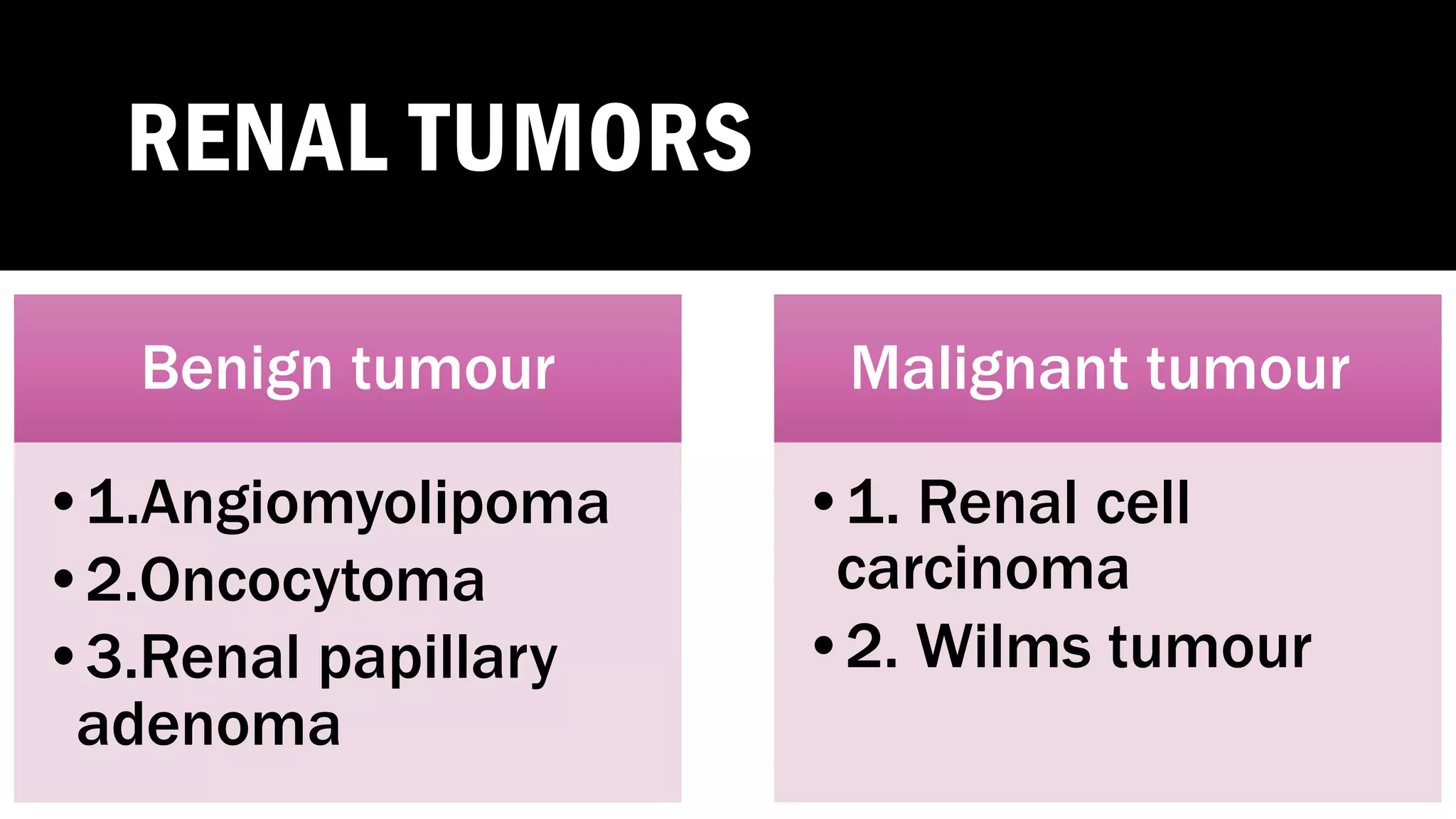
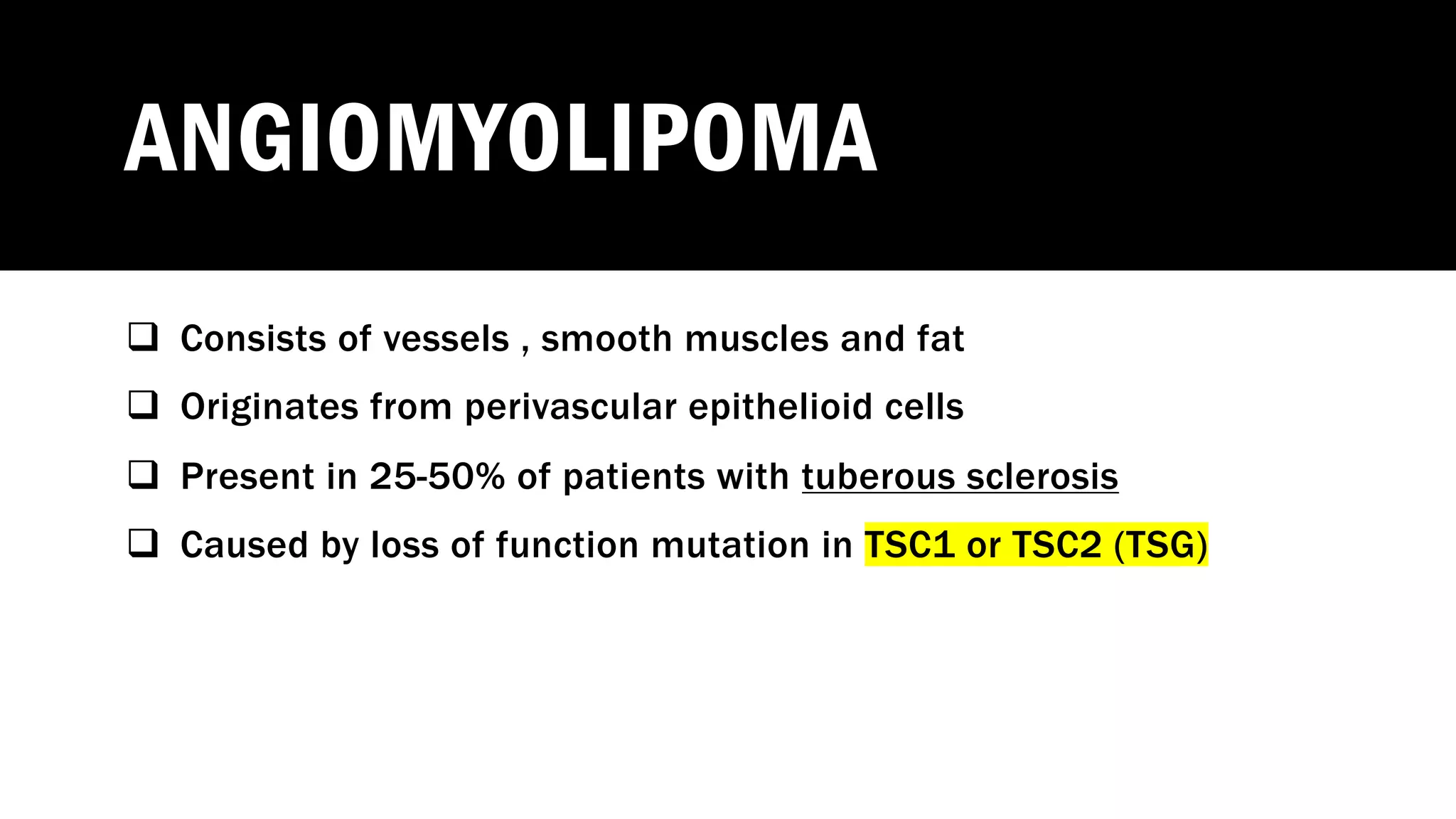
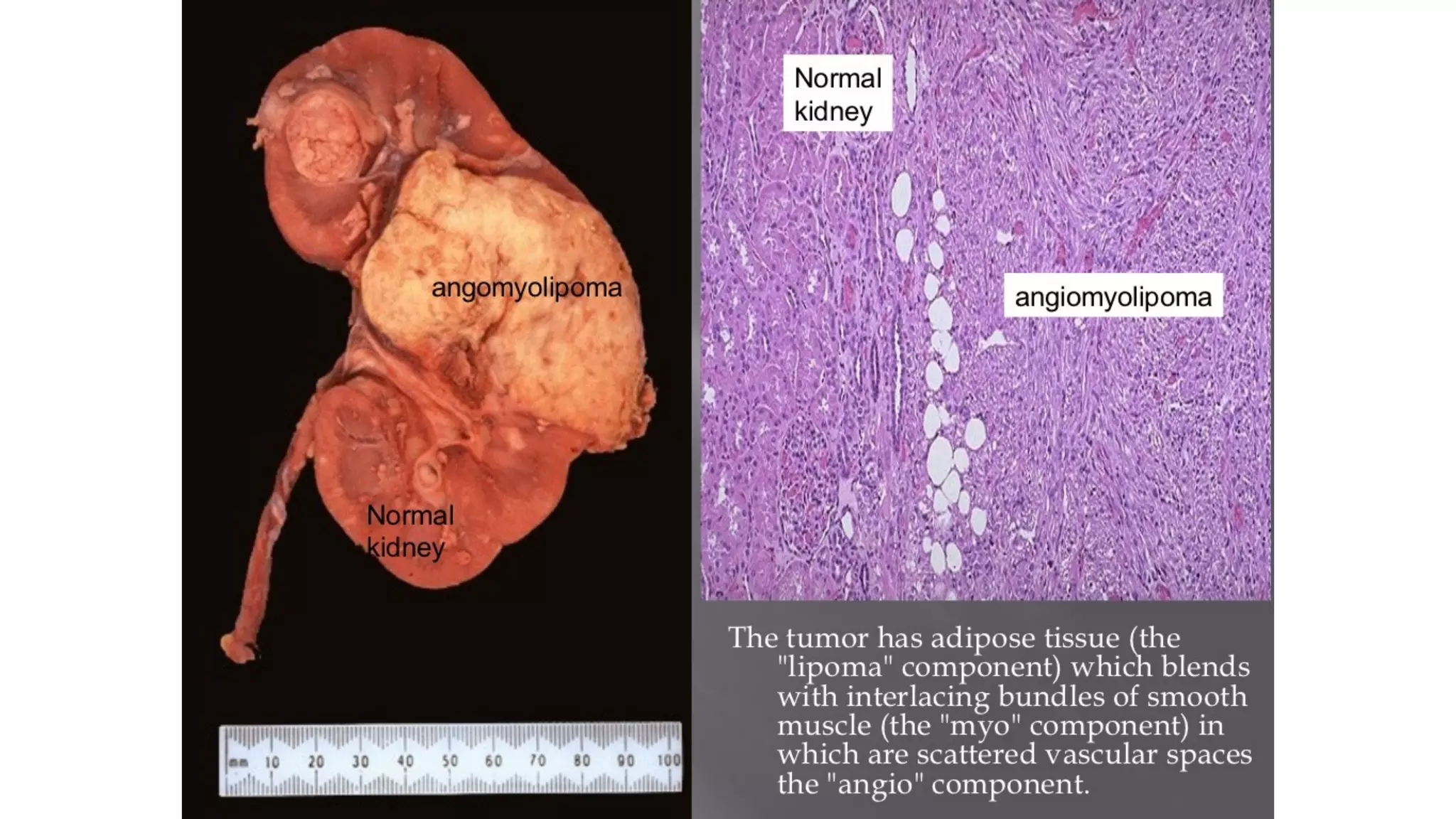
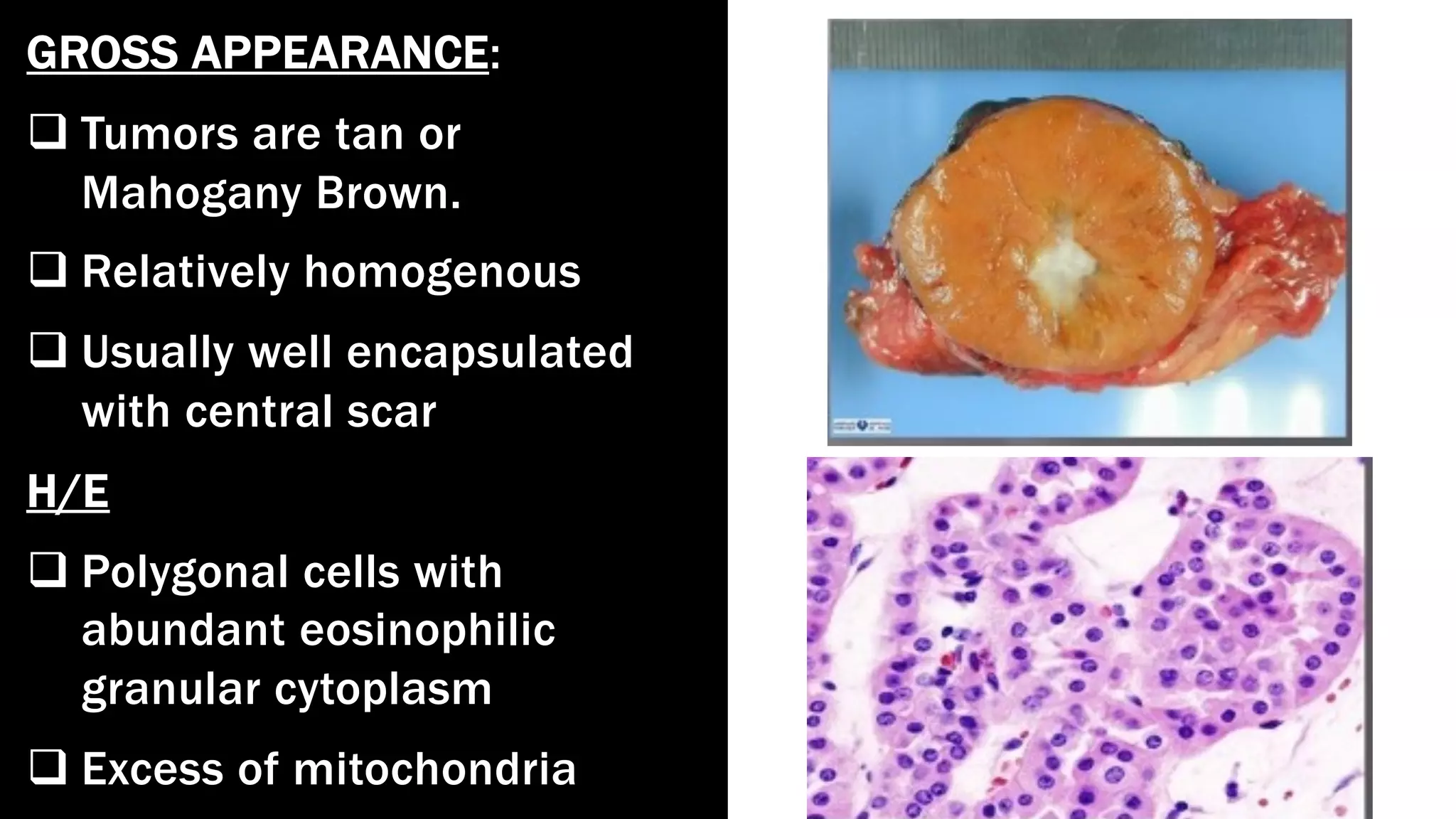
