Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX

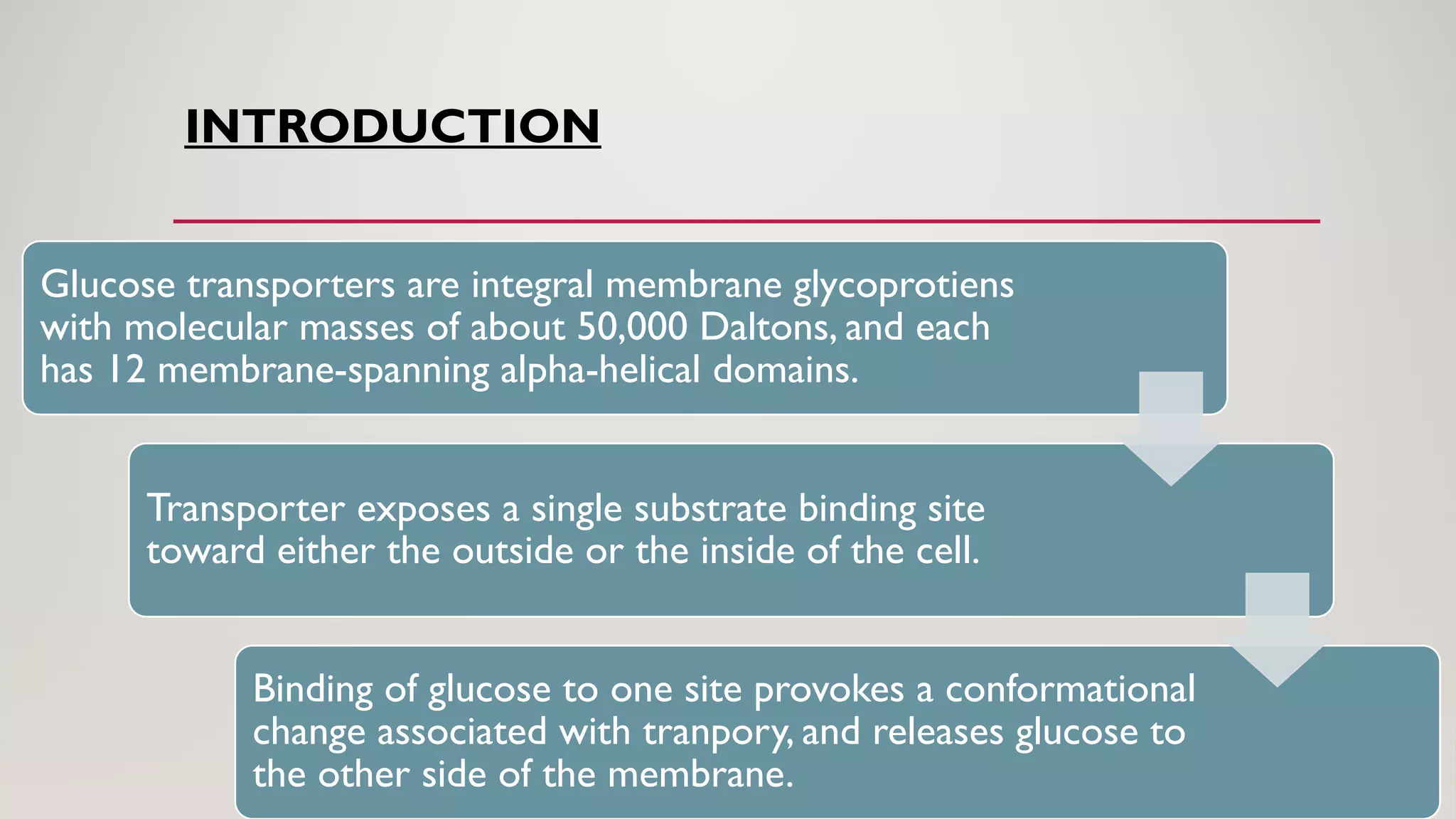
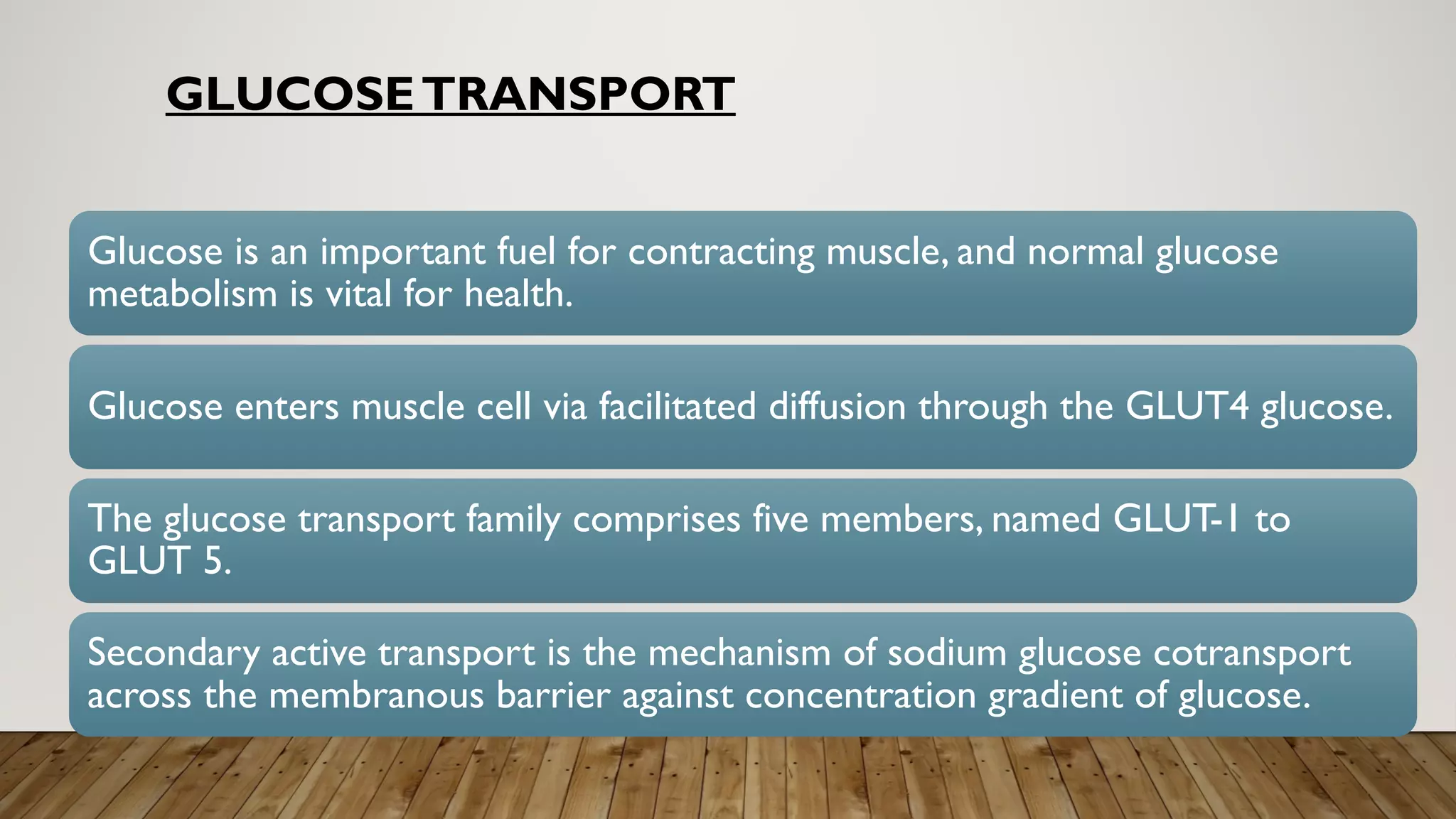
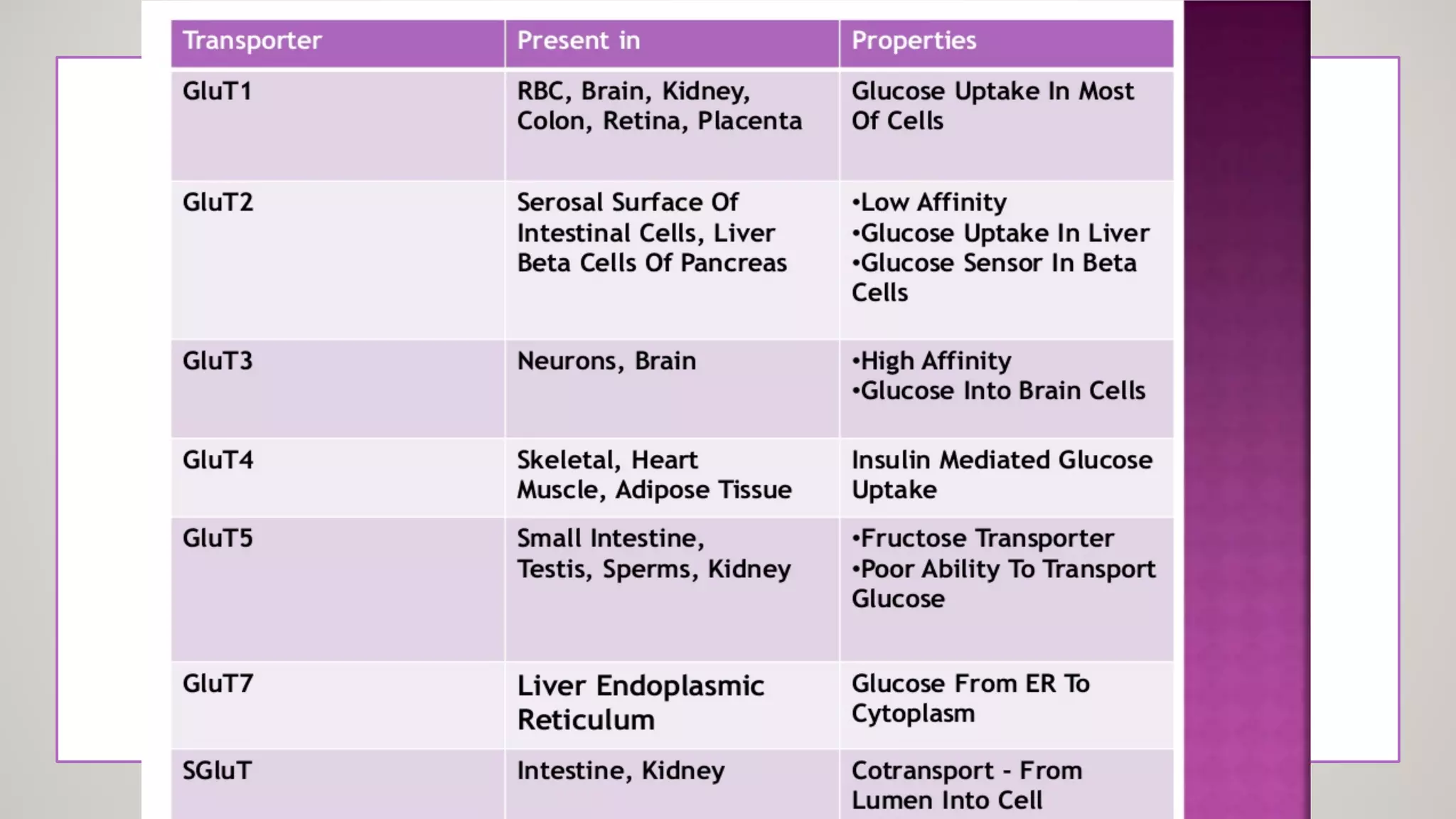

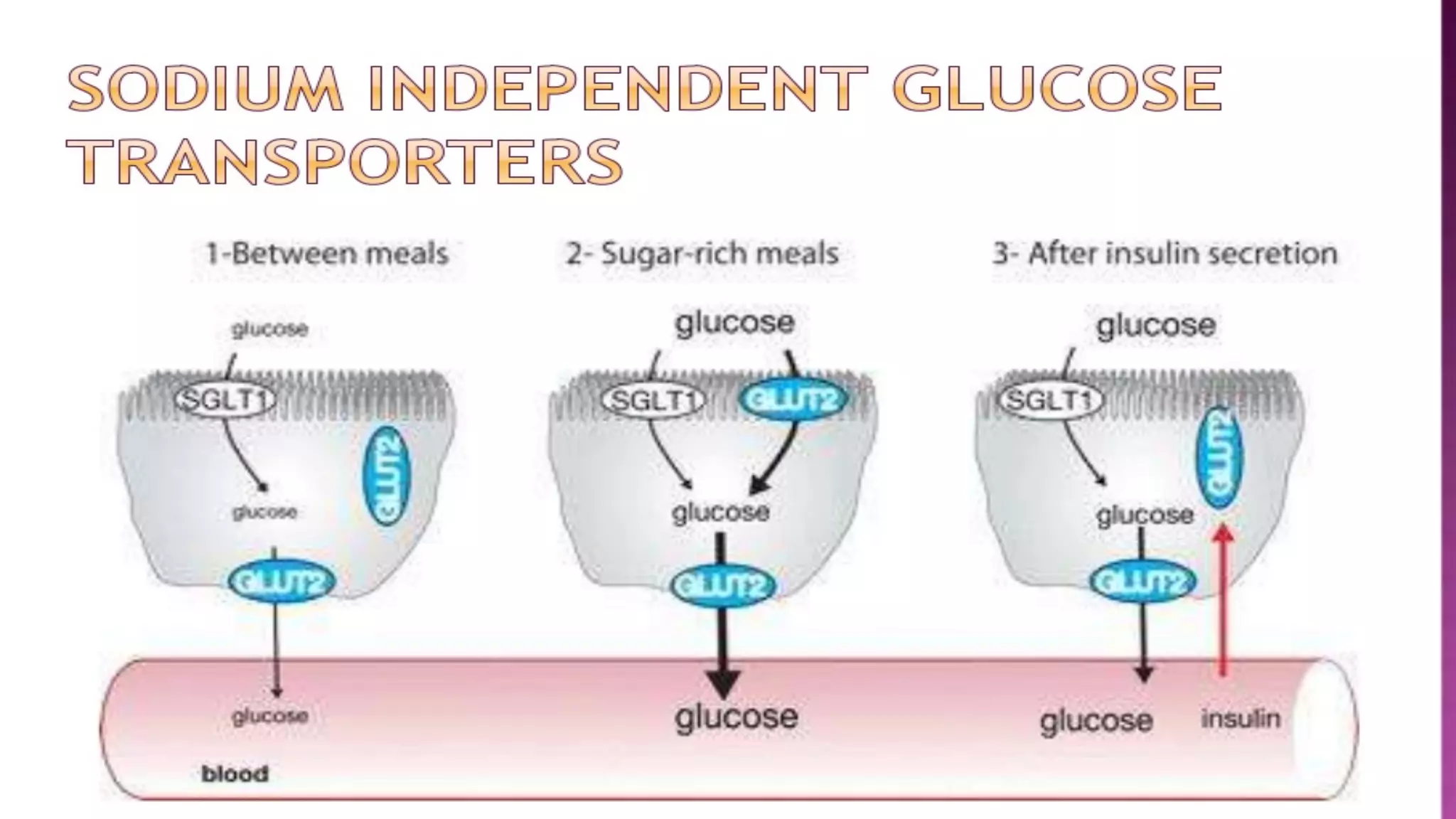

Glucose transporters are integral membrane glycoproteins essential for glucose metabolism, with a primary role in glucose uptake in tissues such as muscle and adipose tissue via mechanisms like facilitated diffusion and co-transport. The GLUT family includes five members (GLUT-1 to GLUT-5), with GLUT-4 being influenced by insulin to enhance glucose entry into cells, while SGLUT-1 and SGLUT-2 facilitate glucose transport in the intestine and kidneys, respectively. Understanding these transporters is crucial for addressing diseases related to glucose metabolism, such as diabetes and malabsorption disorders.
