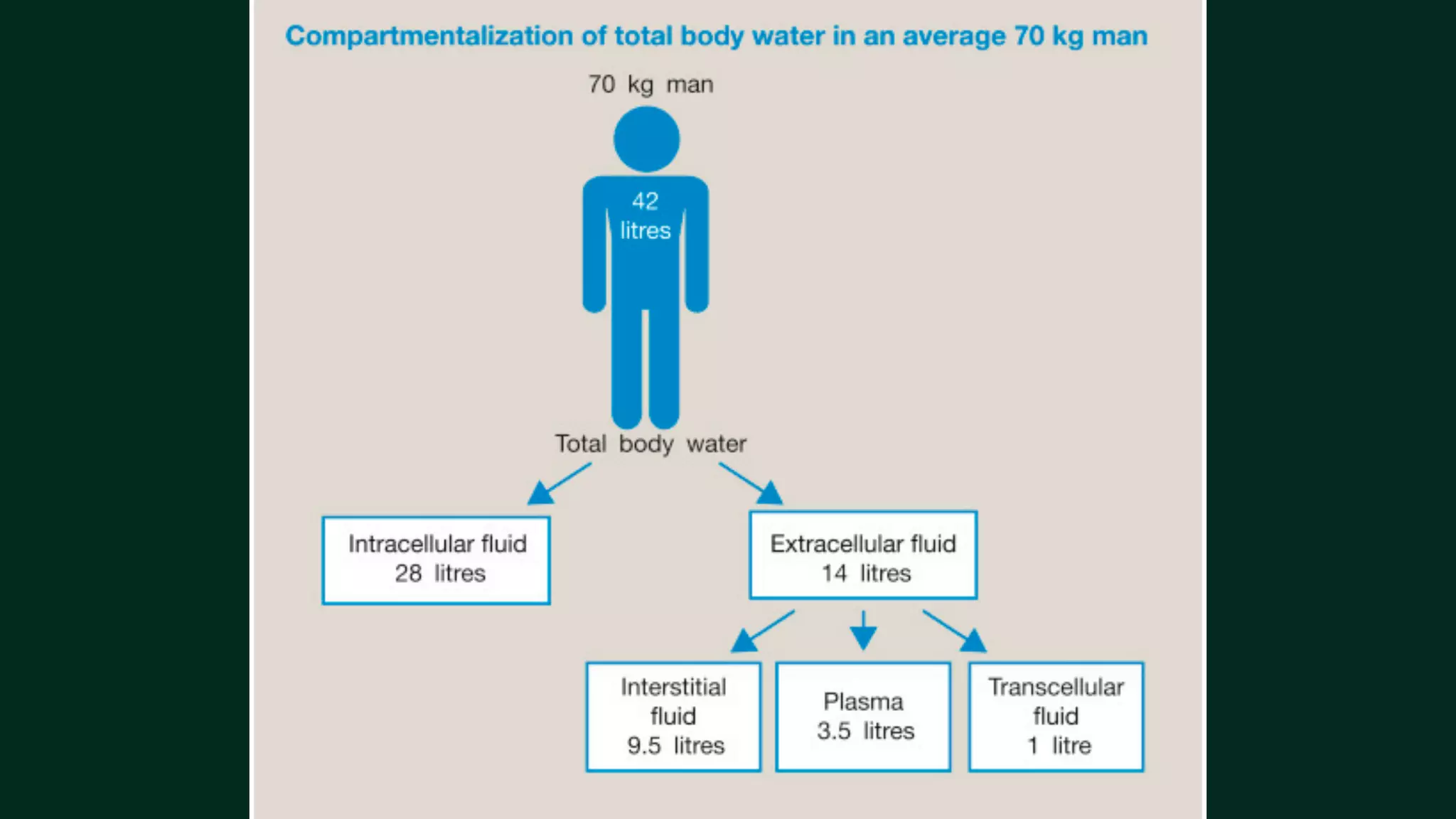
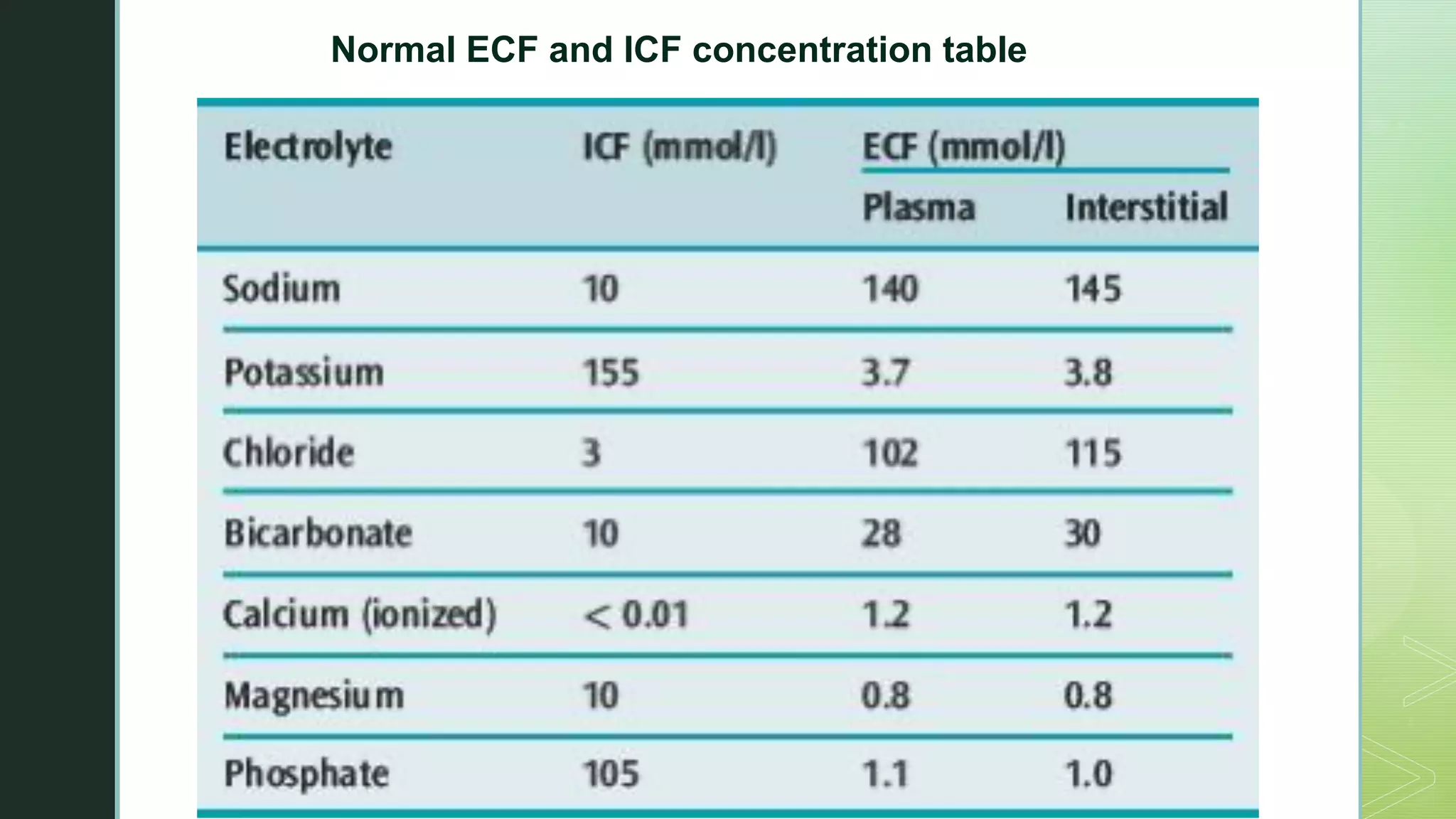
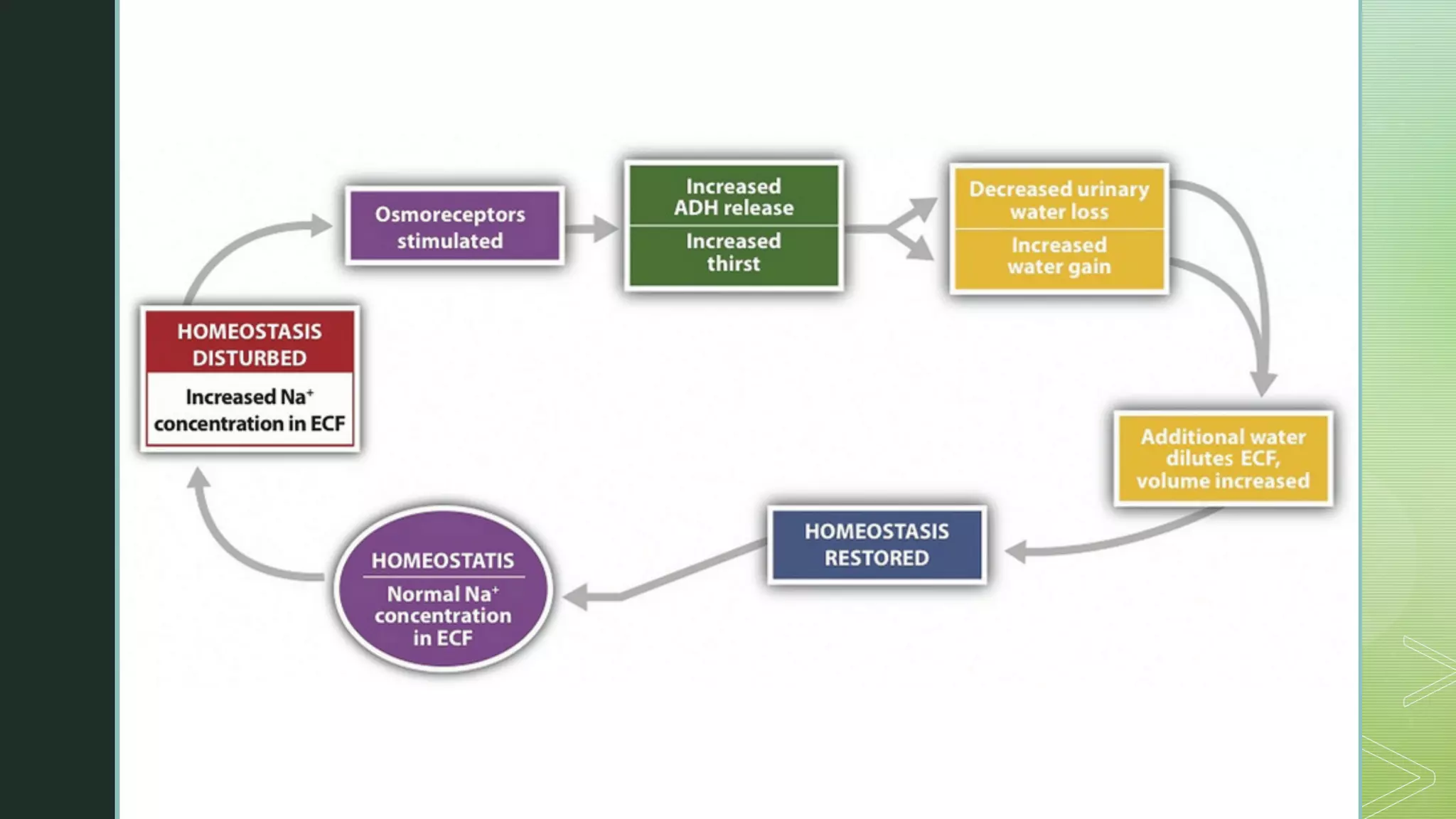
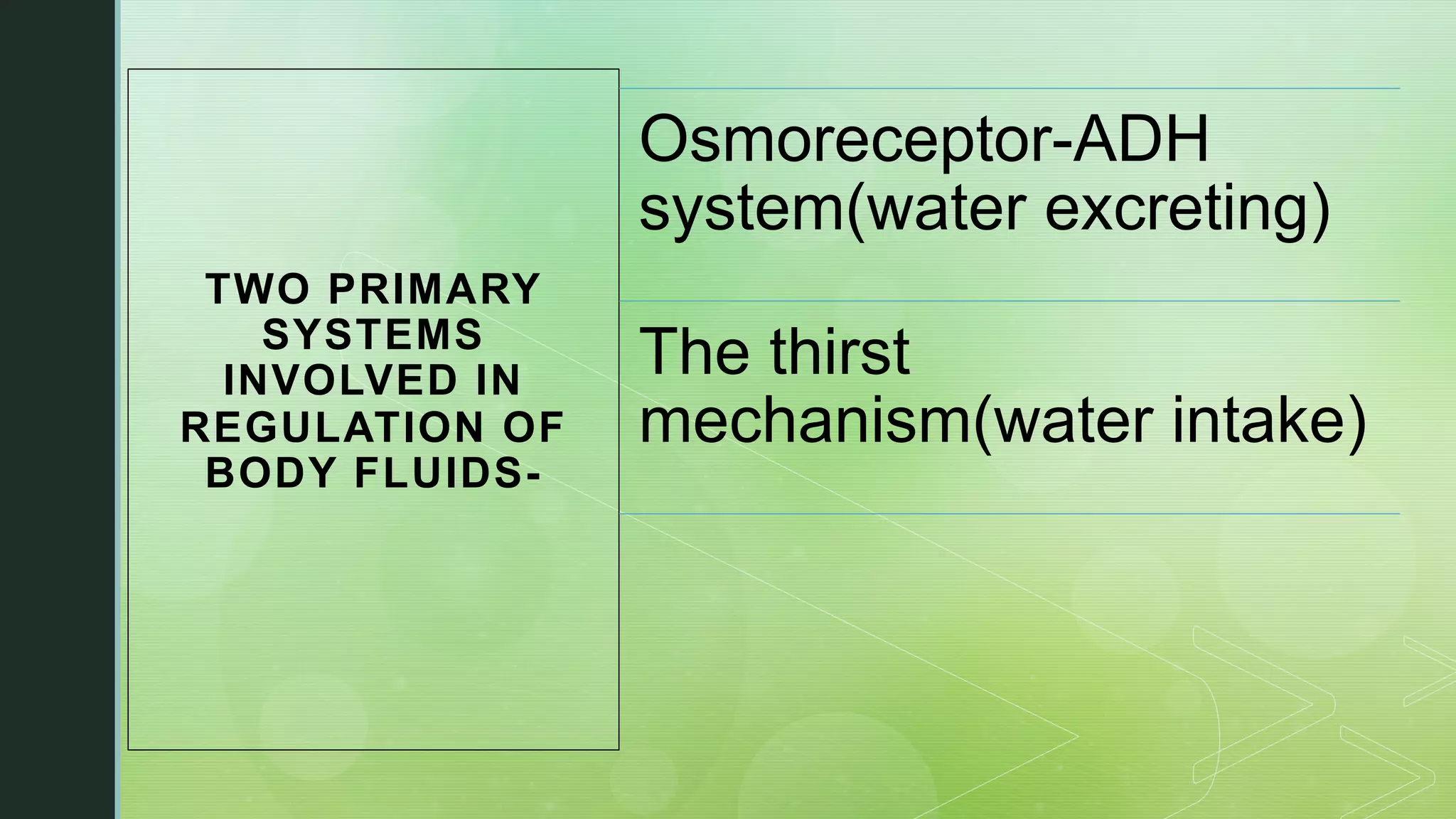