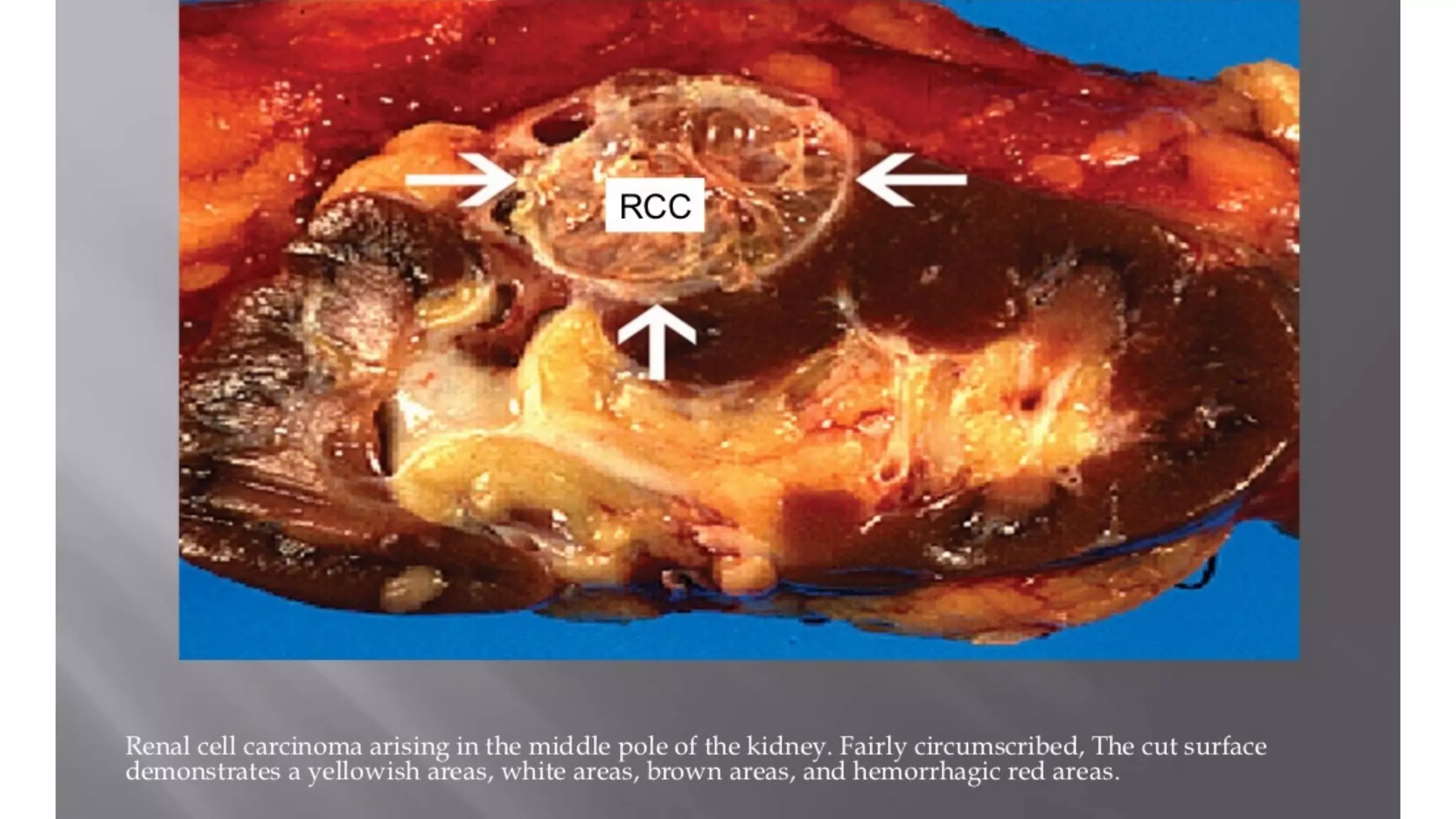
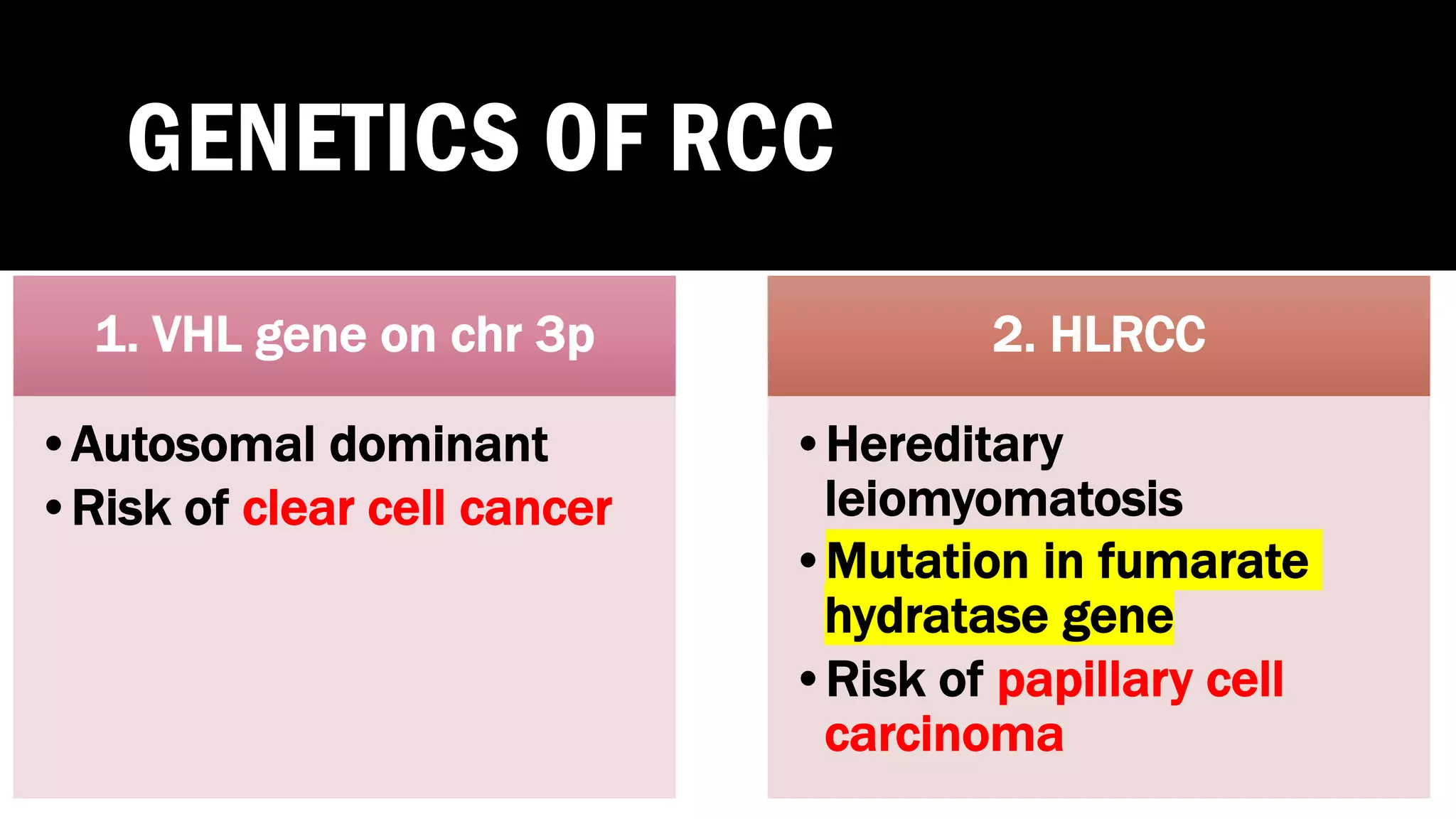
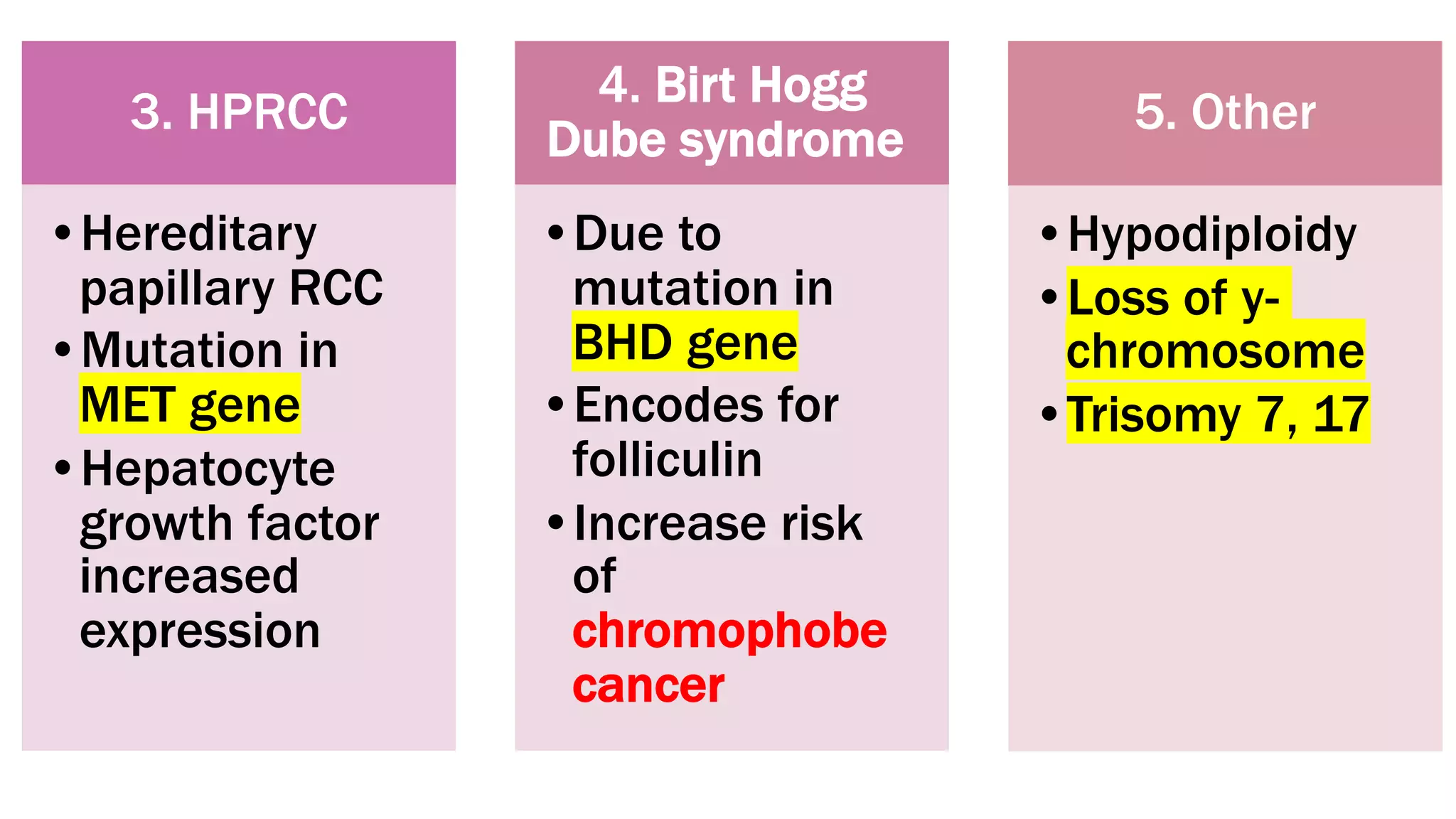
