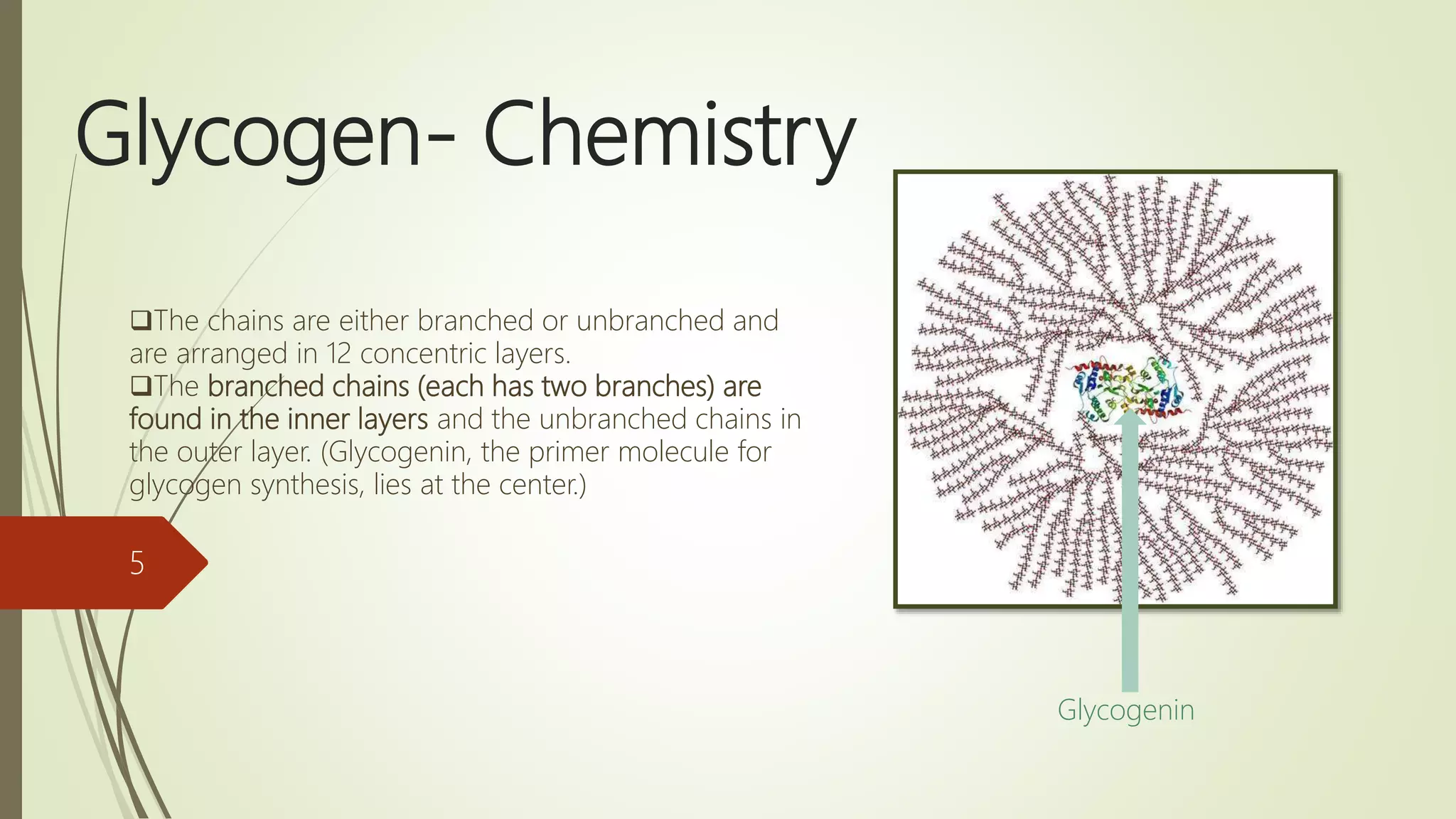
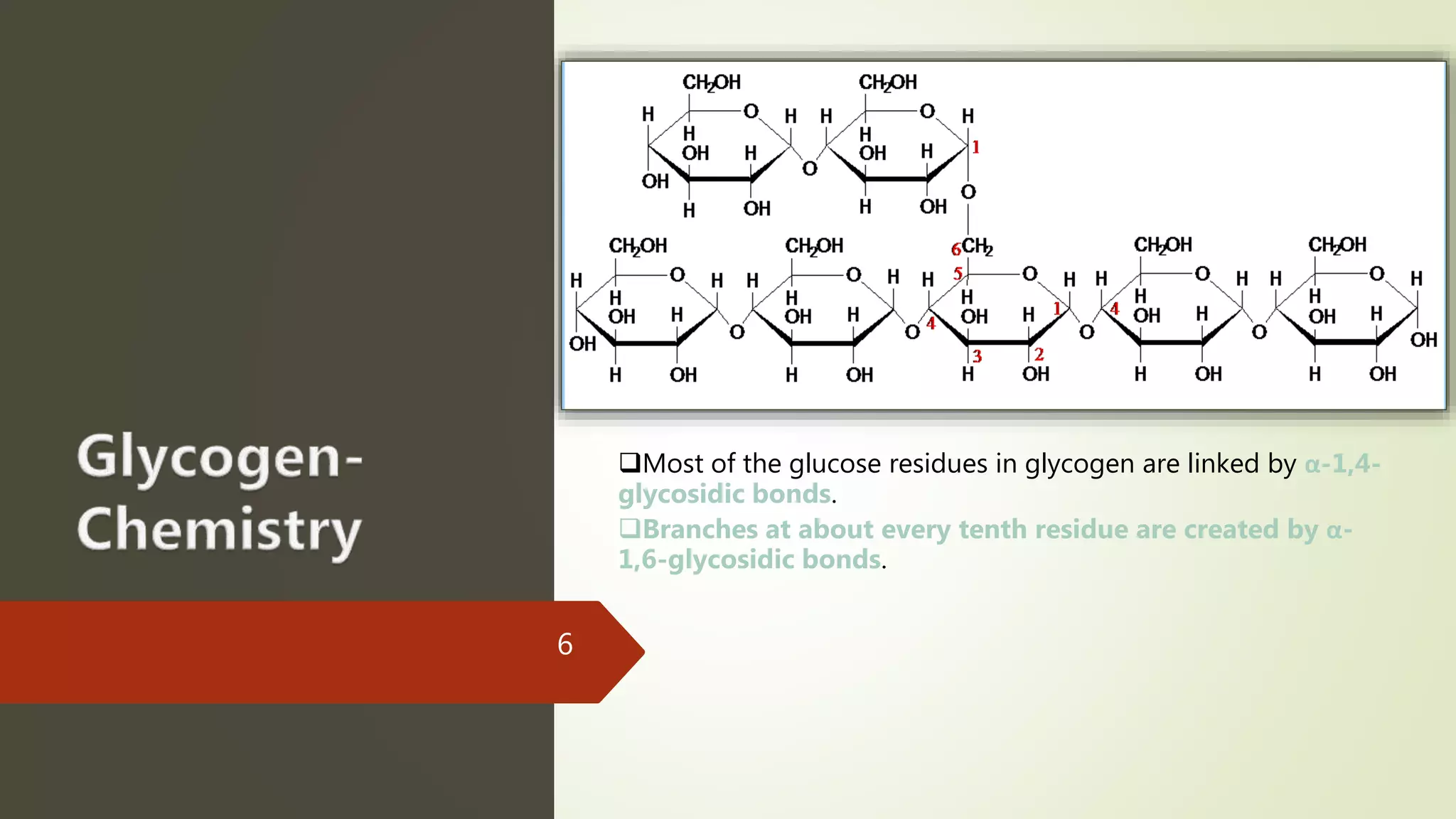
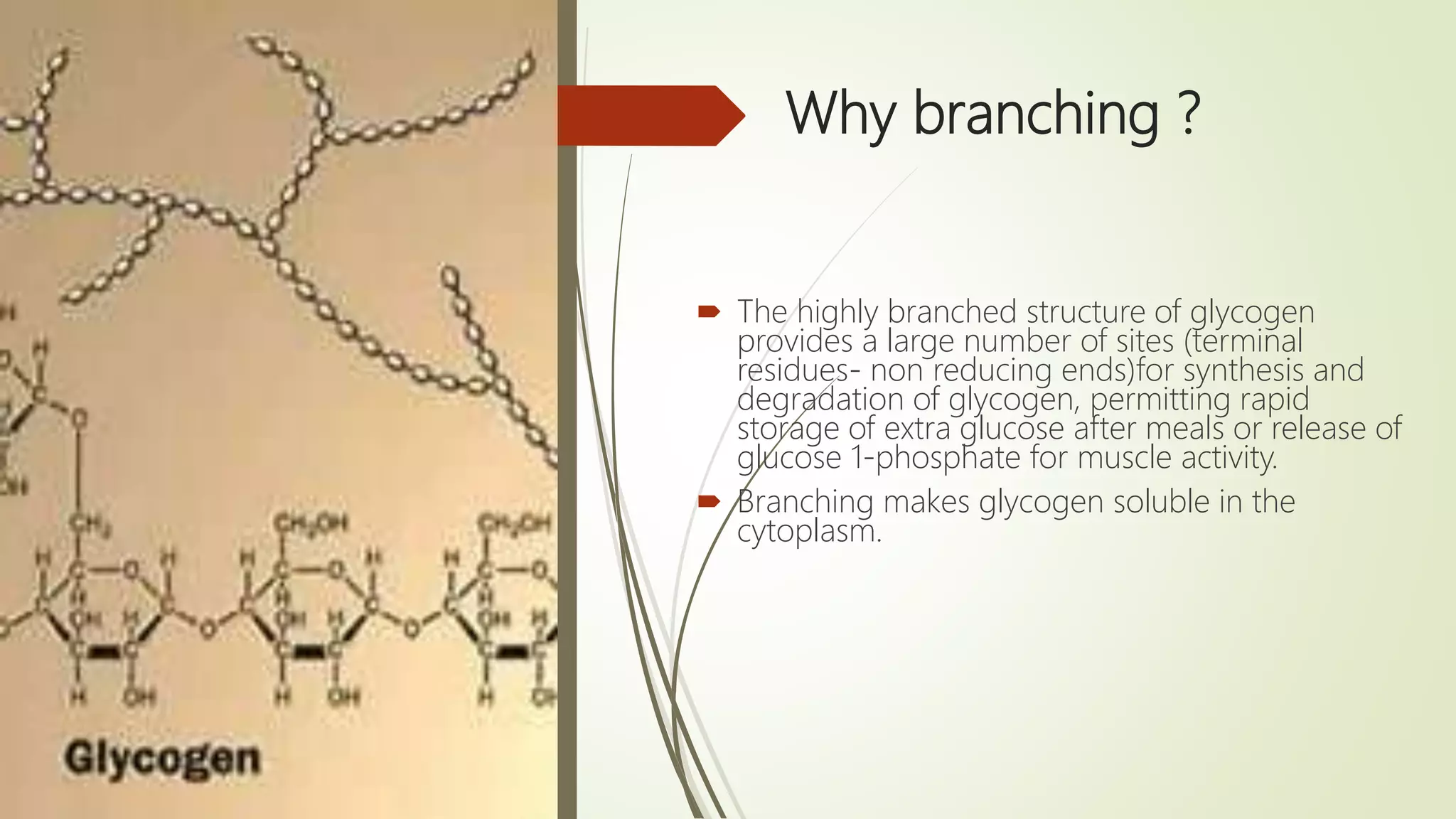
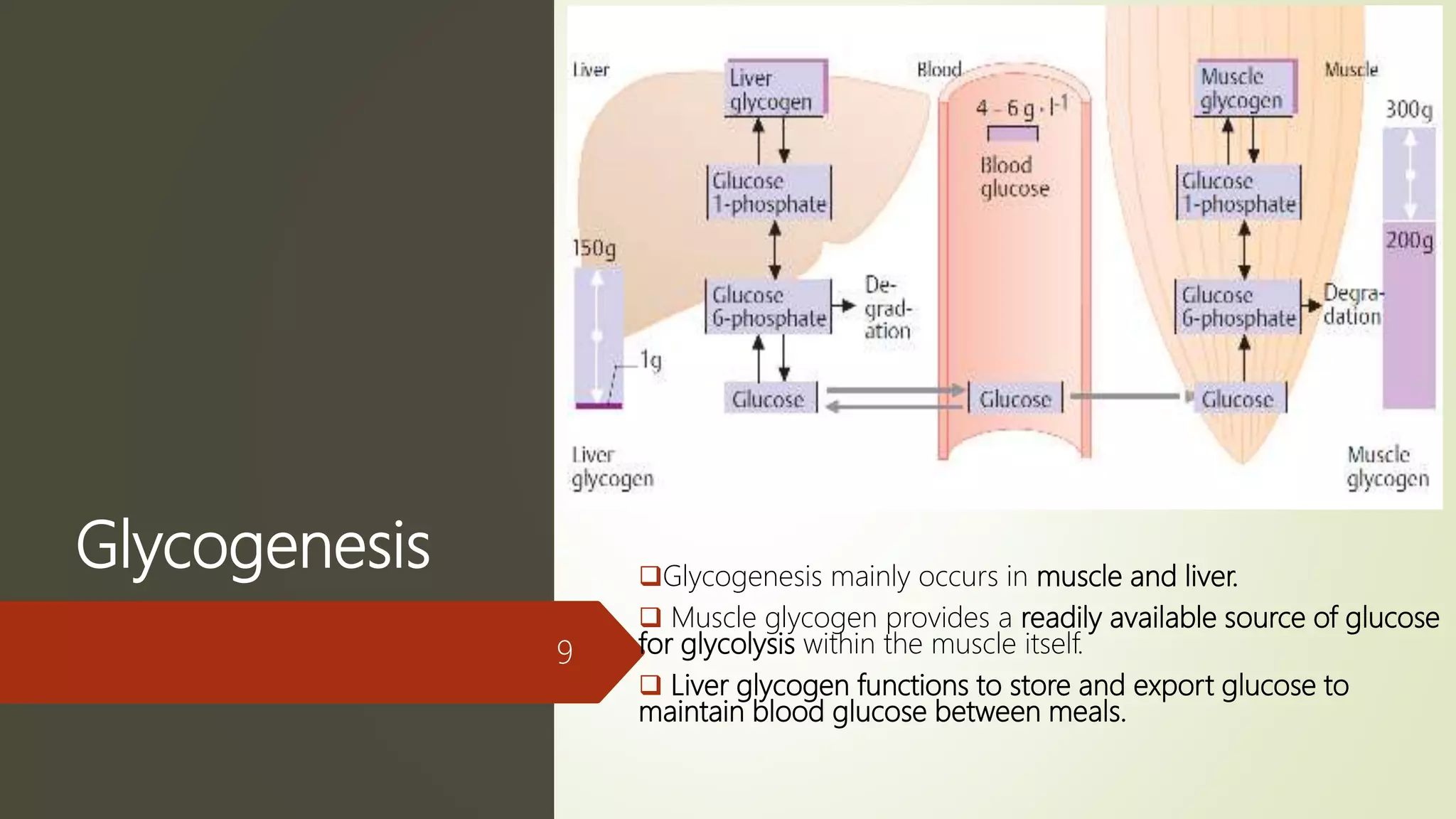