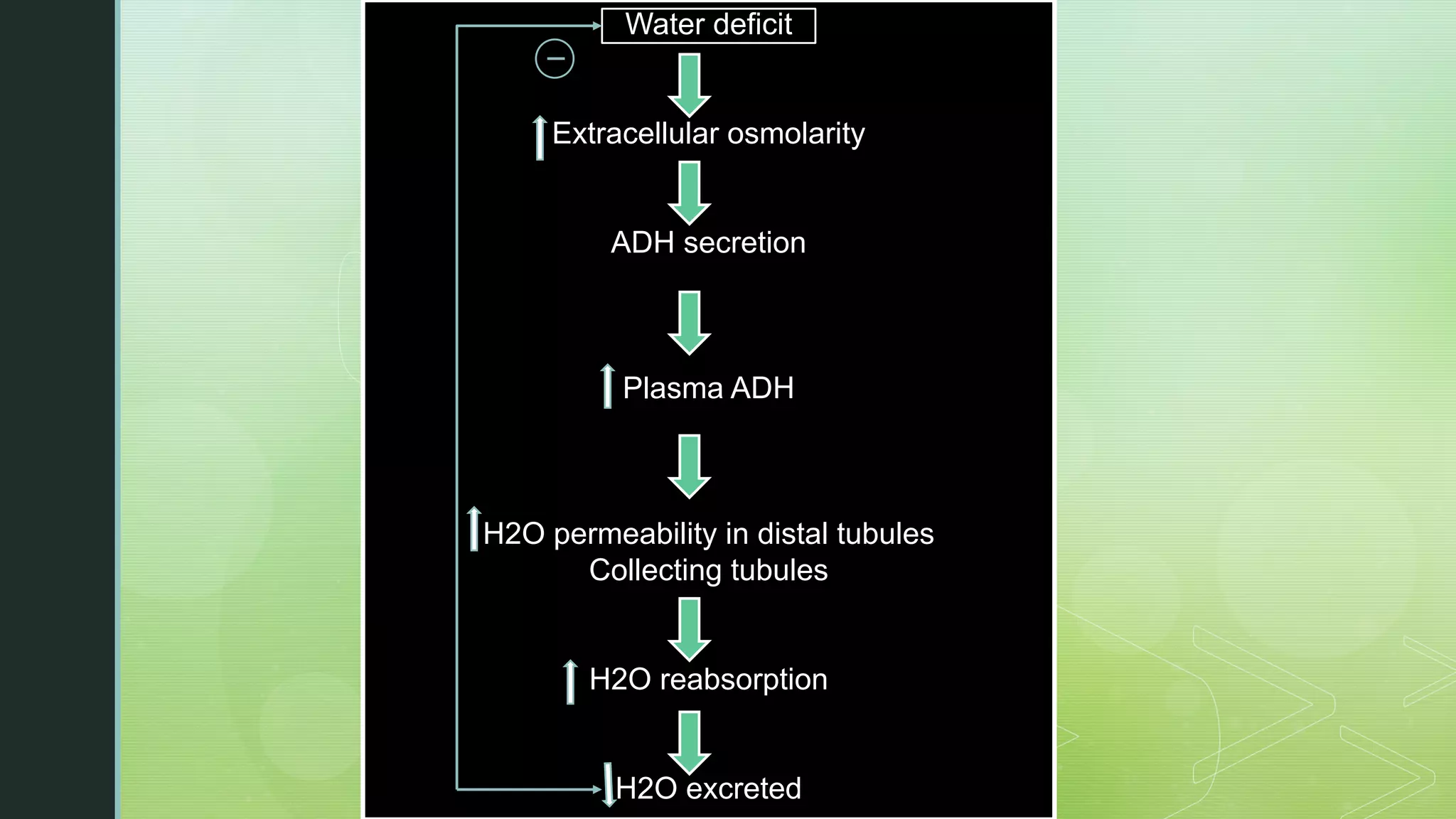
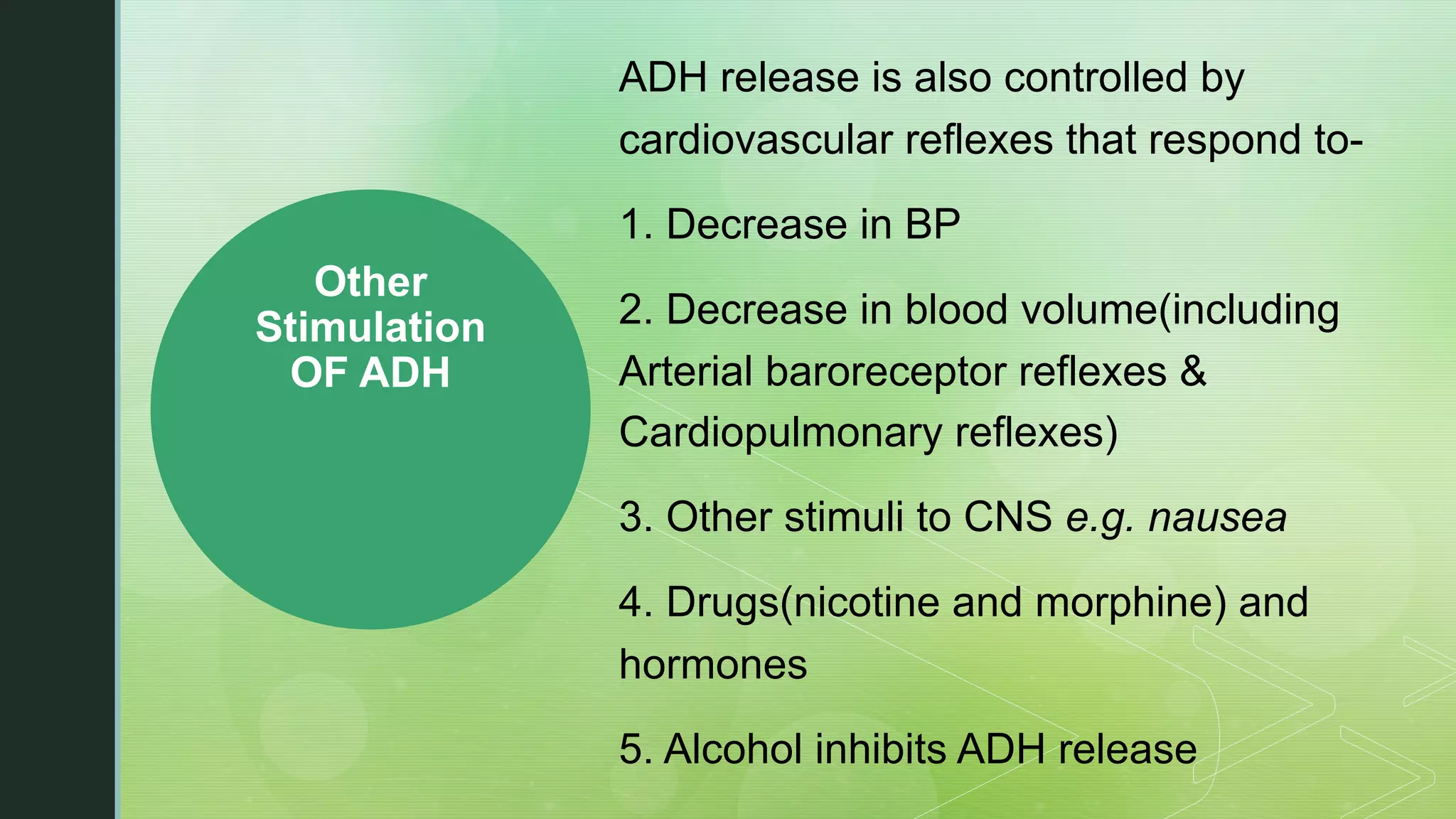
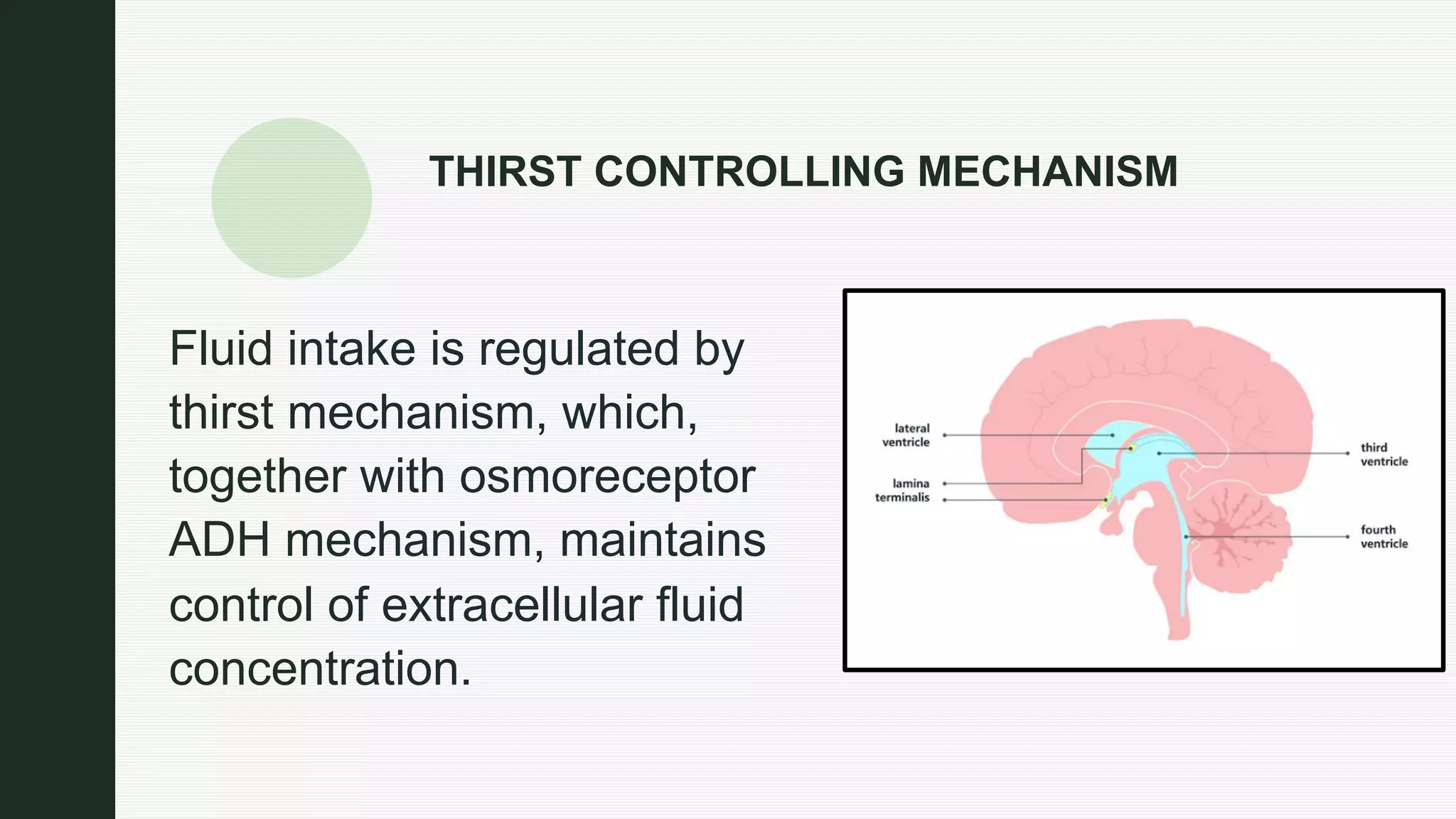