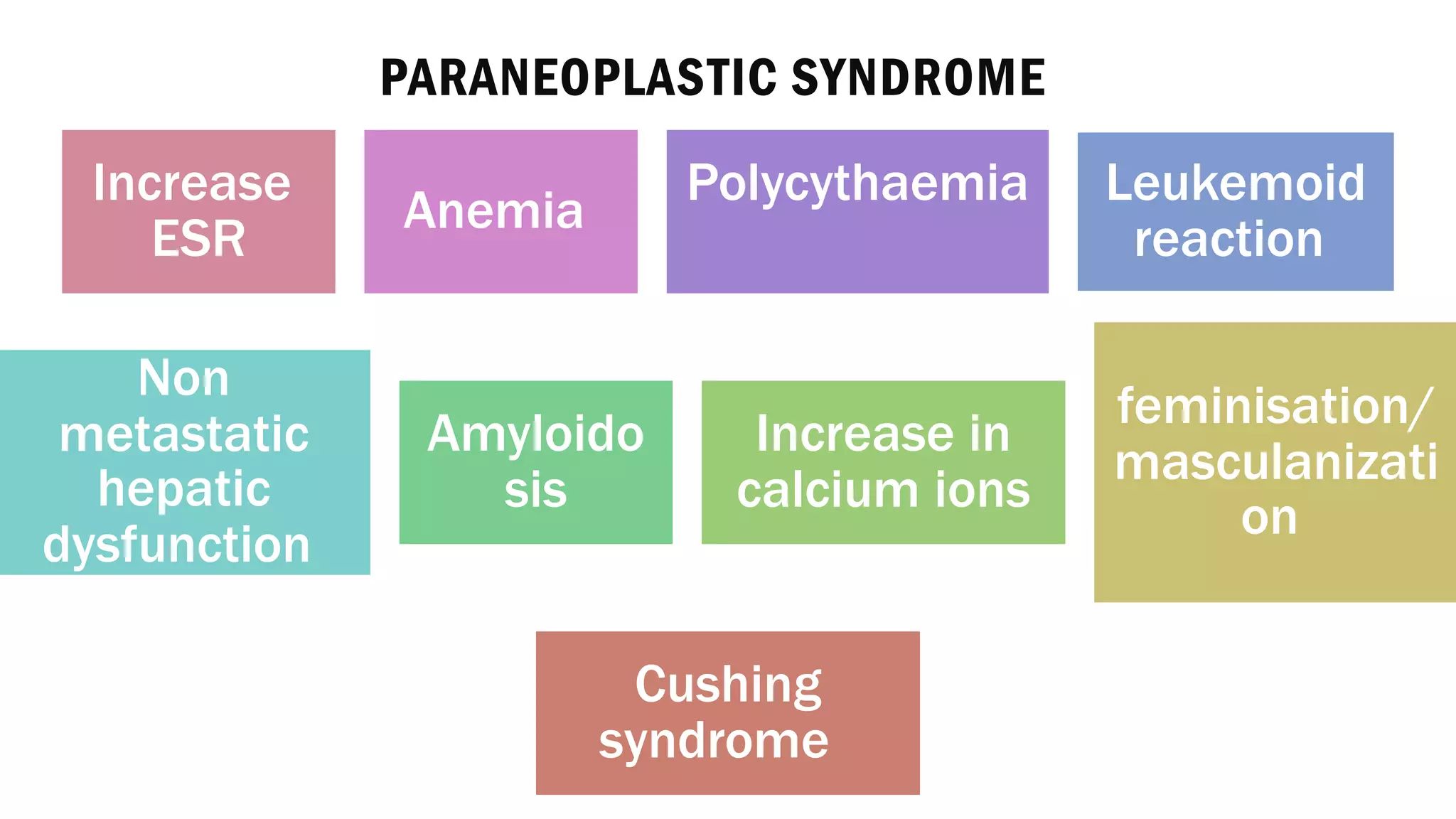
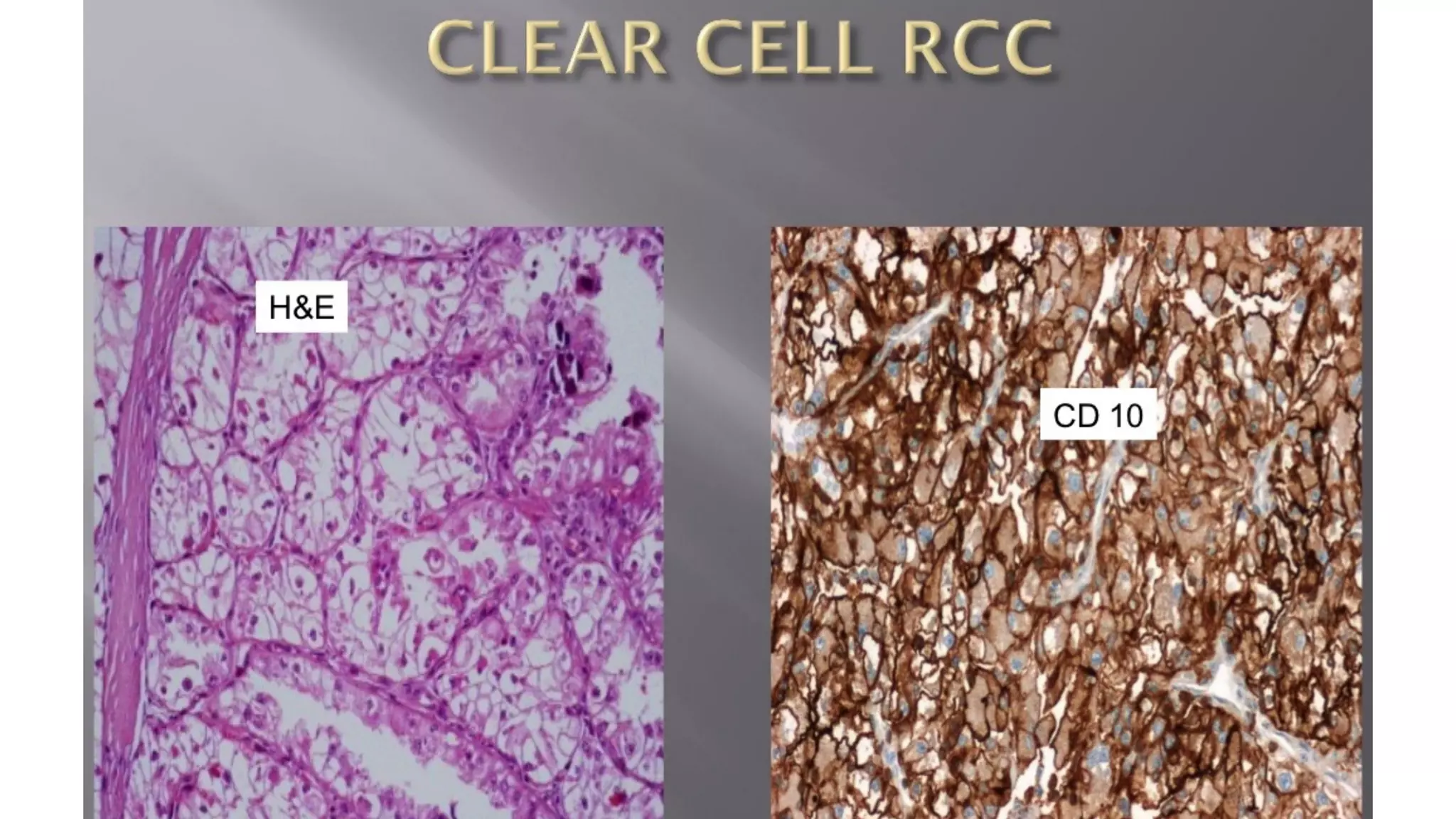
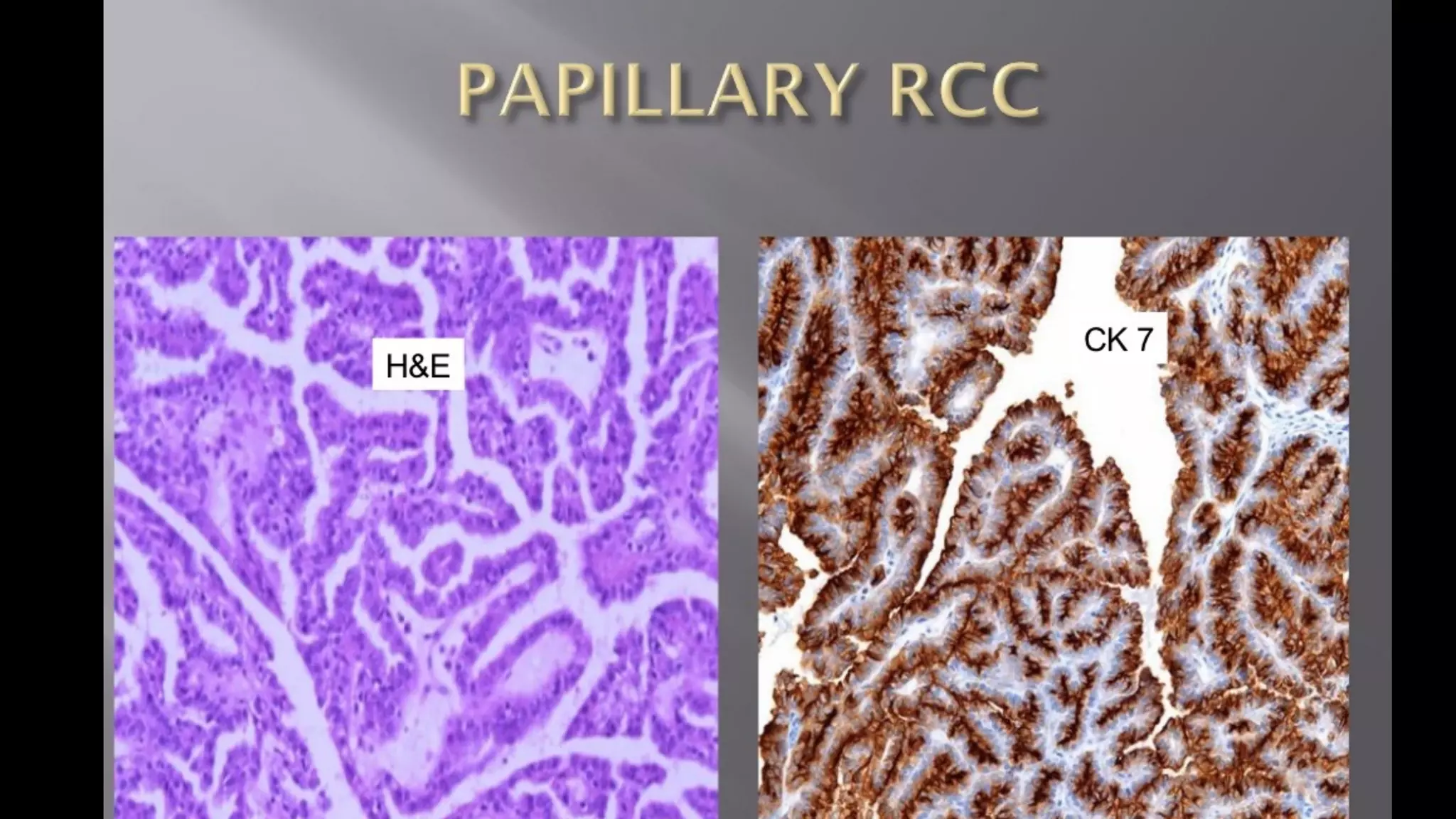
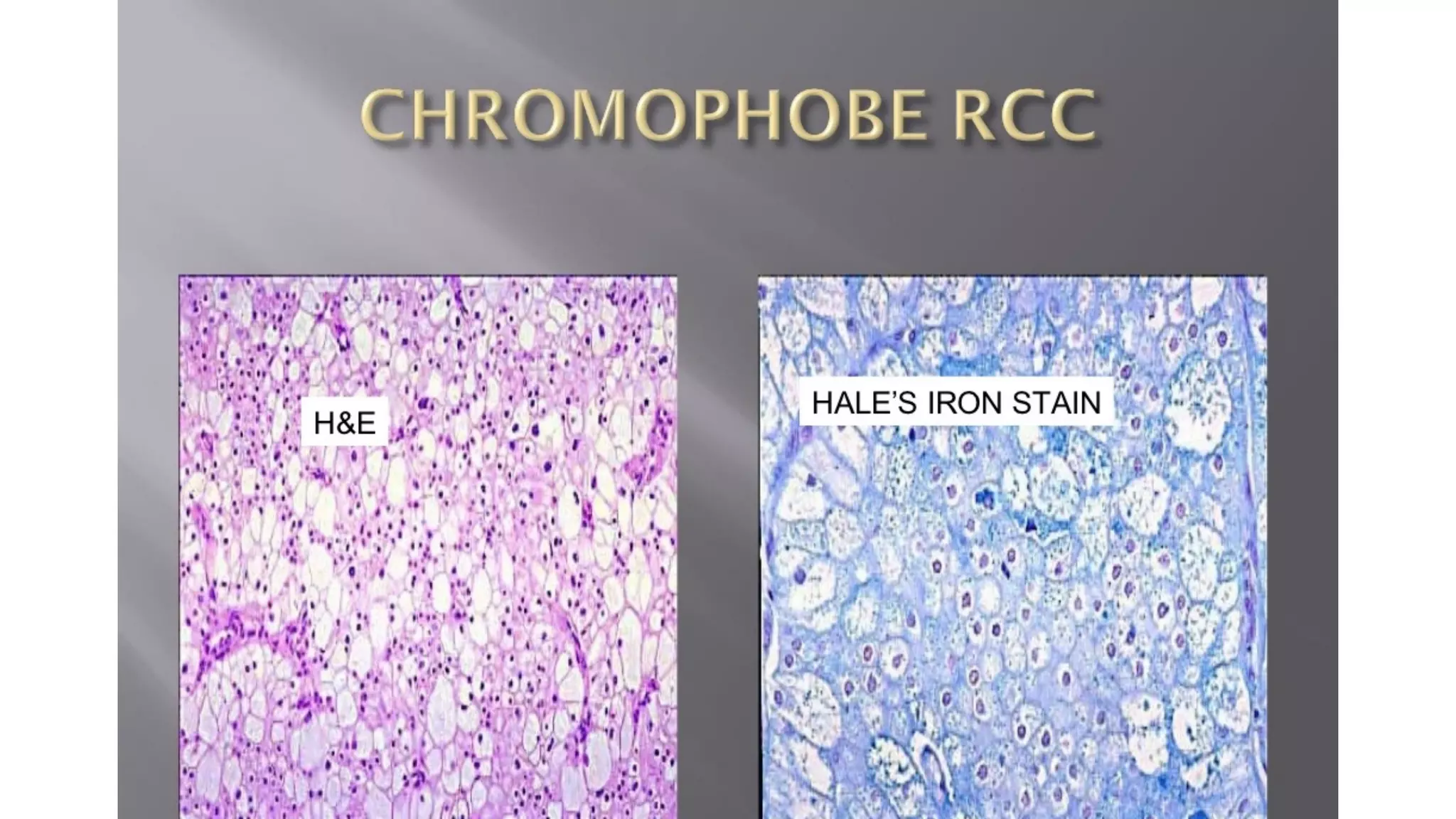