Glucose transporters are glycoproteins with 12 membrane-spanning domains that facilitate glucose transport across membranes.
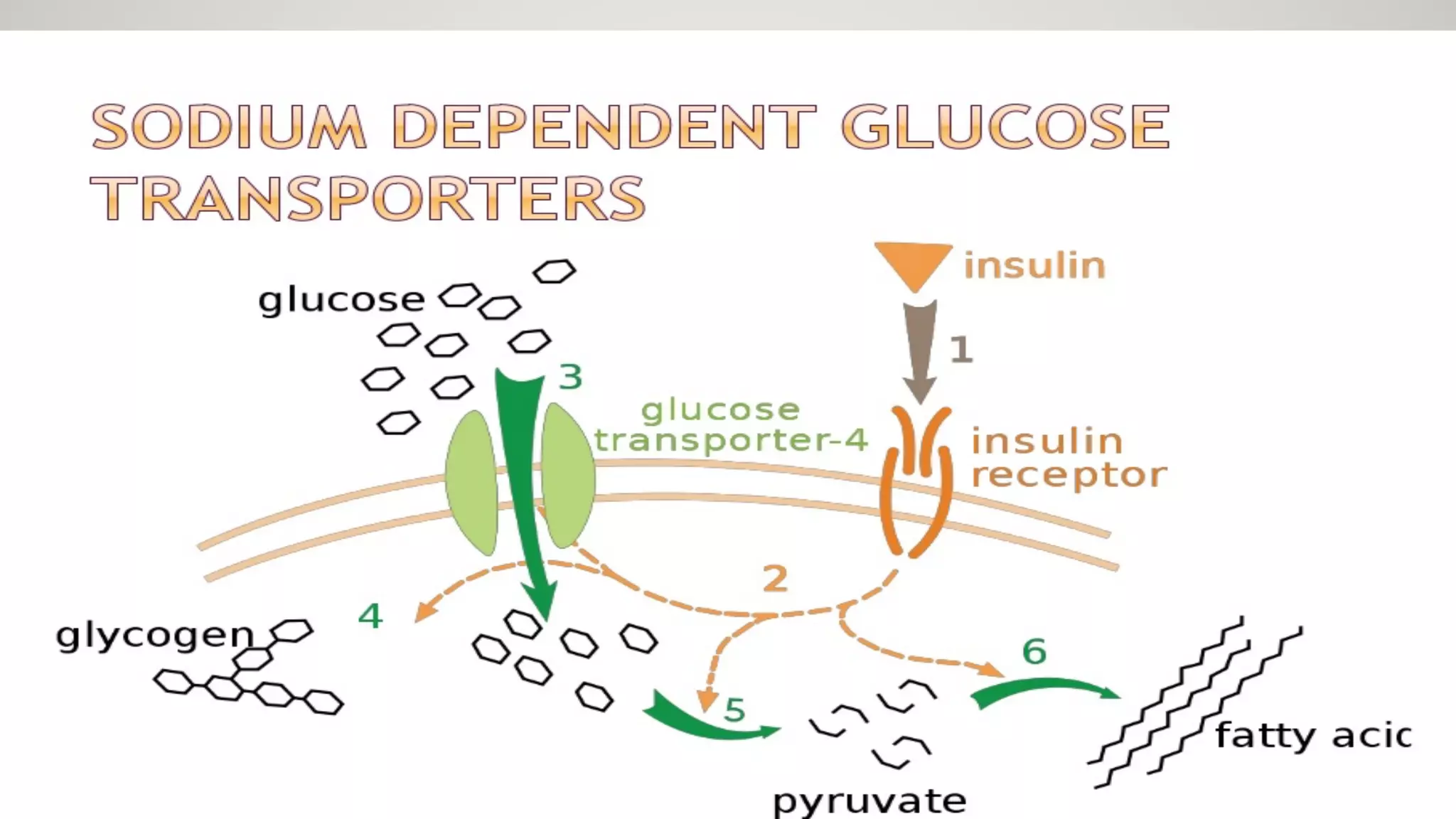
Glucose is crucial for muscle metabolism; GLUT-4 facilitates its uptake, enhanced by insulin, while some tissues can uptake glucose without insulin.
