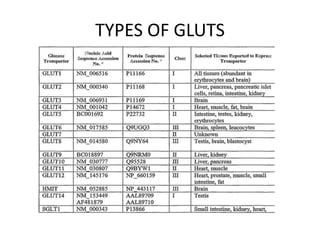
Glucose transporters (GLUTs) are essential membrane proteins that facilitate the transport of glucose across plasma membranes in eukaryotic cells, accounting for 2% of erythrocyte membrane proteins. Various types of GLUTs, such as GLUT1, GLUT2, GLUT3, and GLUT4, differ in their distribution, glucose affinity, and response to insulin, playing critical roles in glucose metabolism. Additionally, sodium-glucose cotransporters (SGLTs) actively transport glucose against a concentration gradient, with mutations in these transporters linked to metabolic disorders.