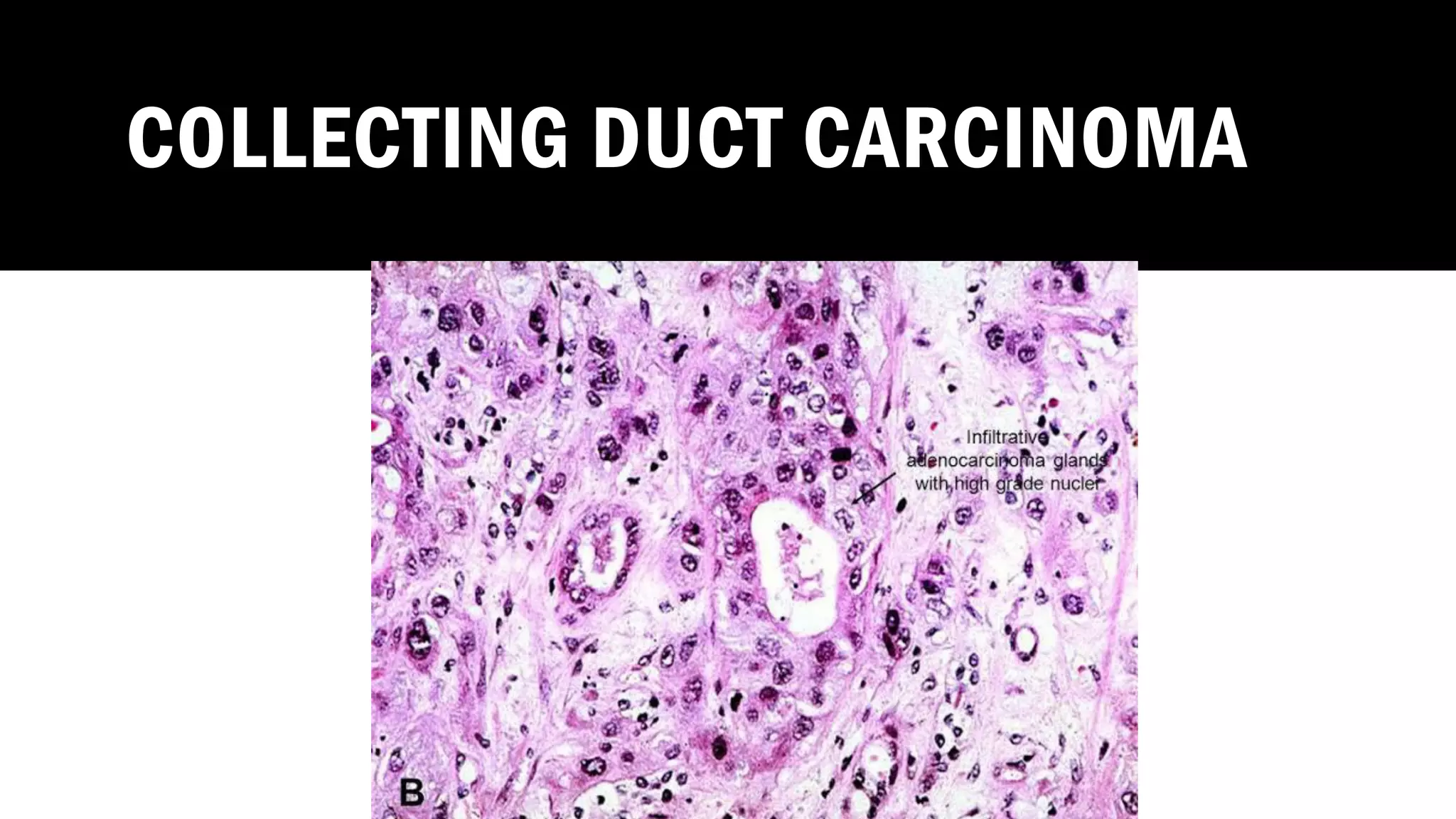
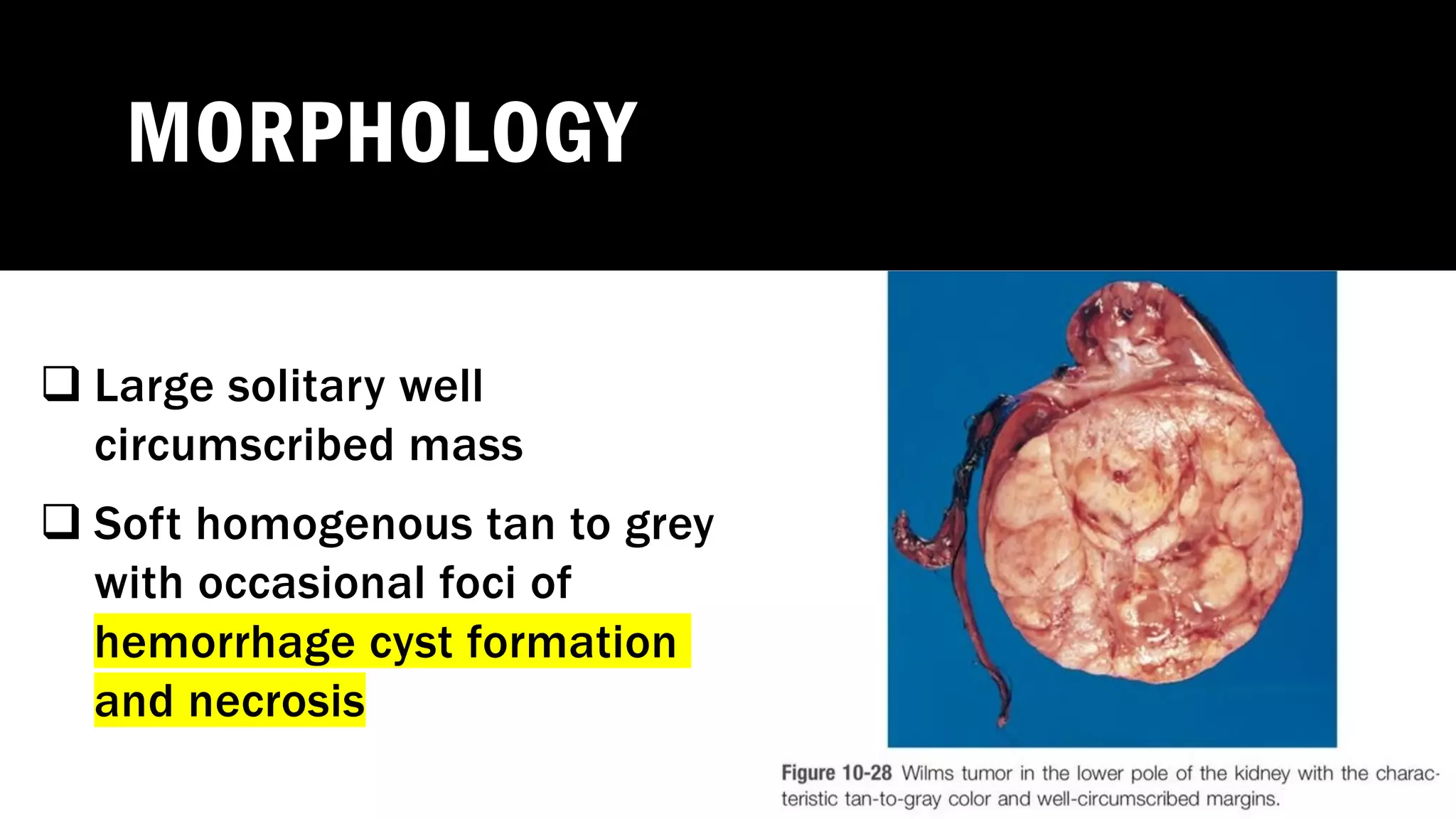
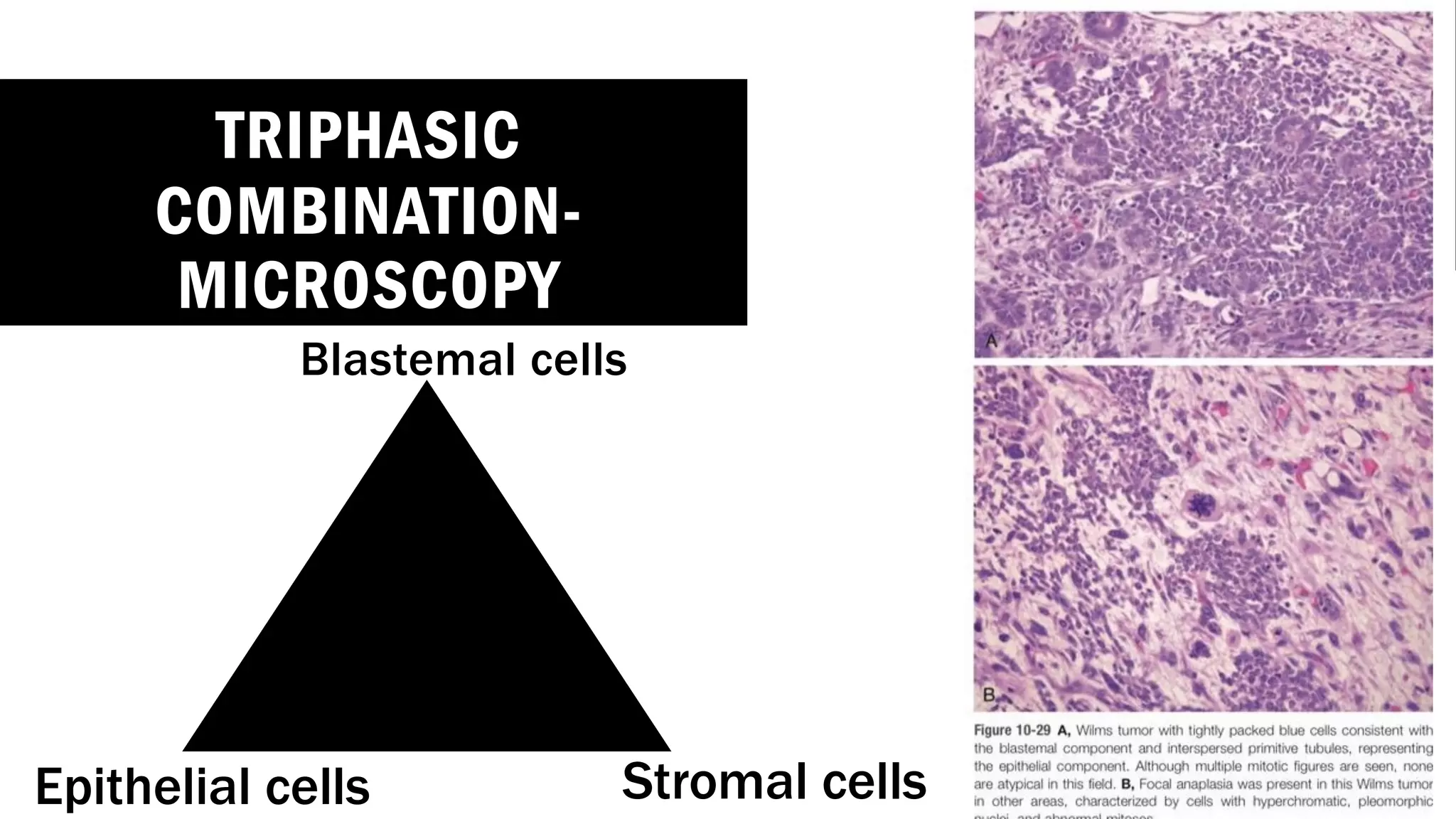
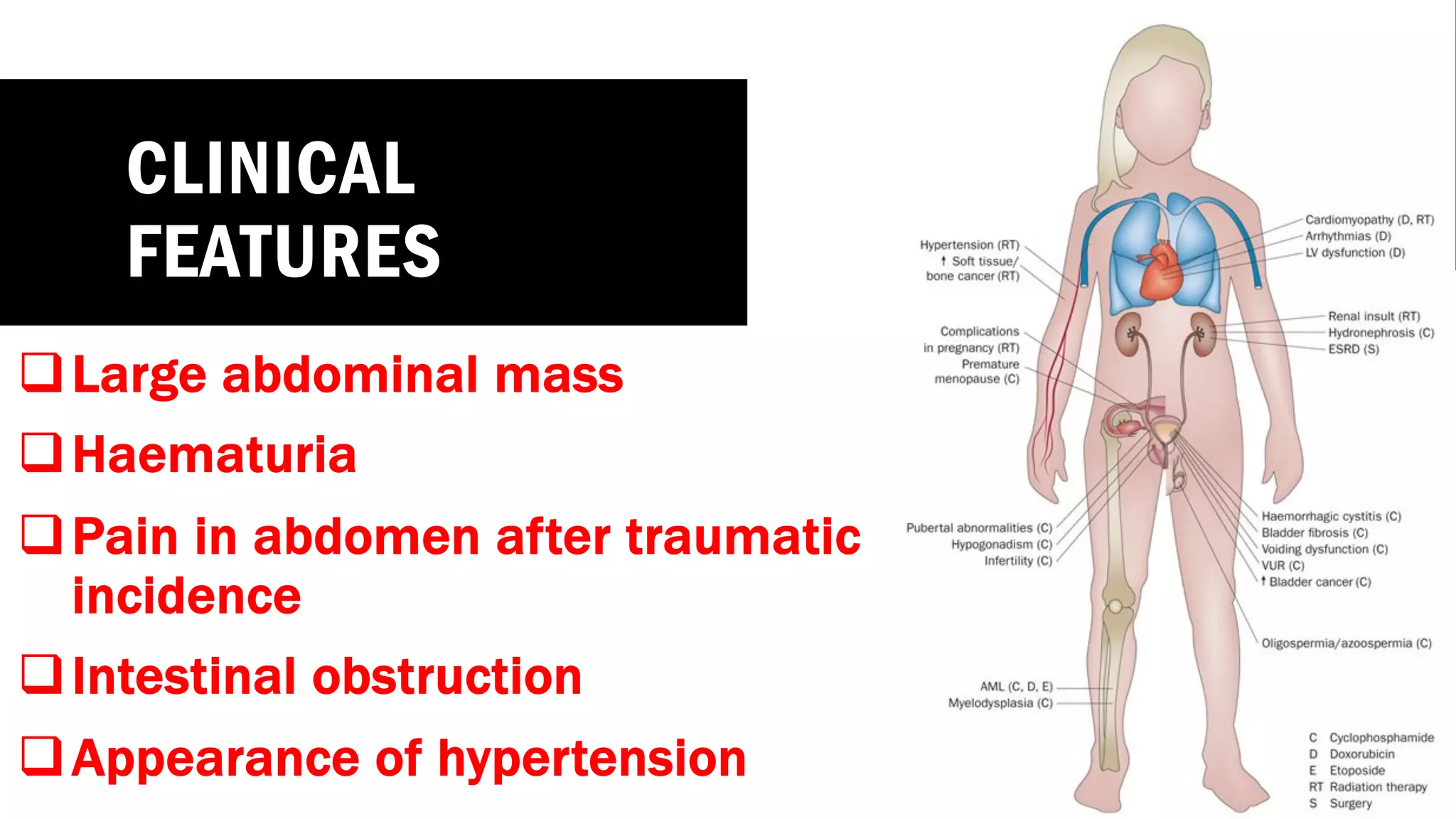