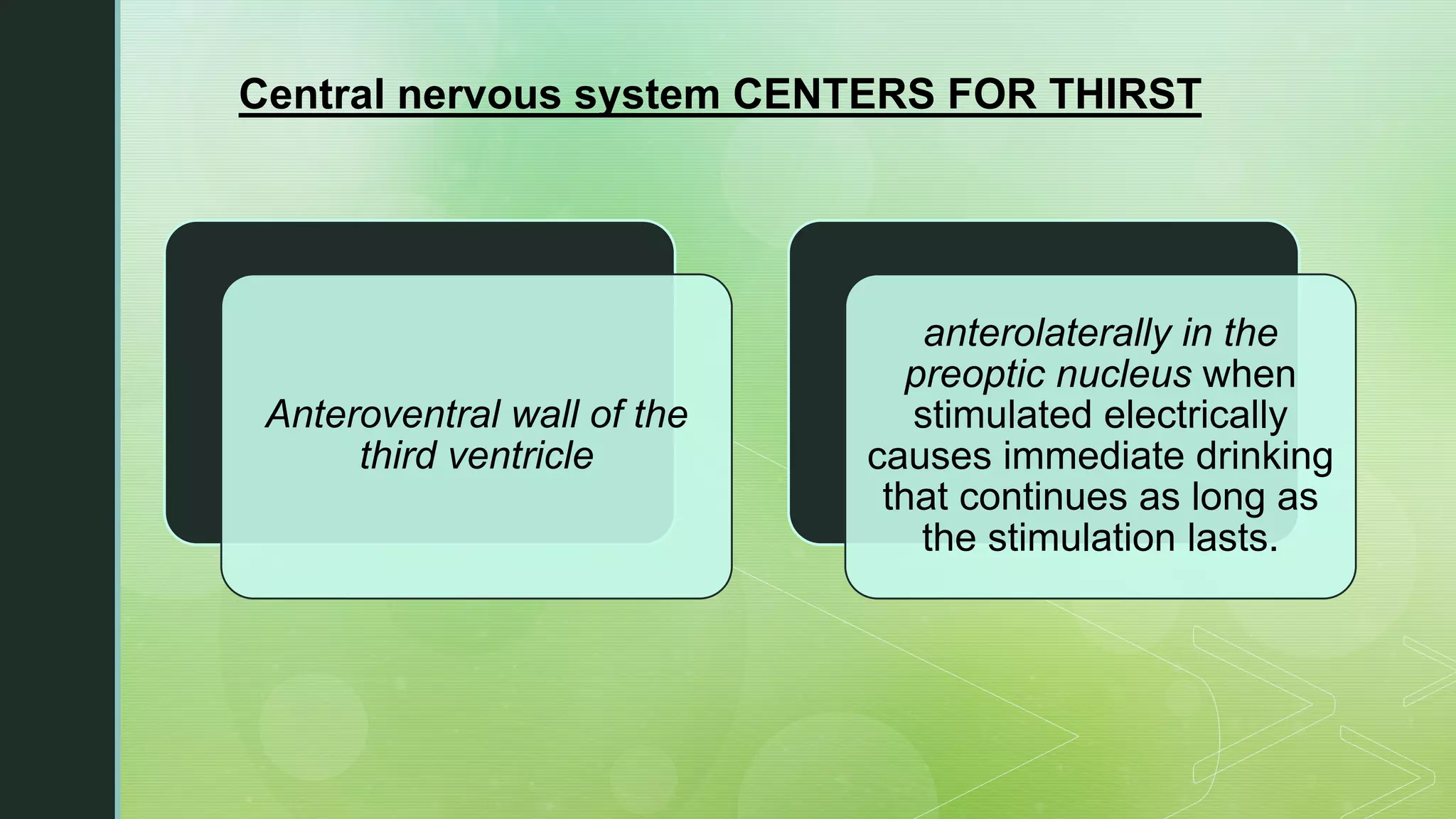
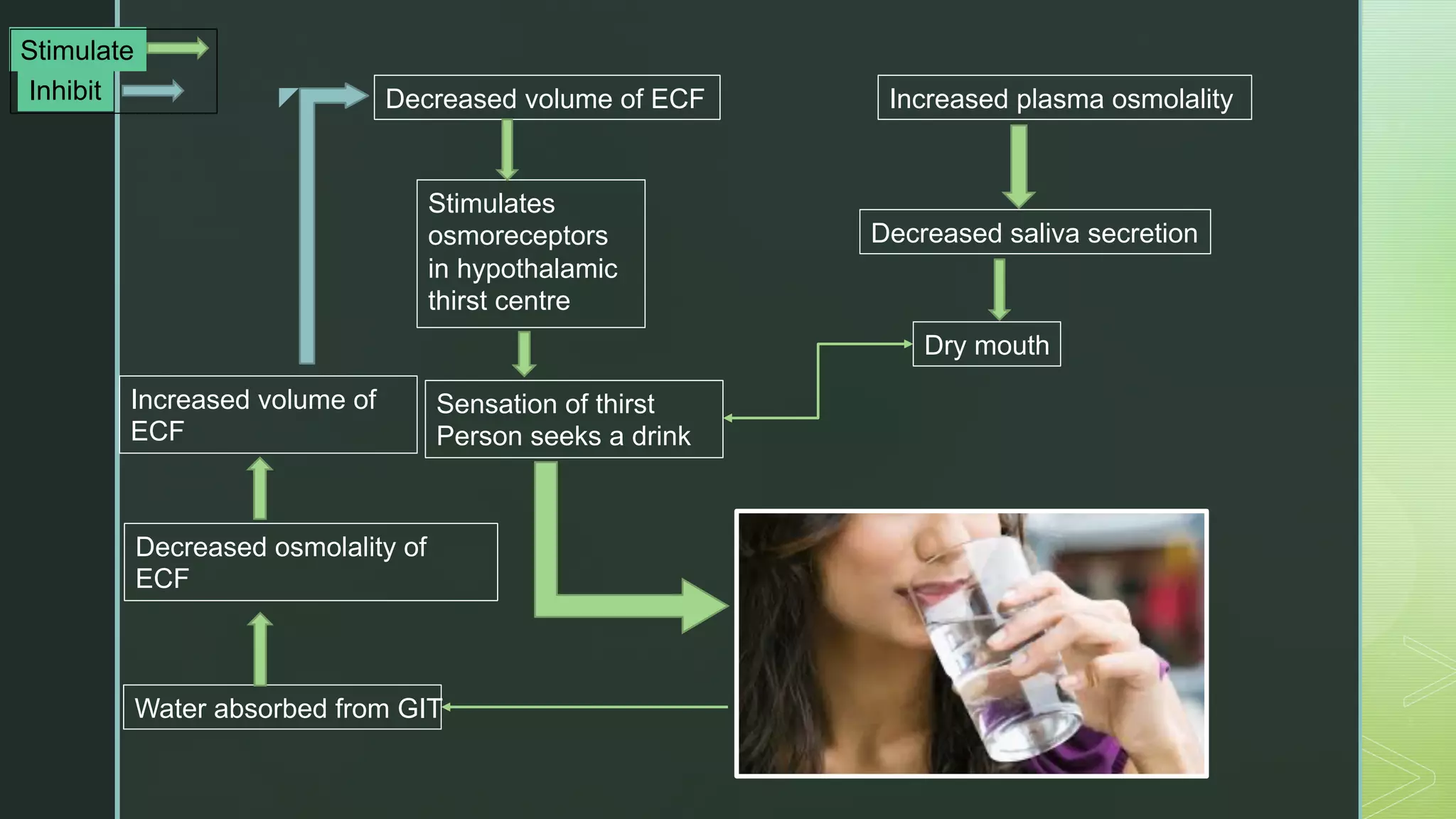
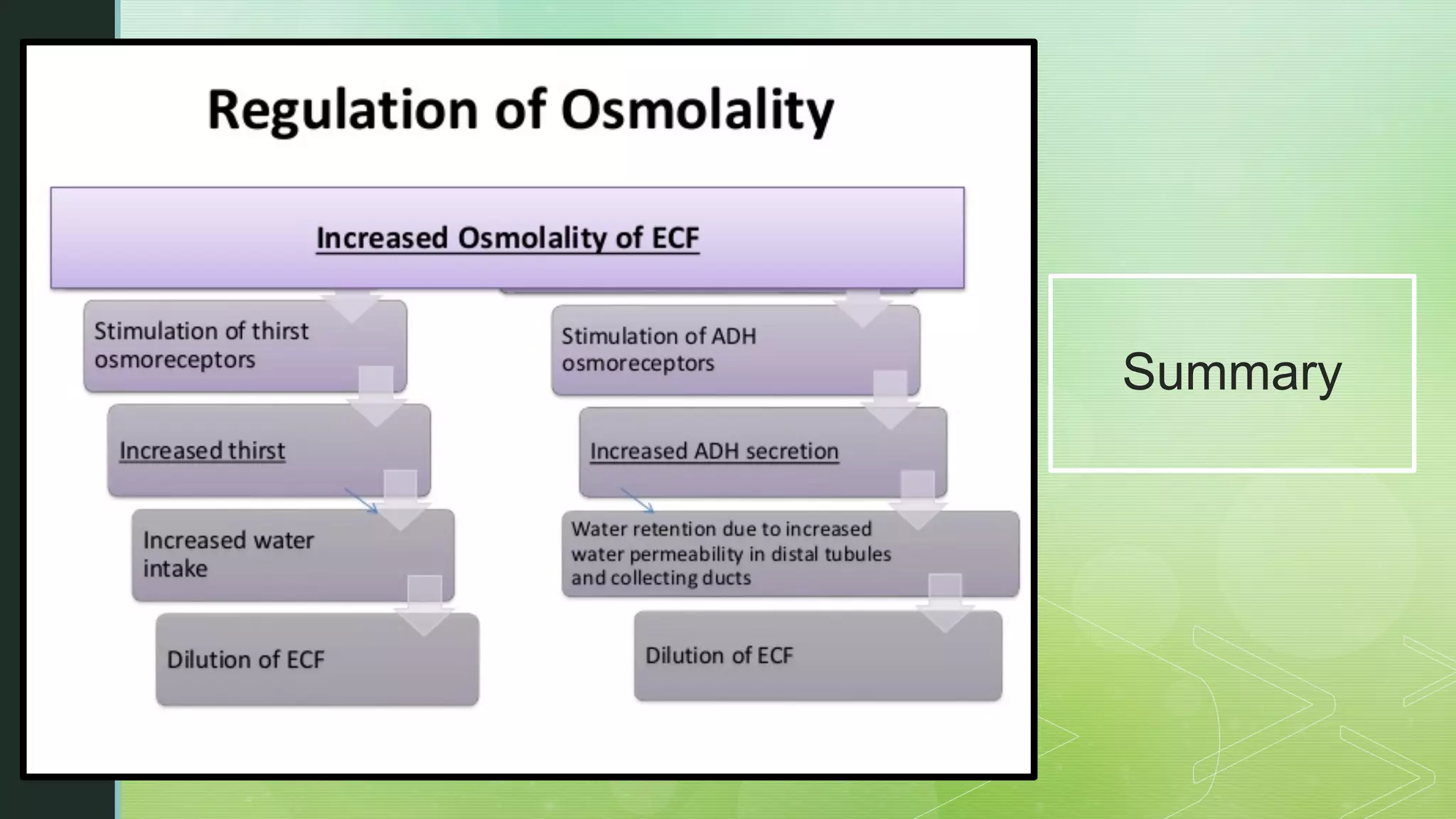
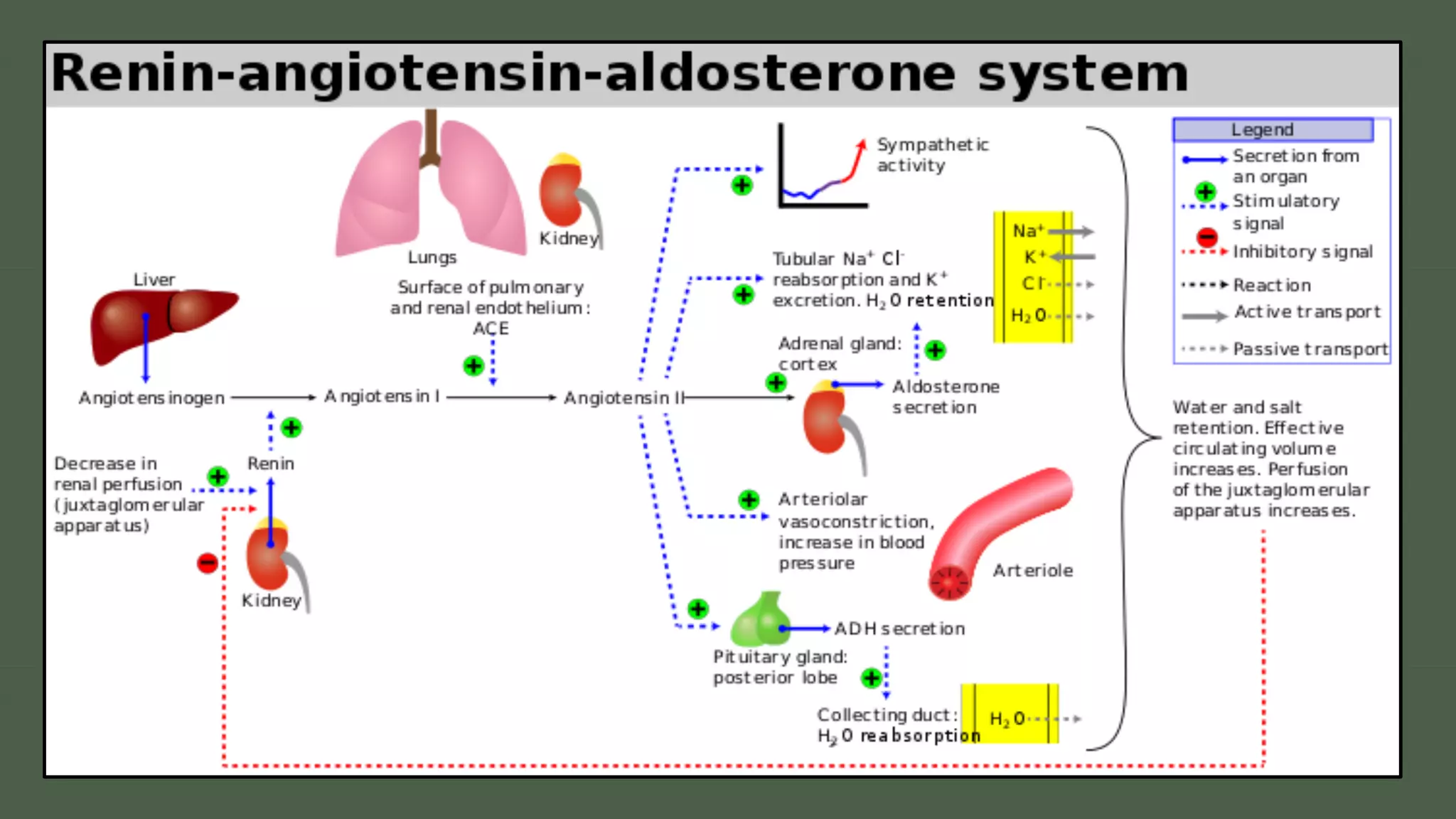