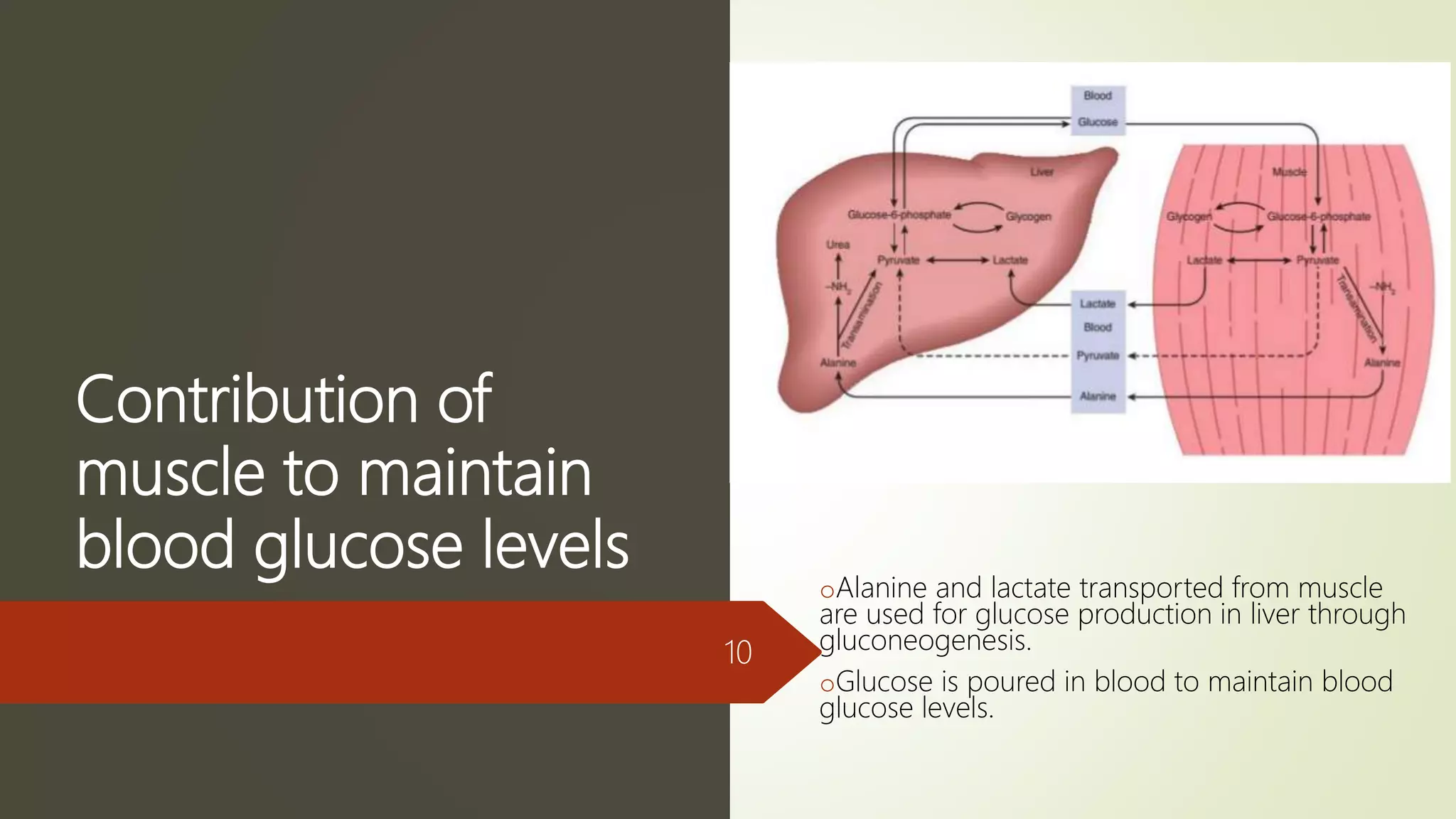
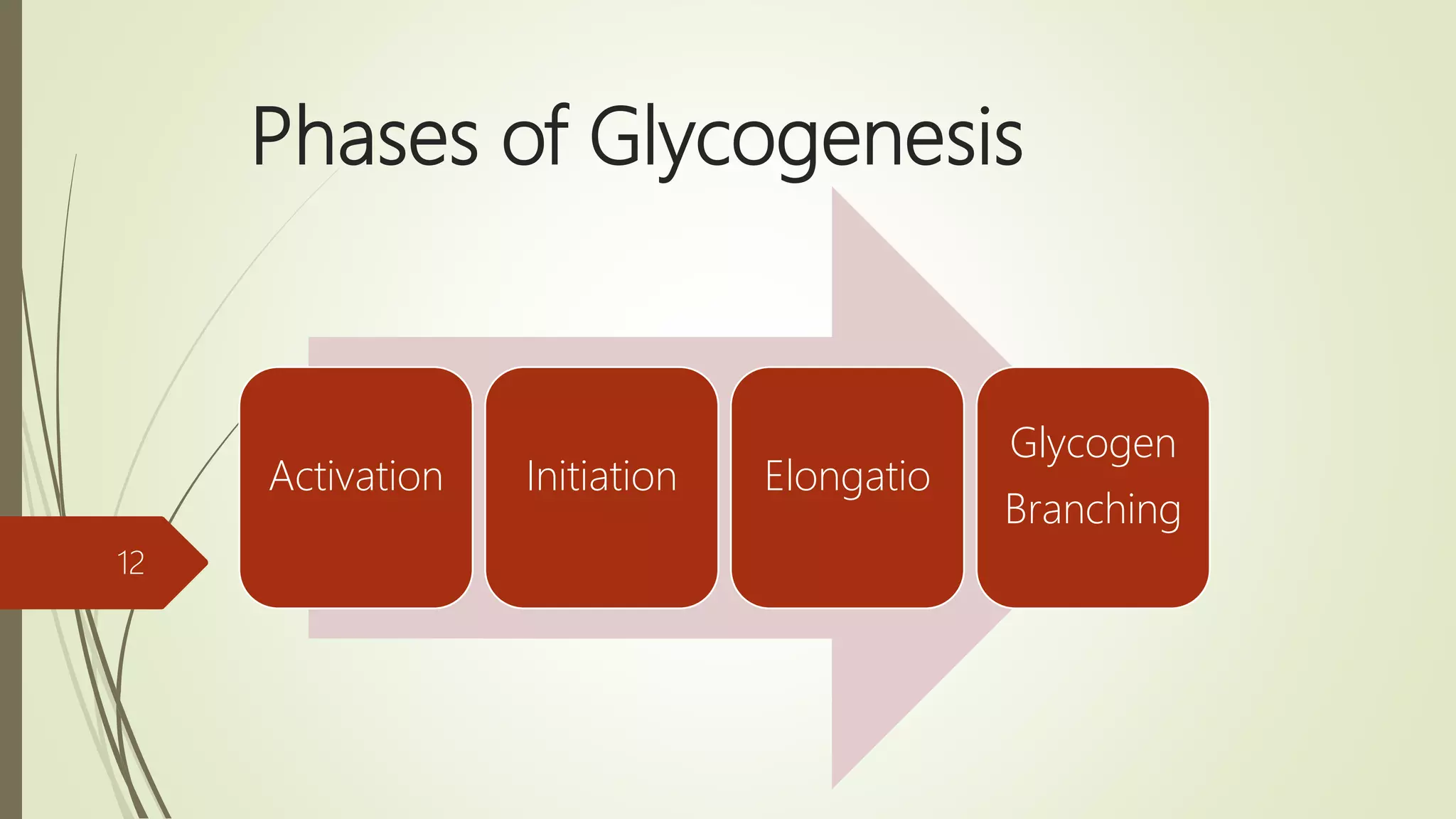
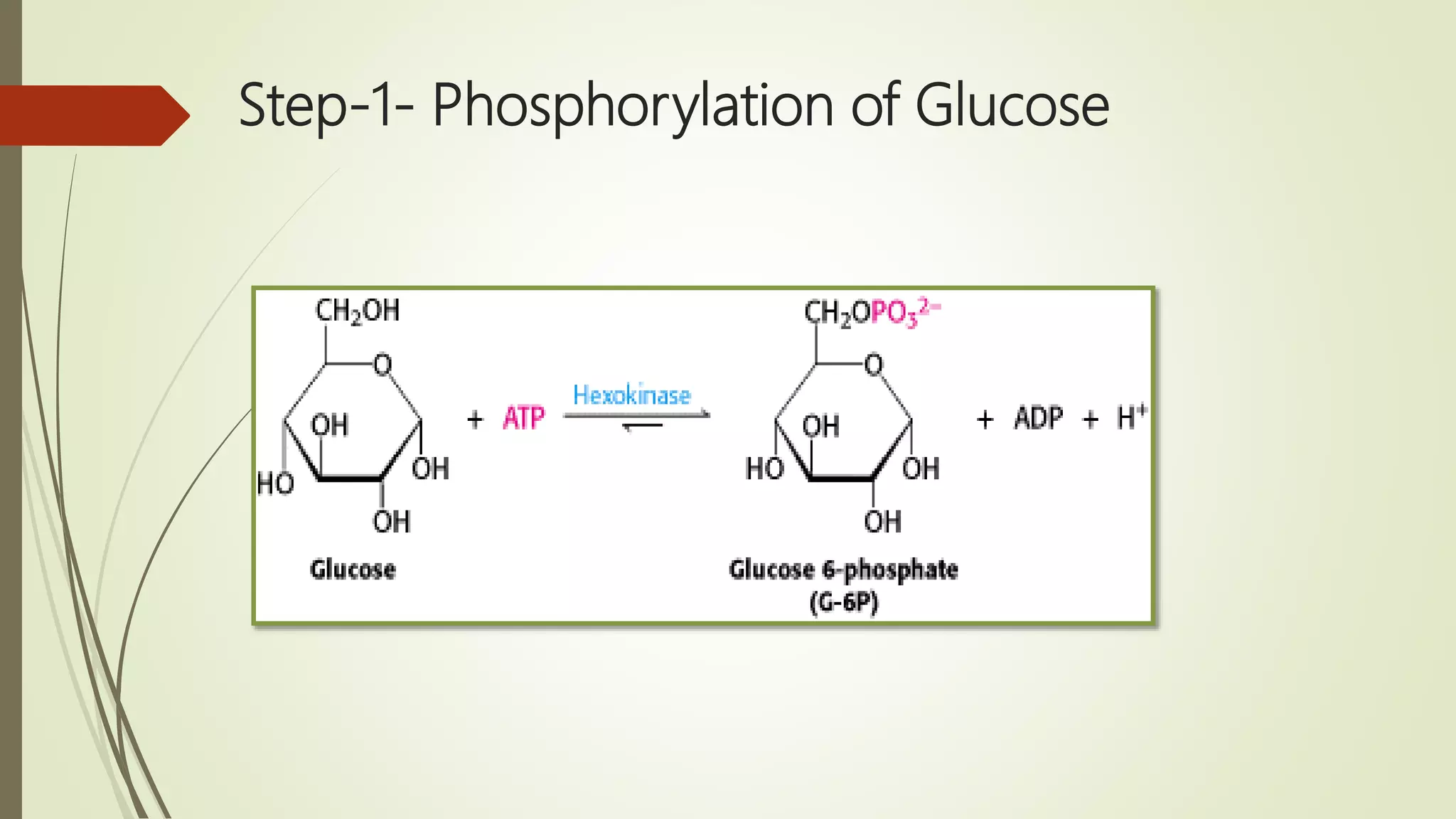
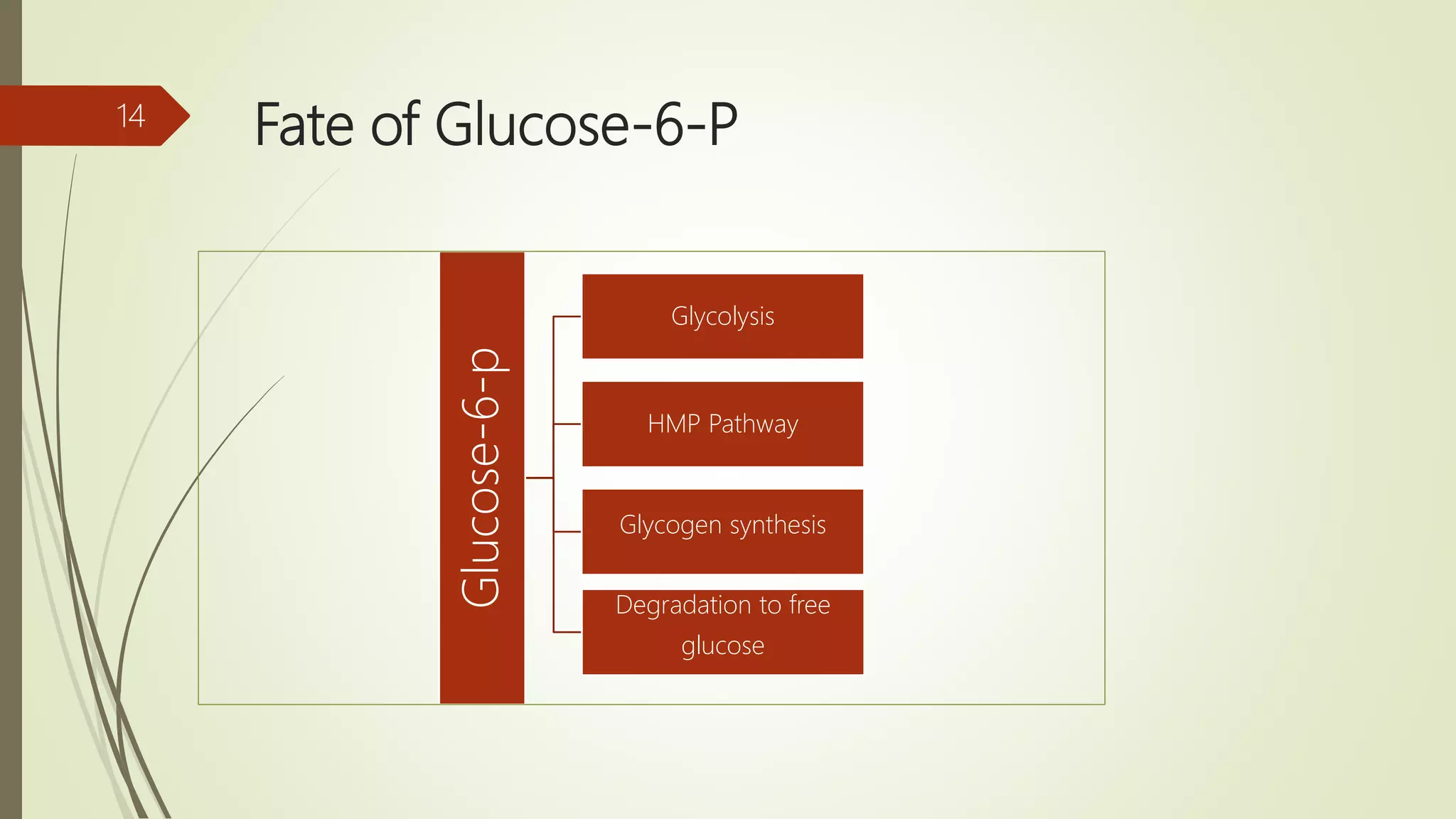
