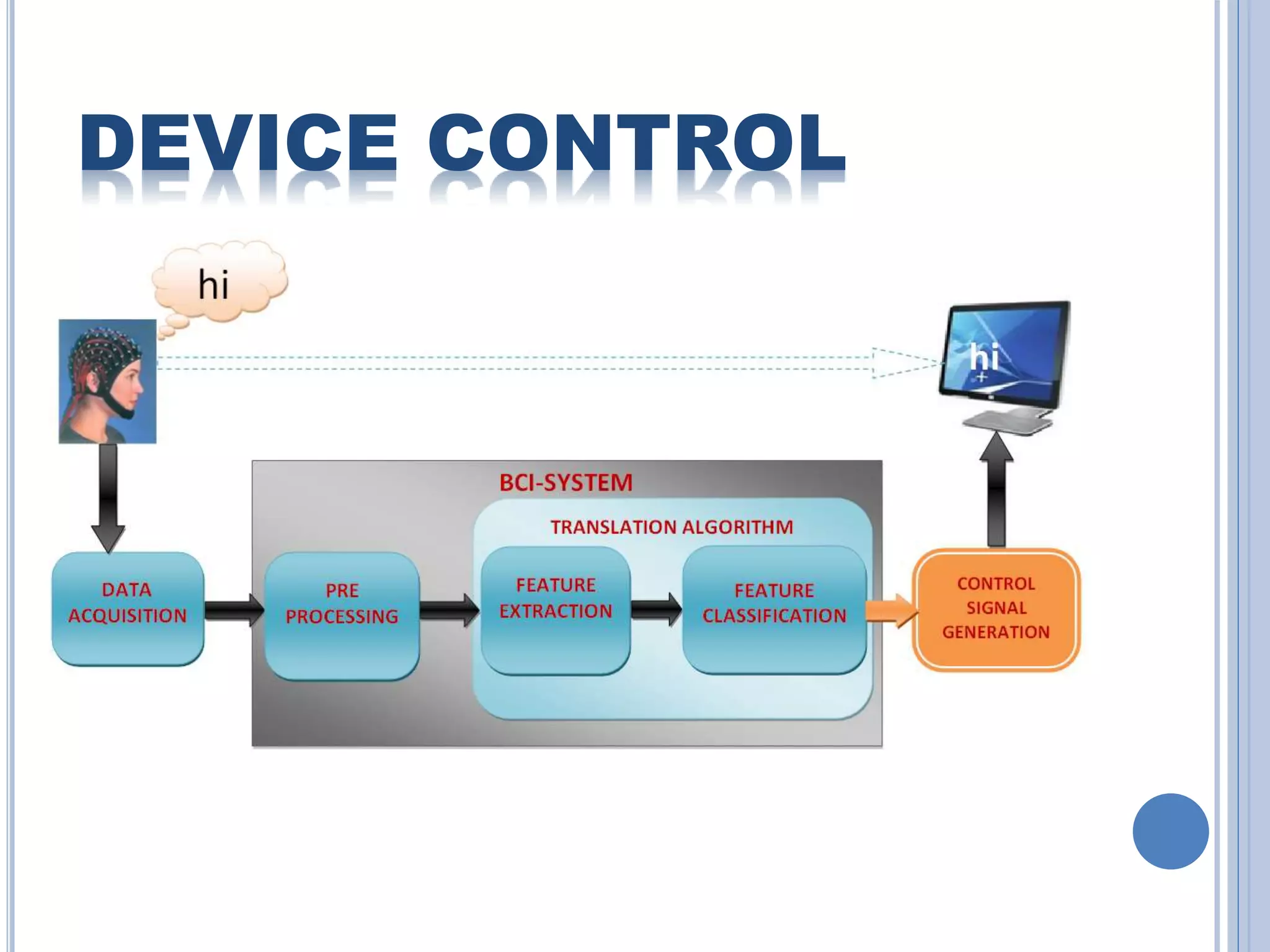
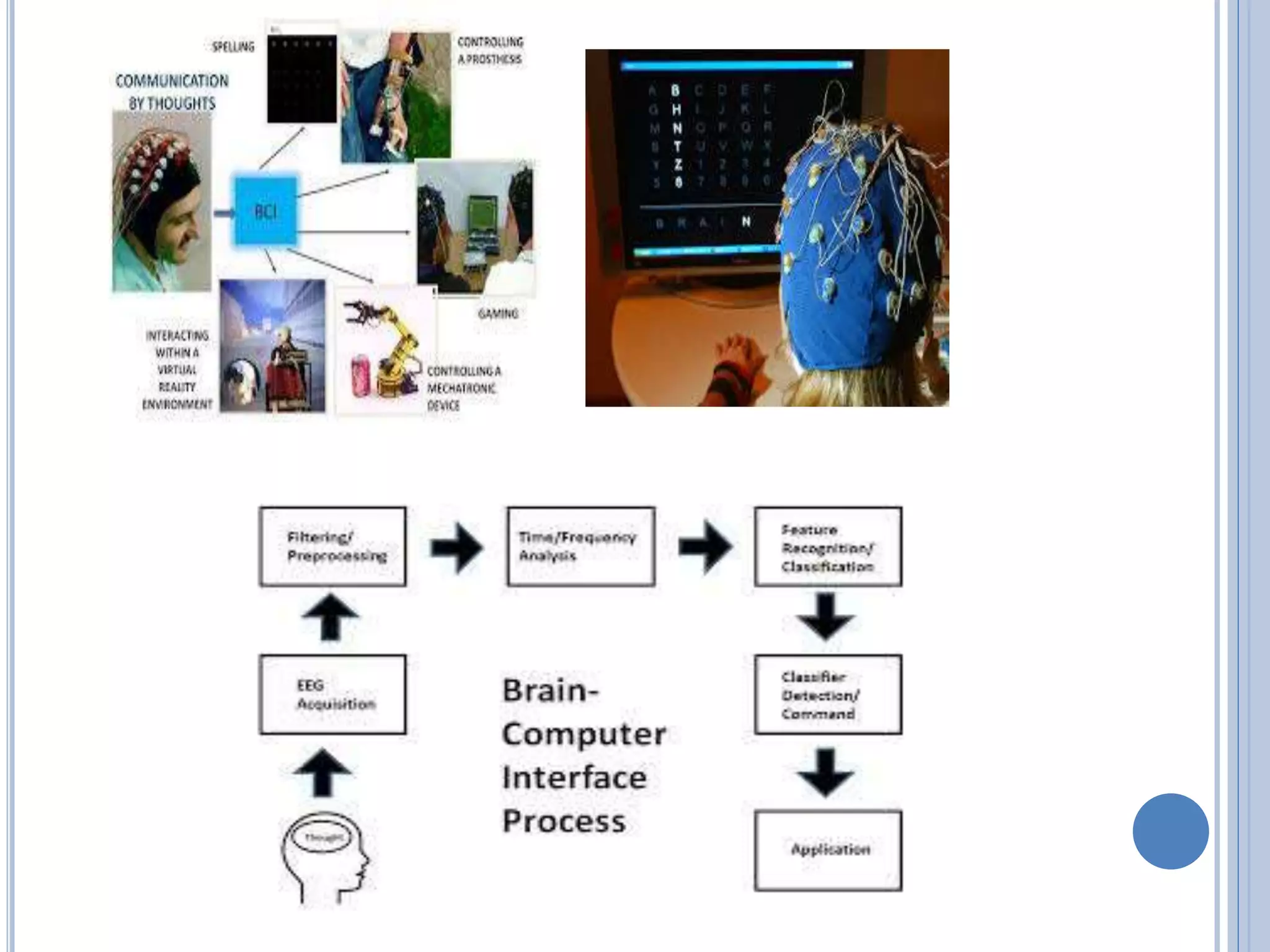
The document presents an overview of Brain-Computer Interface (BCI), discussing its definition, brain wave basics, and the various stages of BCI, including data acquisition methods like EEG, MEG, and fMRI. It outlines pre-processing techniques for artifact removal, feature extraction through methods like Autoregressive Moving Average (ARMA), and feature classification for command generation. The applications of BCI are extensive, ranging from basic communication aids to controlling artificial limbs and sensory devices for individuals with disabilities.