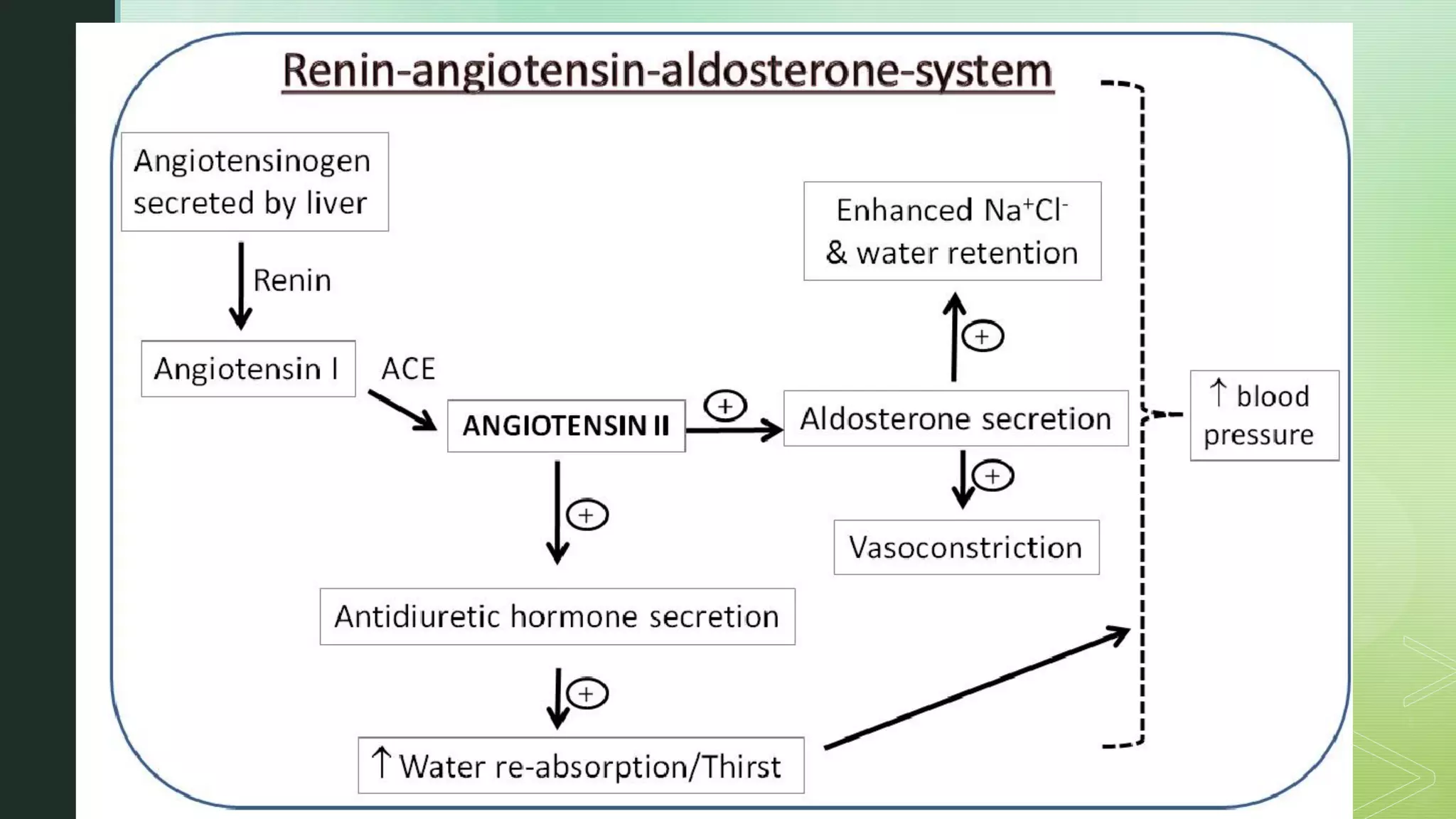
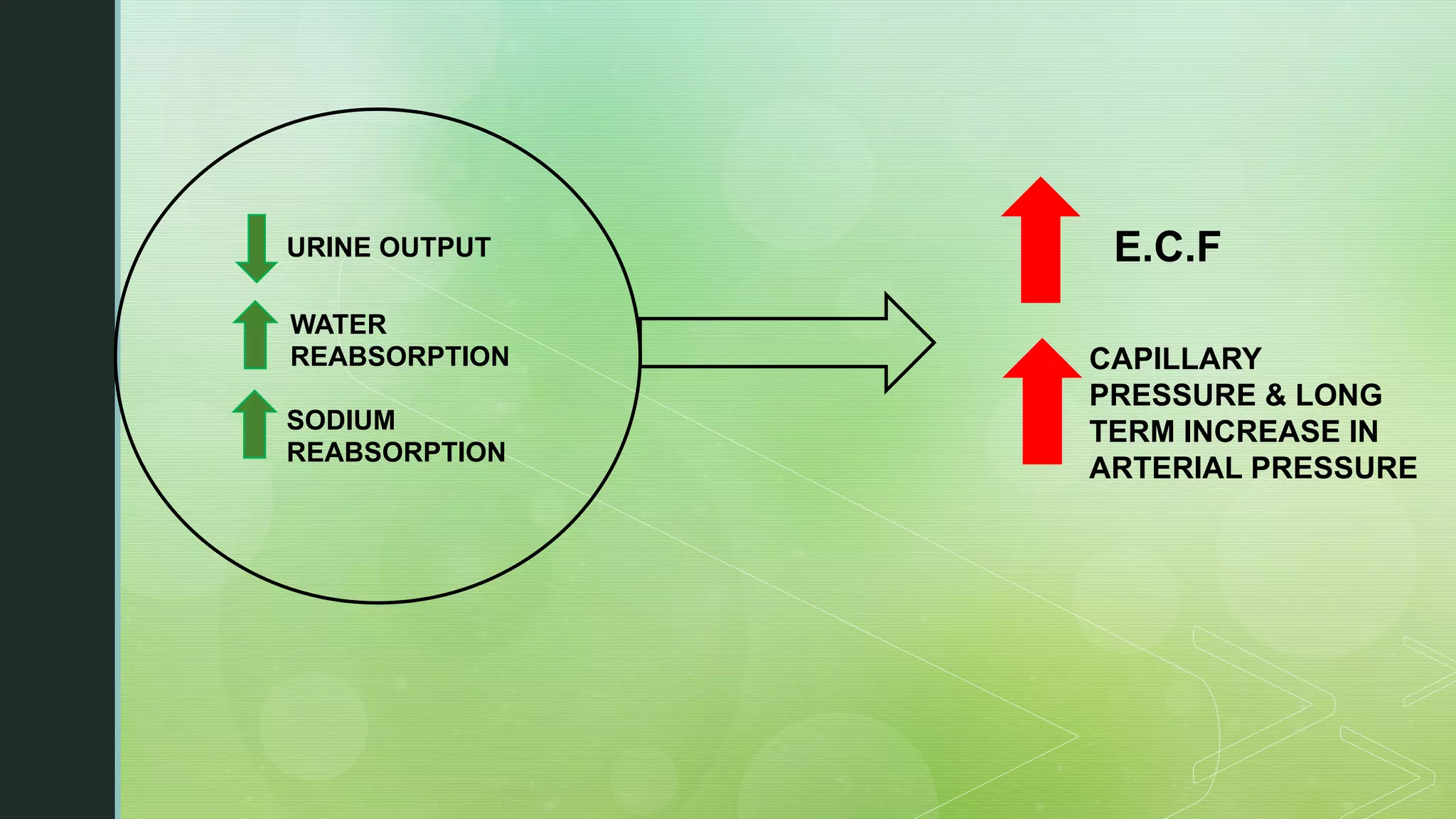
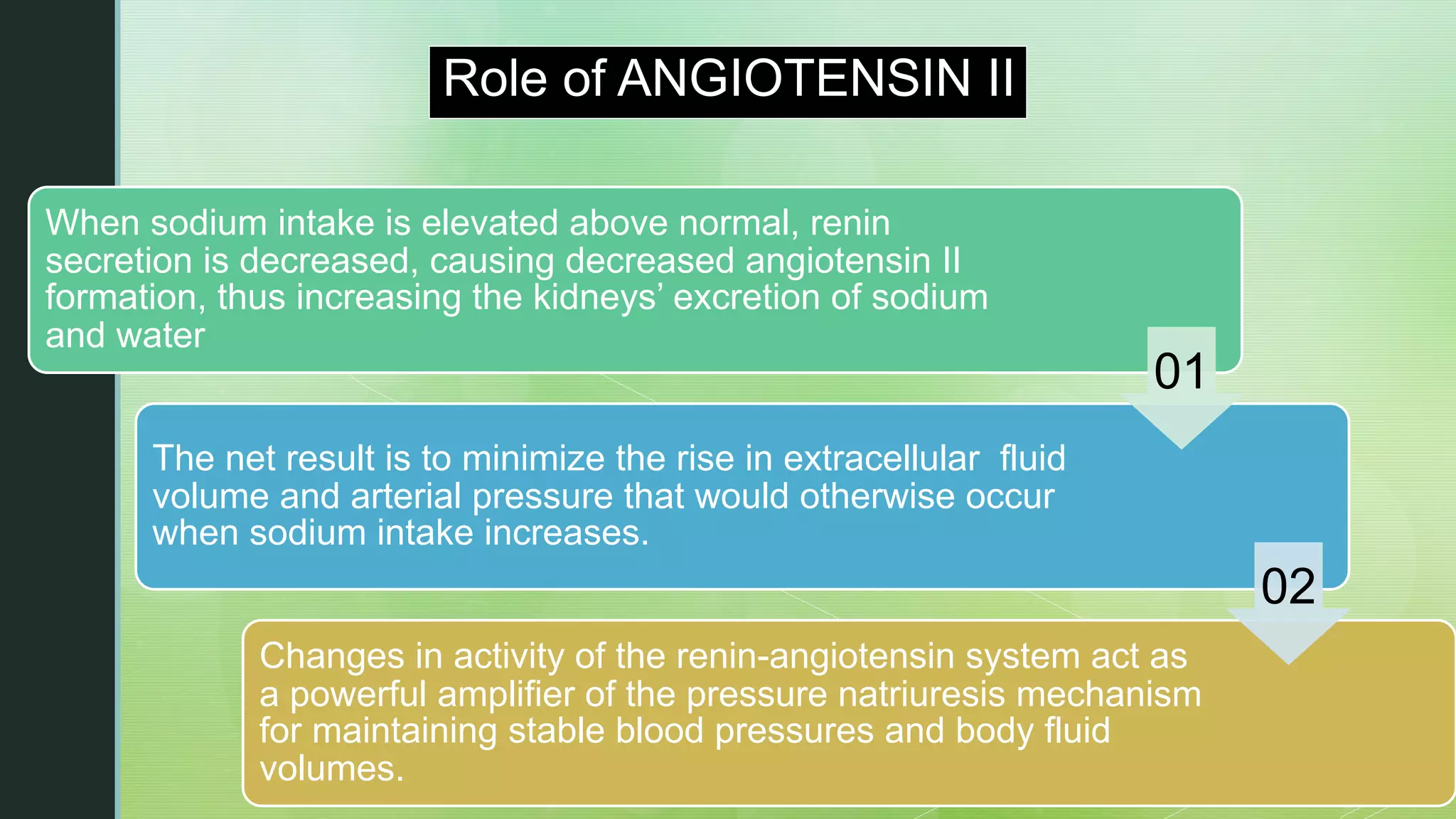
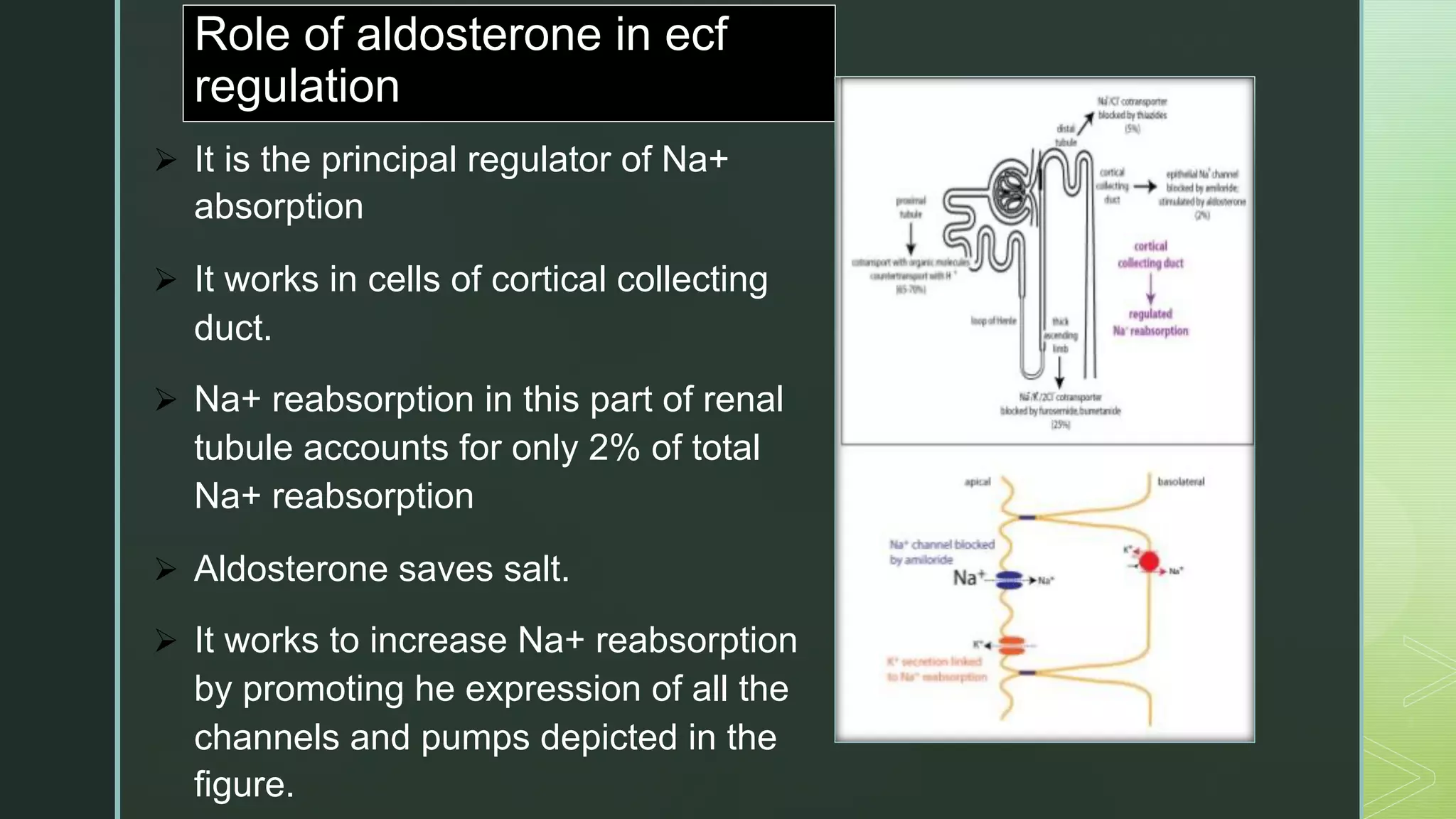