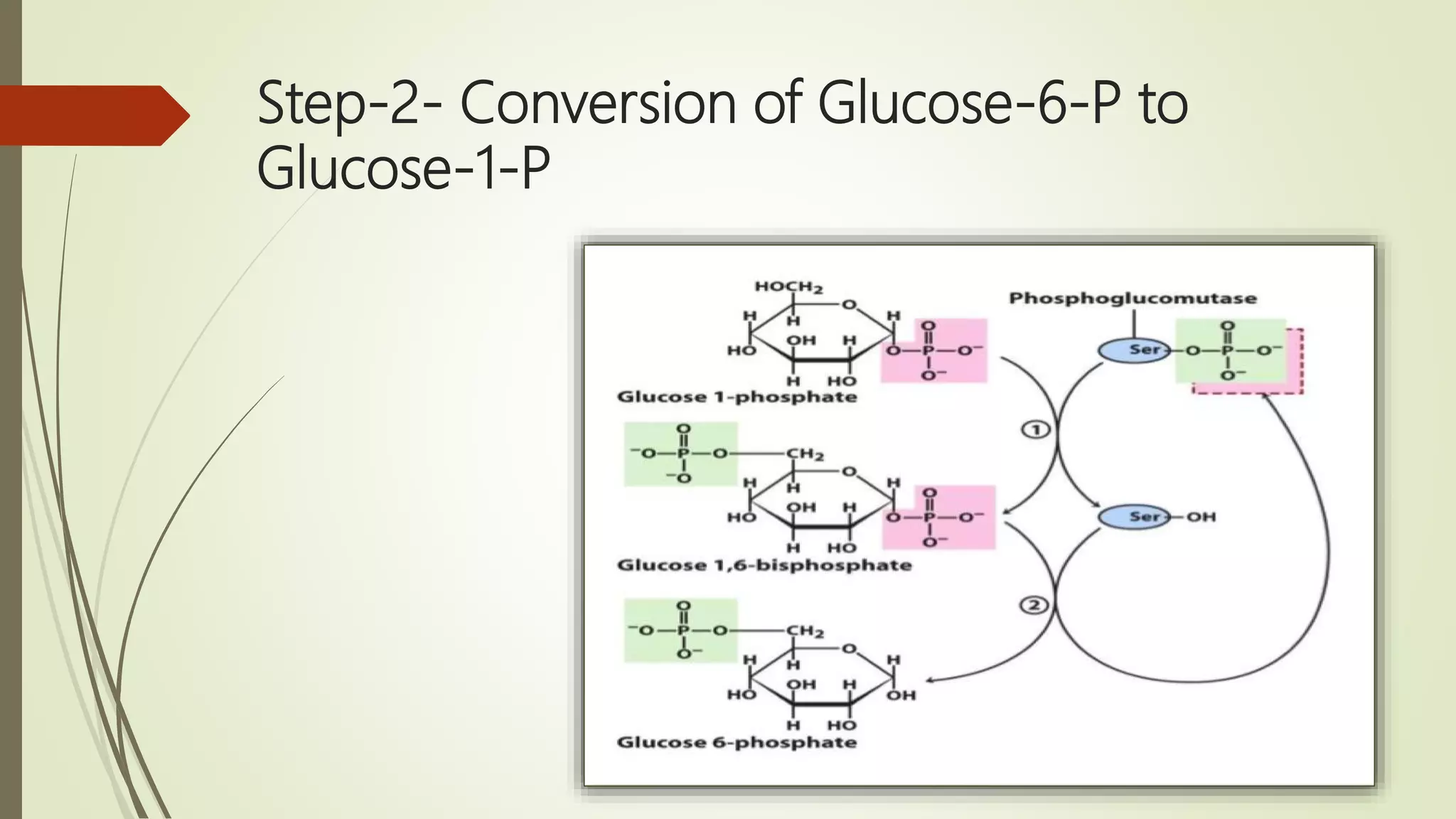
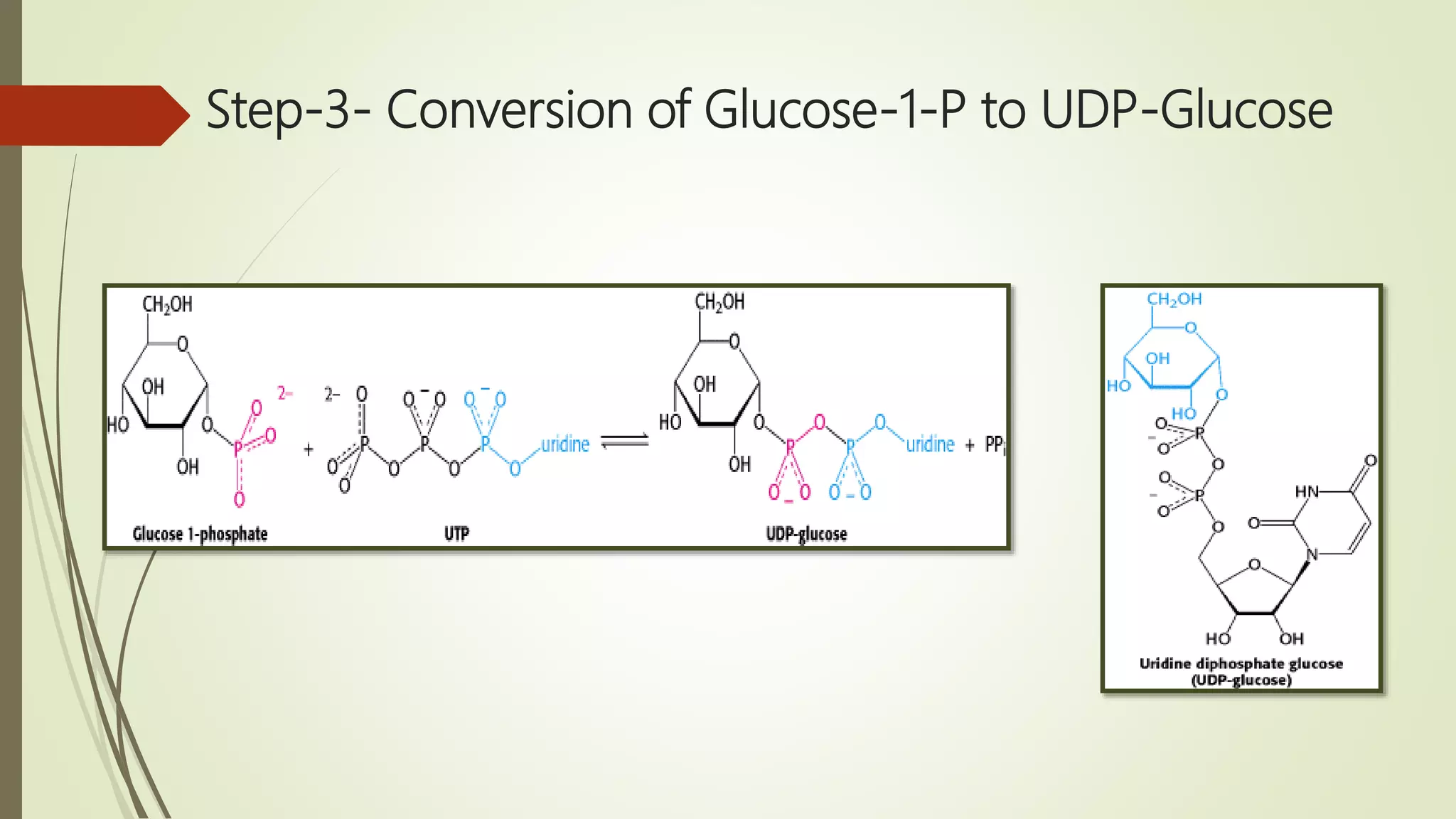
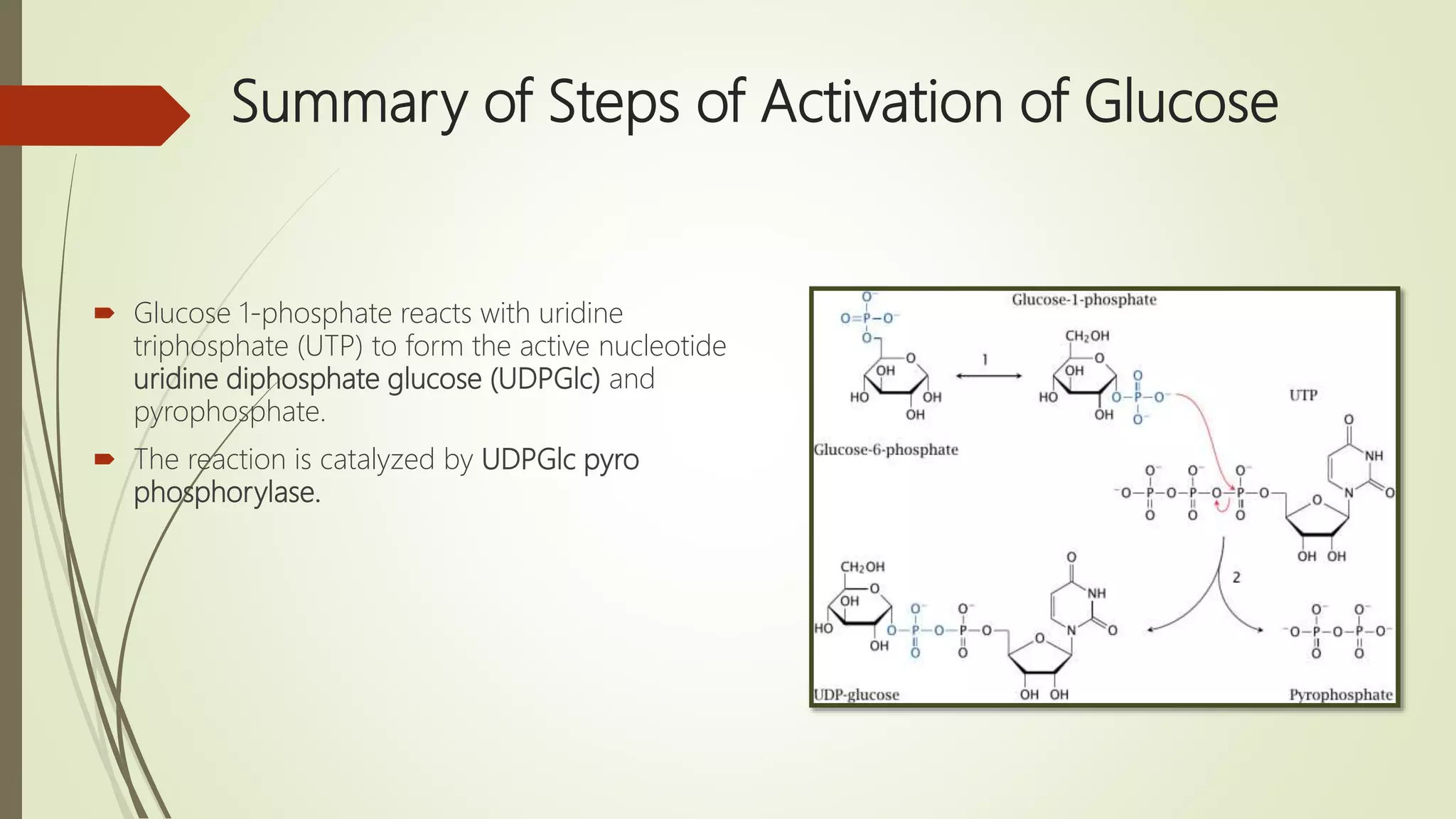
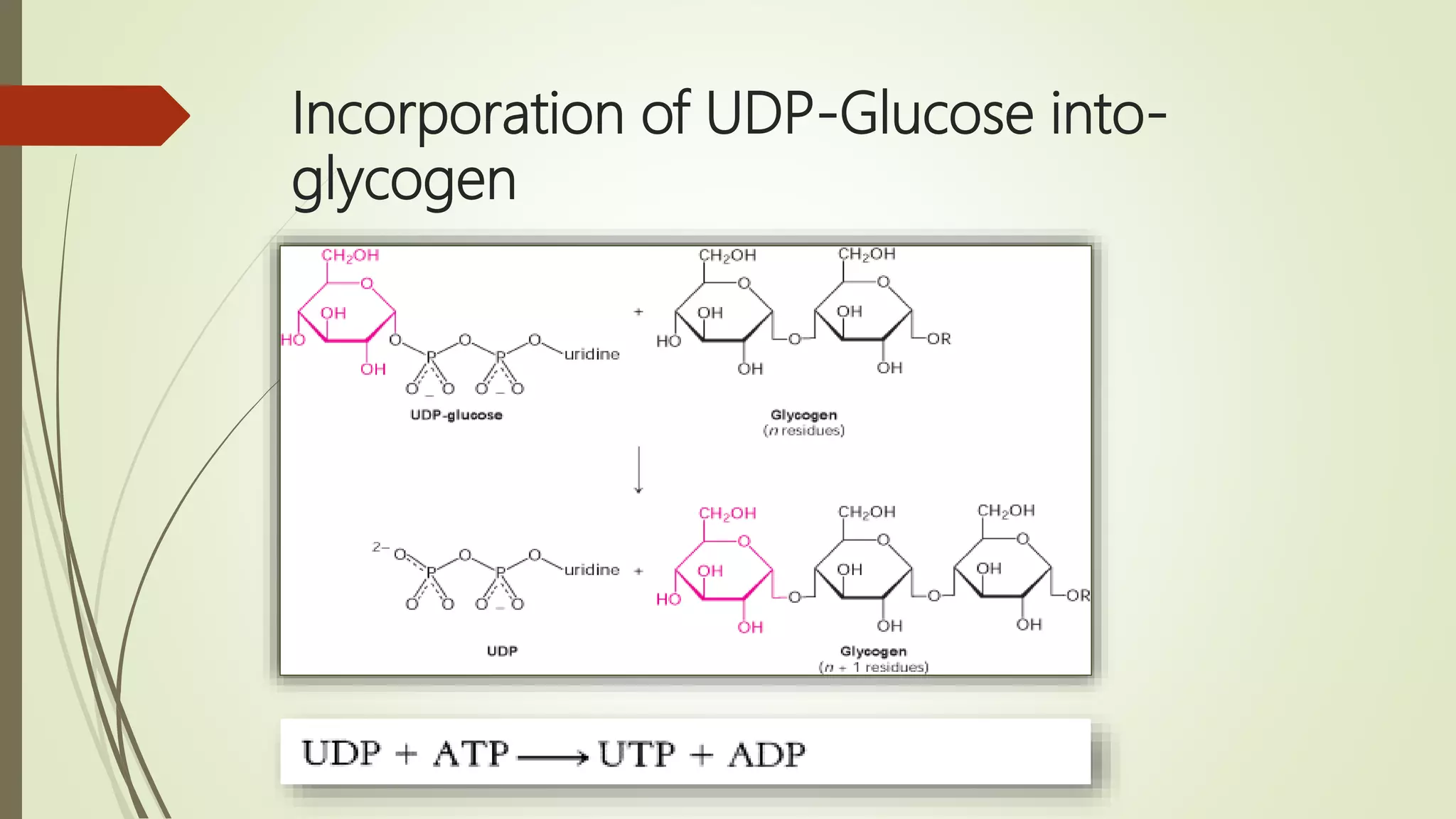