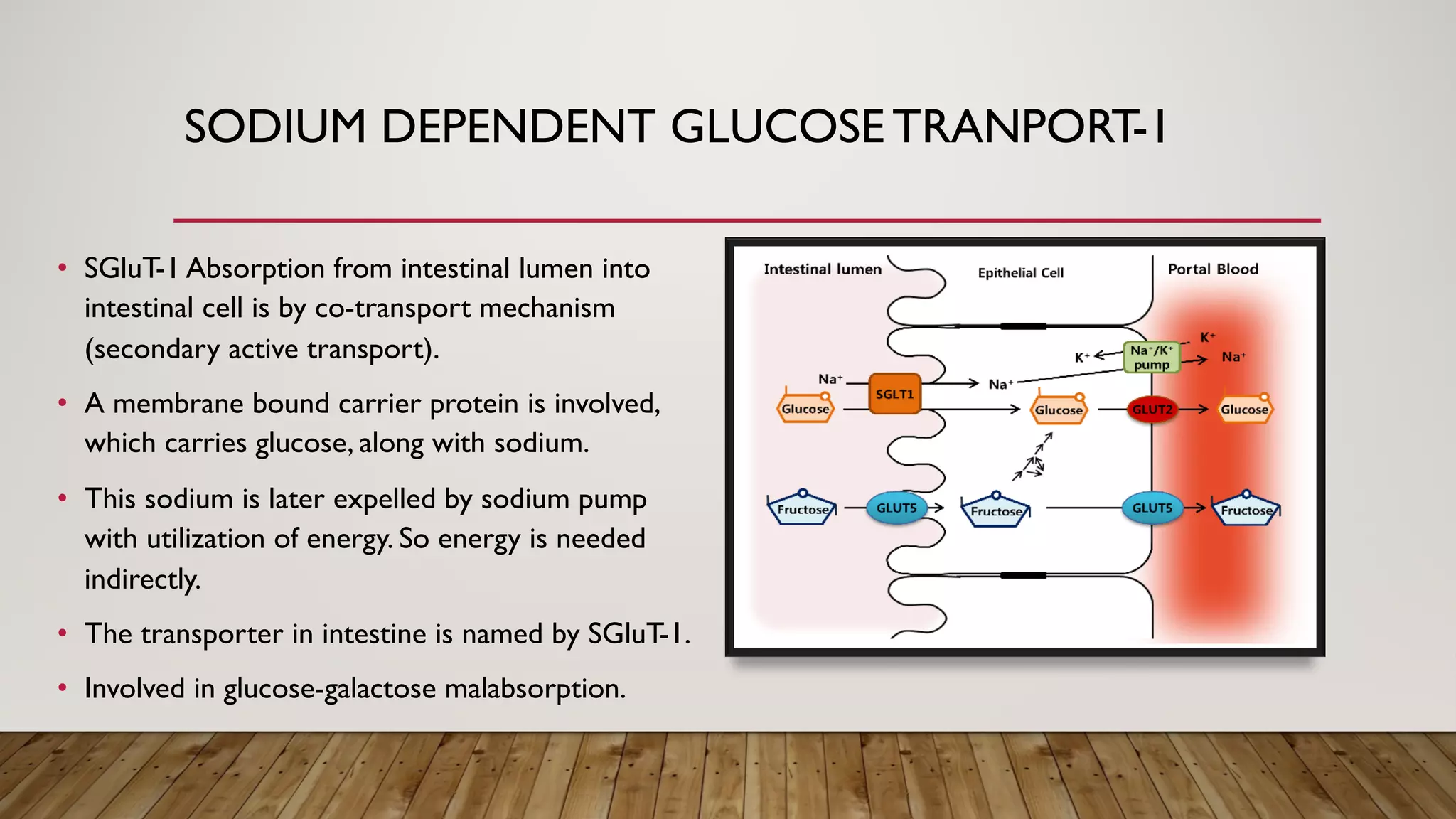
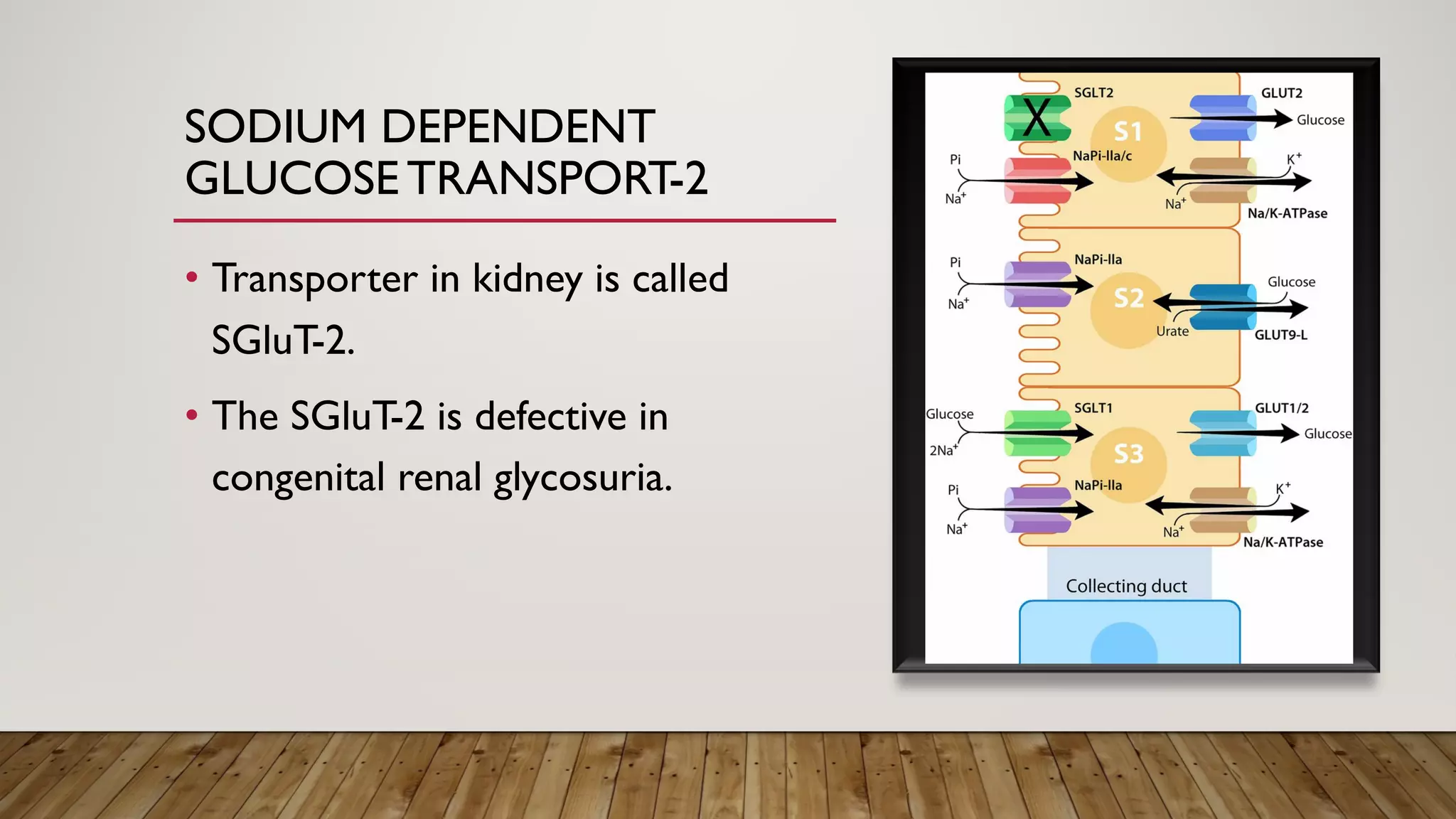
SGluT-1 and SGluT-2 assist in glucose transport; SGluT-1 for intestinal absorption and SGluT-2 linked to renal function.
Thank you for the presentation on glucose transport mechanisms.