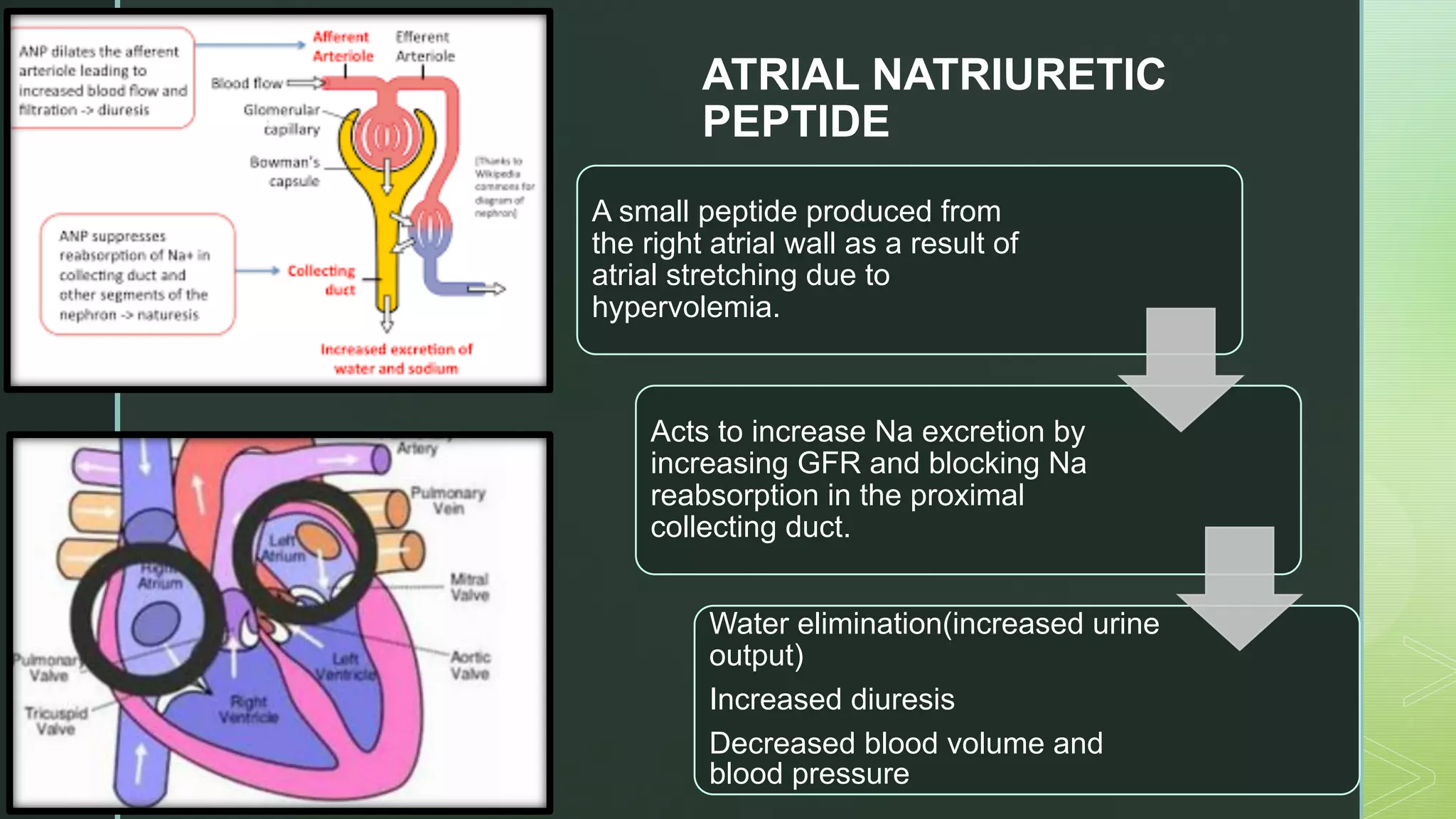
The document discusses the regulation of body fluids and osmolality, emphasizing the kidneys' crucial role in maintaining extracellular fluid volume to ensure proper blood pressure and tissue perfusion. It details the osmoreceptor-ADH system and thirst mechanism as primary regulators, along with the effects of various hormones such as aldosterone and atrial natriuretic peptide on sodium and water balance. Additionally, it covers clinical implications of conditions like hyponatremia and hypernatremia related to water and sodium imbalances.