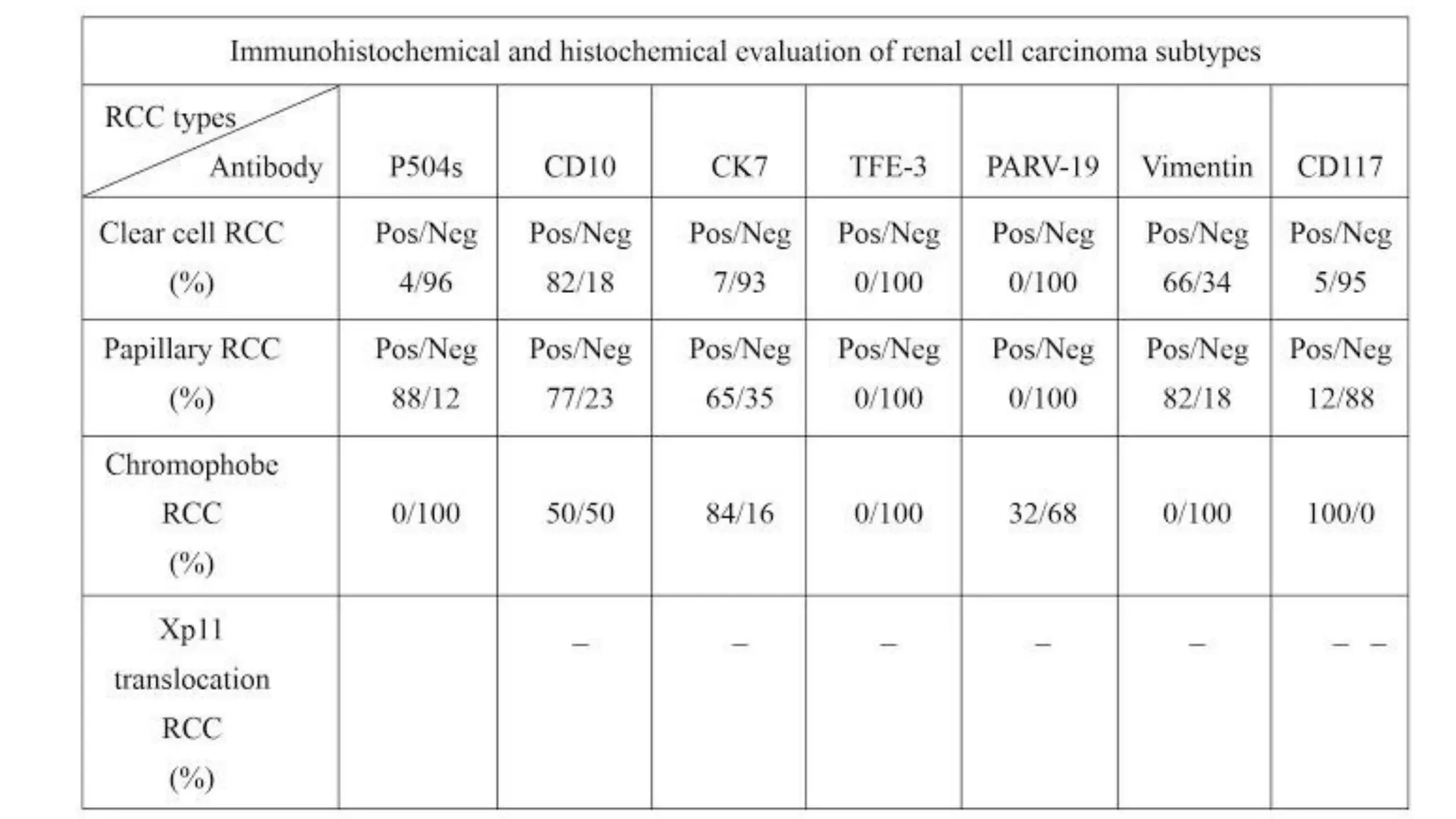
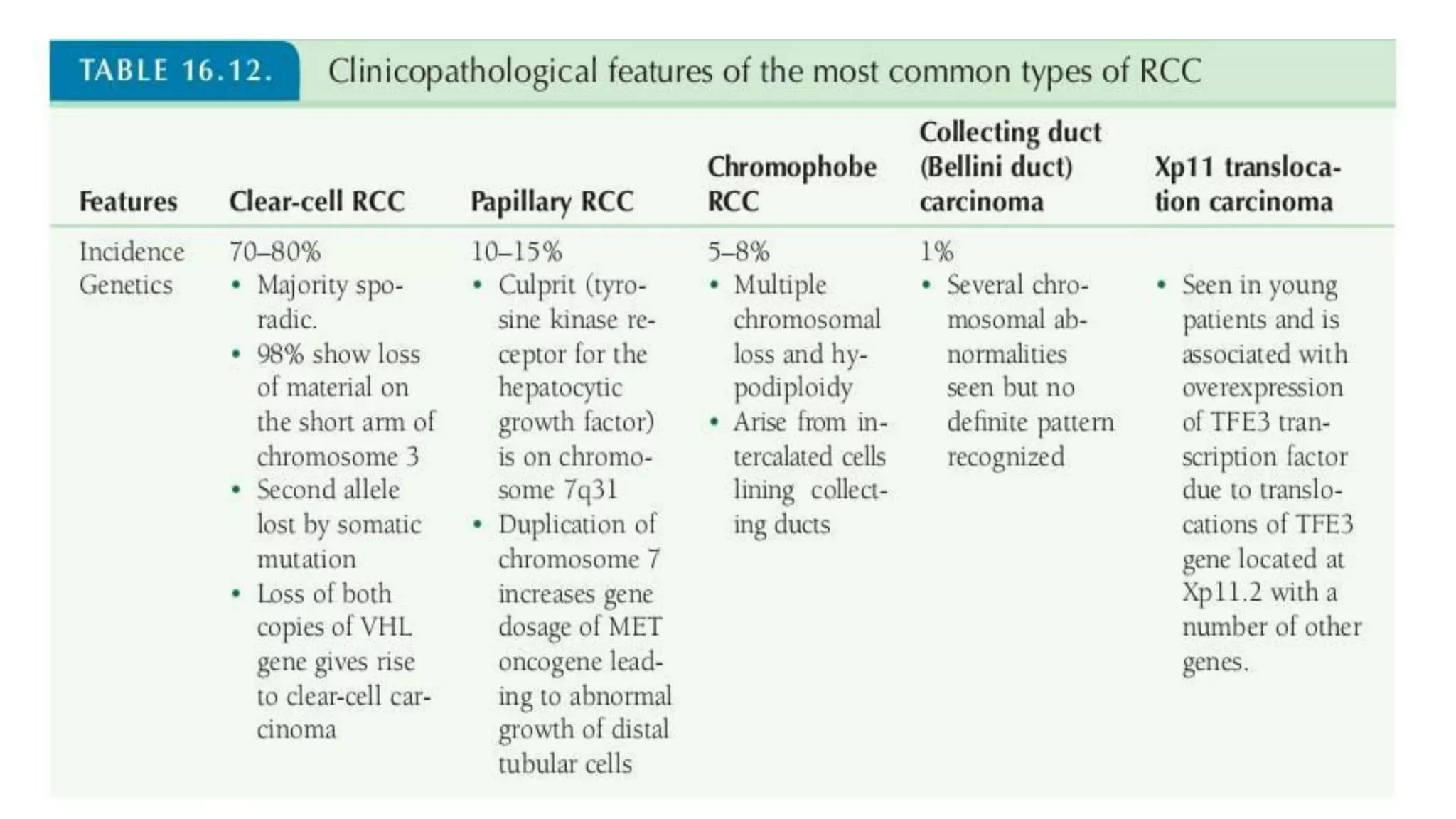
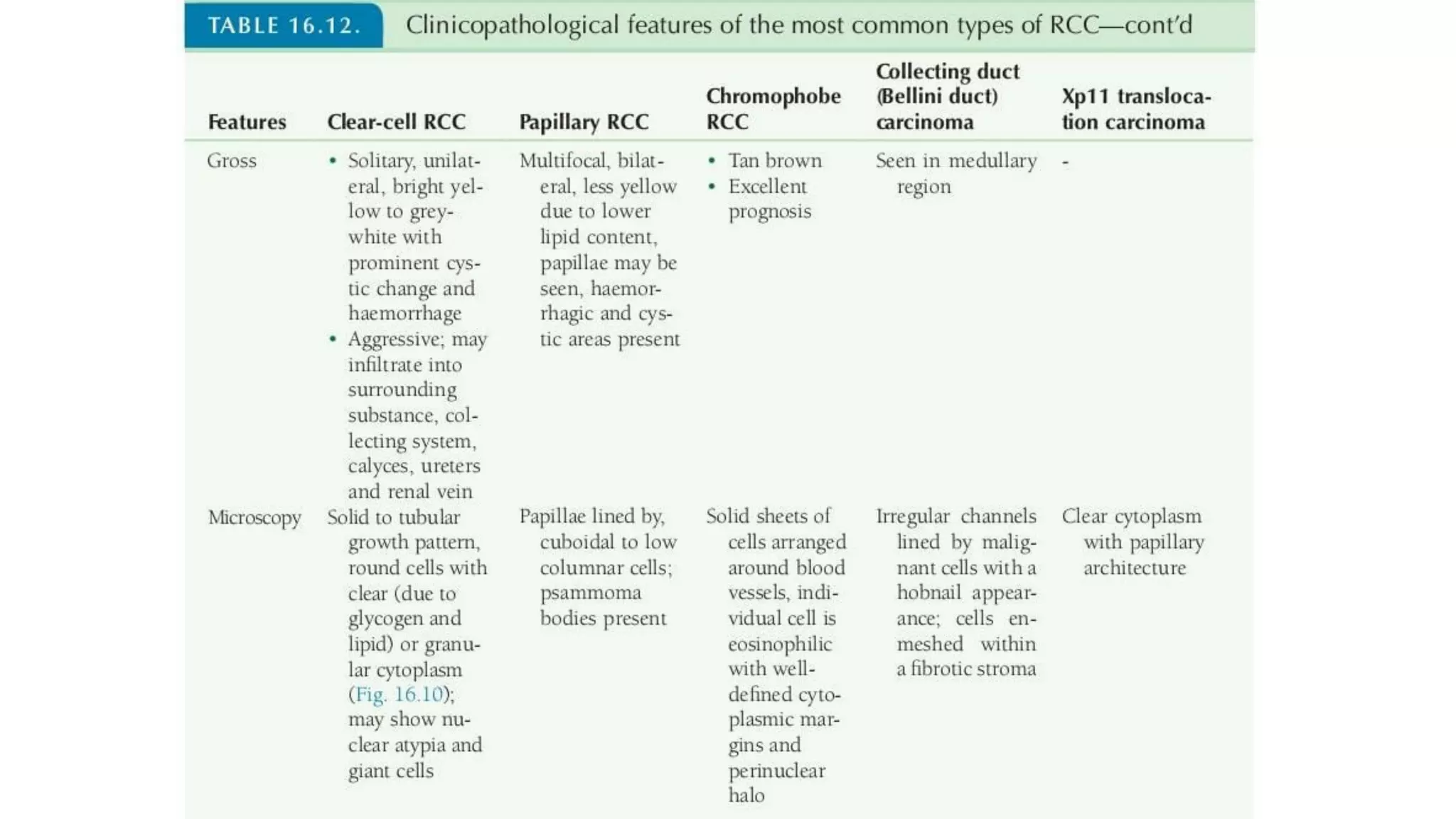
The document reviews the pathology of kidney tumors, detailing both benign tumors like angiomyolipoma and oncocytoma, as well as malignant tumors such as renal cell carcinoma and Wilms tumor. It discusses the characteristics, genetic factors, and risk factors associated with renal tumors, highlighting the clinical features and morphology of each type. Additionally, it poses a clinical case and related questions to test understanding of the content.