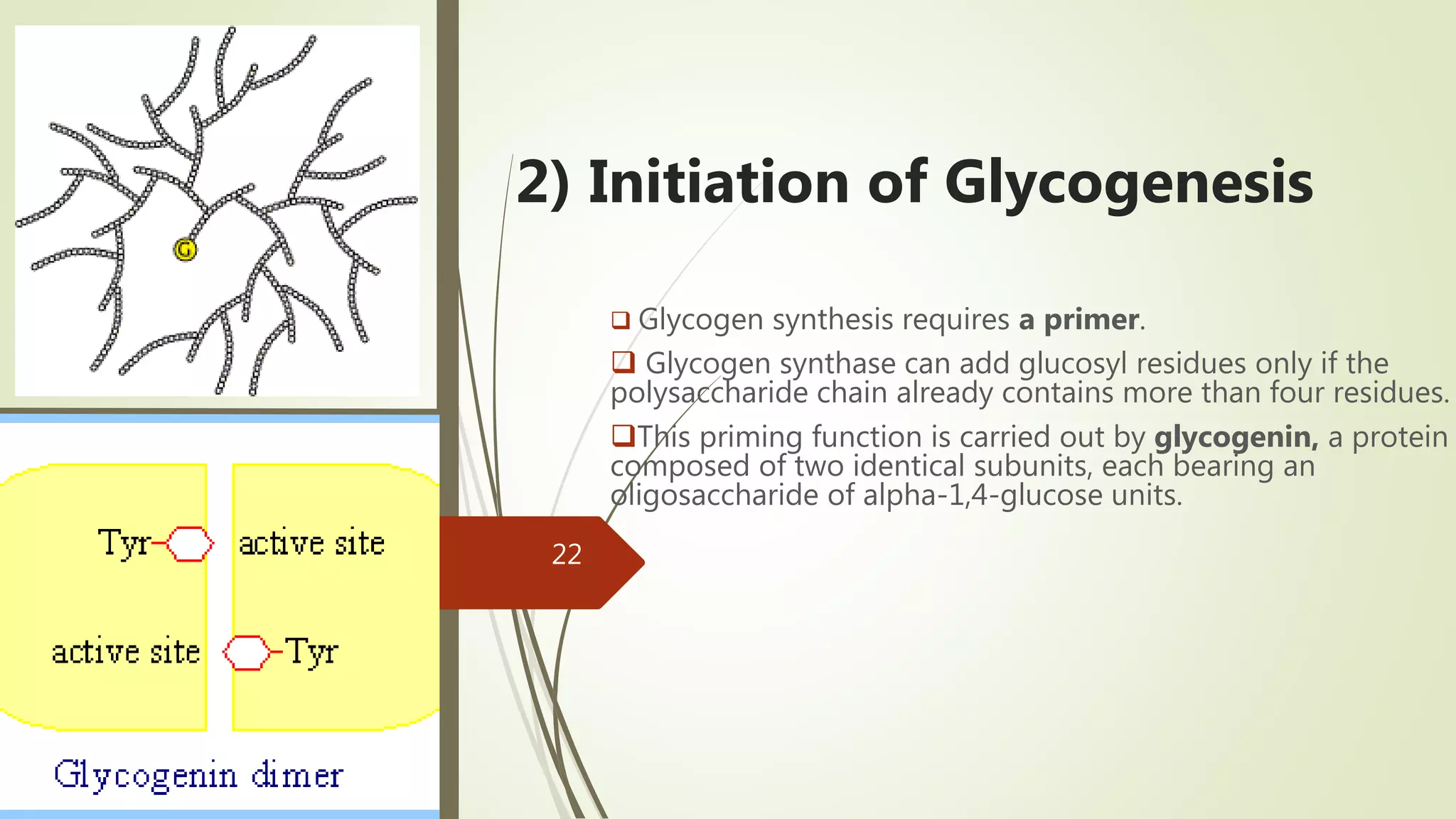
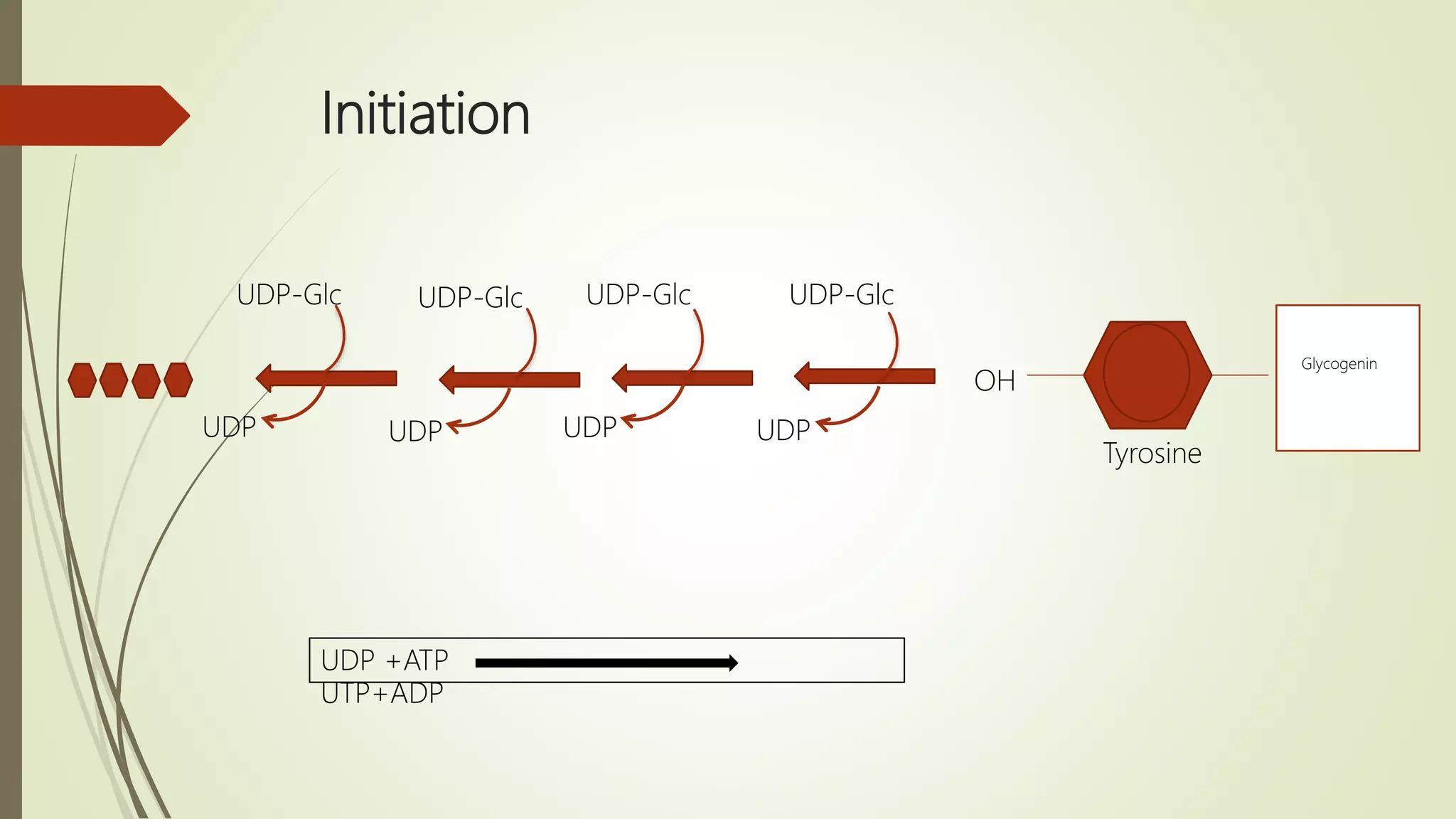
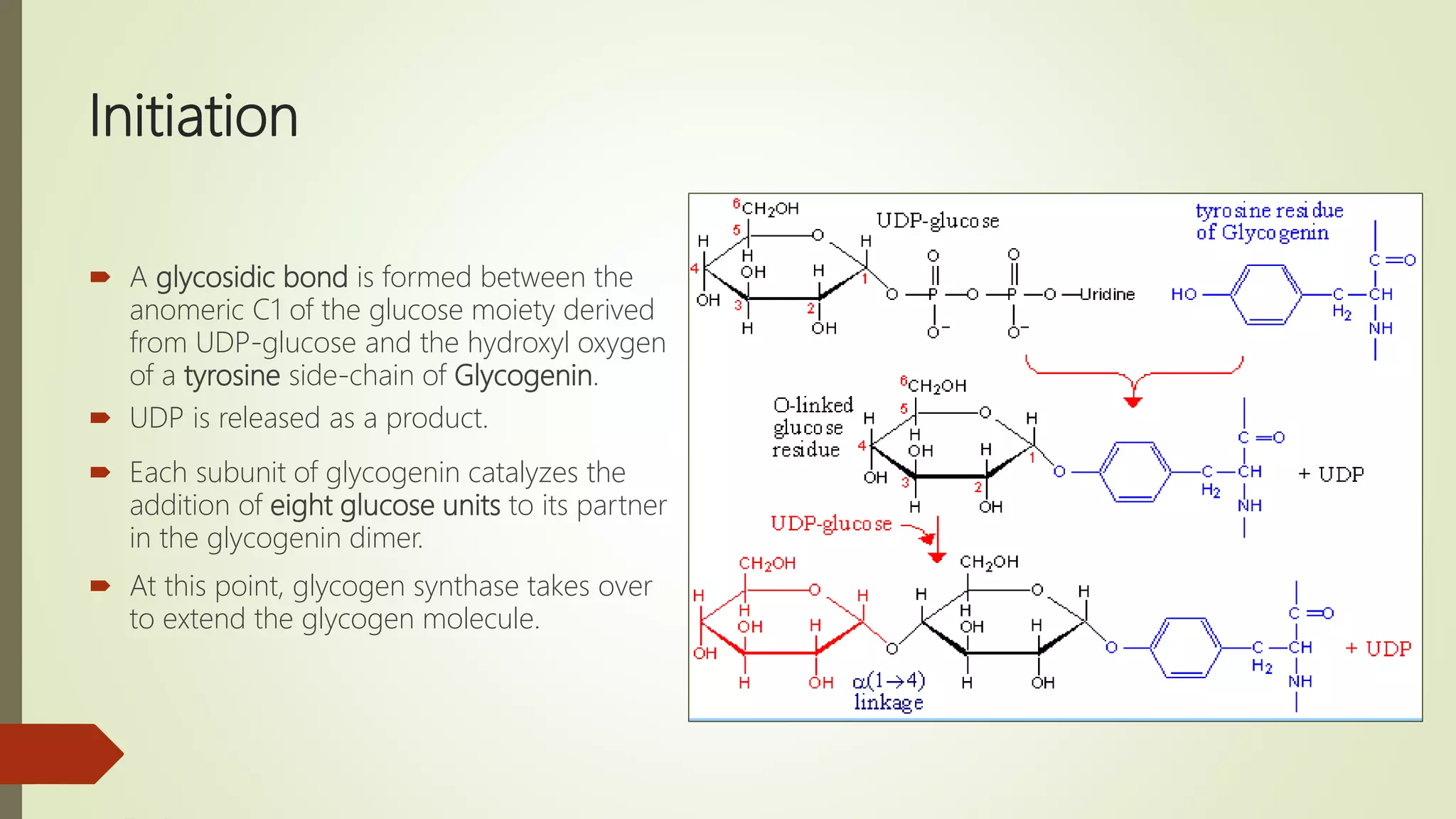
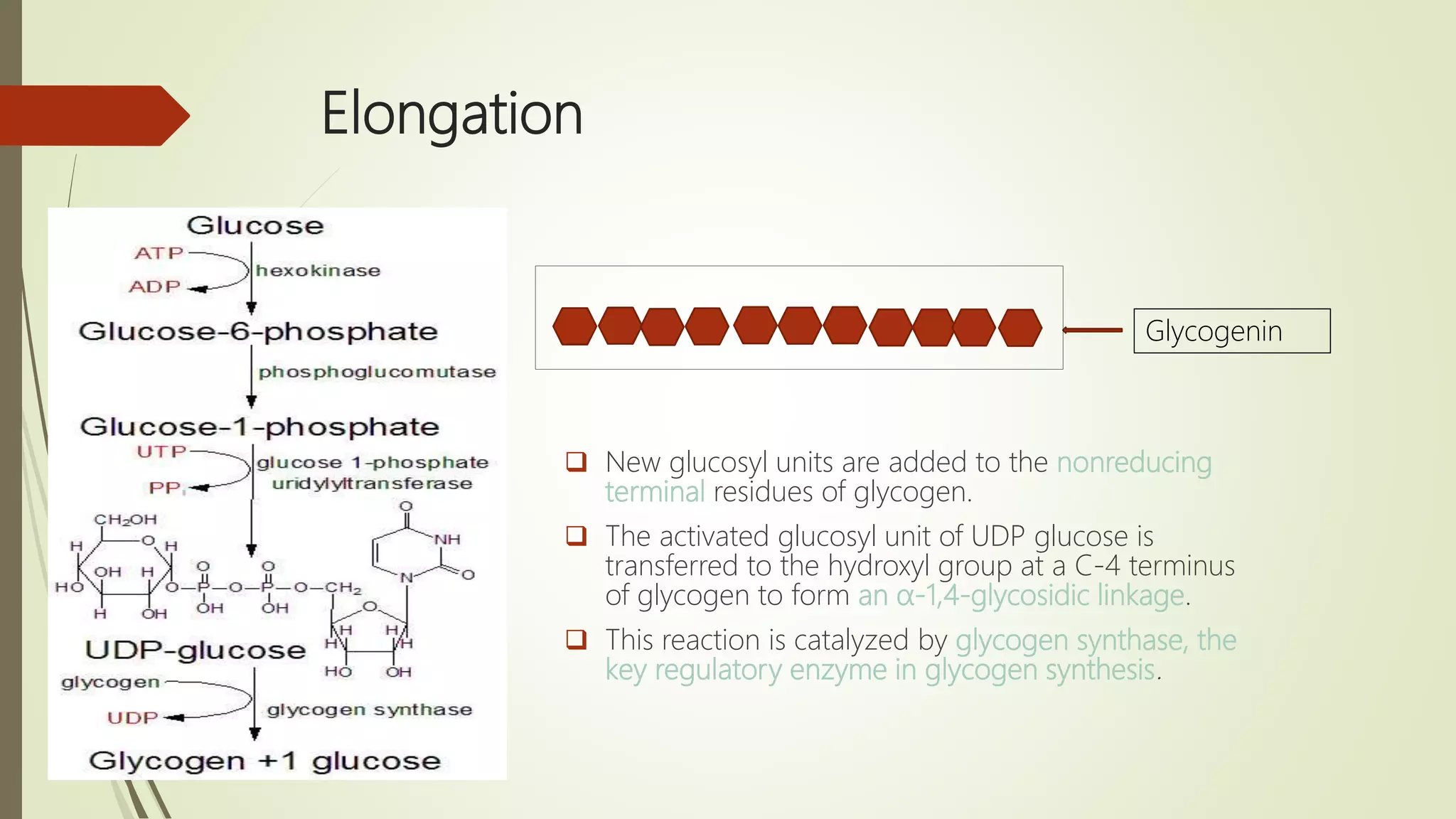
Glycogen is a readily available storage form of glucose found mainly in the liver and muscle. It is synthesized through glycogenesis, which involves four steps - activation of glucose to UDP-glucose, initiation using the primer glycogenin, elongation by glycogen synthase adding glucose units via alpha-1,4 glycosidic bonds, and branching every 7-10 units via alpha-1,6 bonds by branching enzyme. Glycogen synthesis requires two enzymes - glycogen synthase which elongates the chain and branching enzyme which introduces branches, and continues till sufficient glycogen is synthesized or glucose is no longer available.