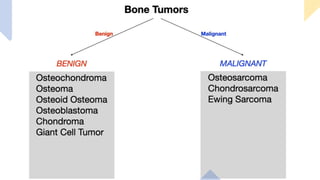
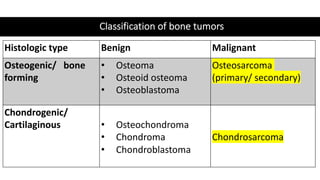
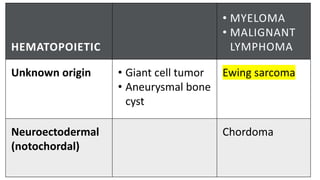
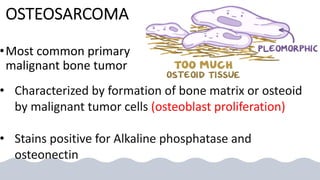
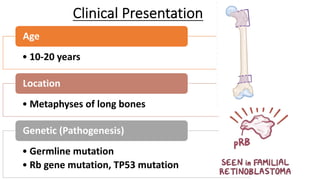
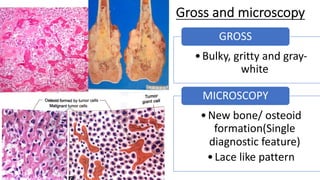
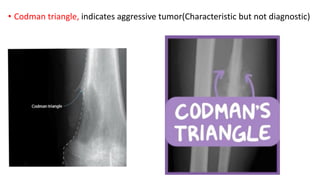
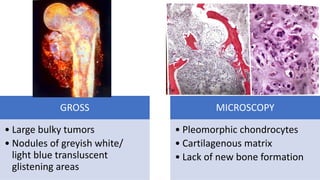
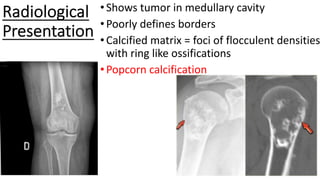
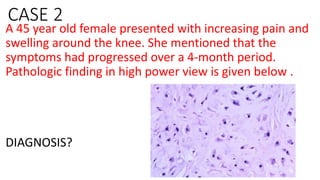
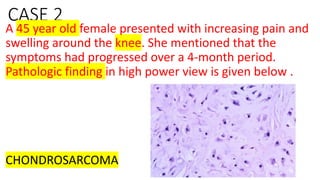
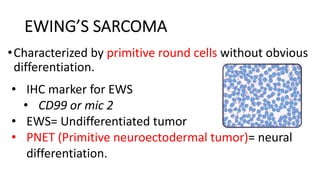
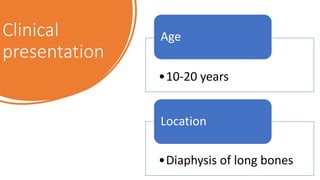
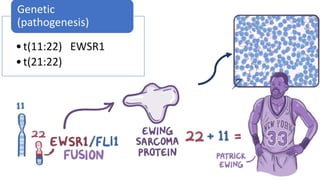
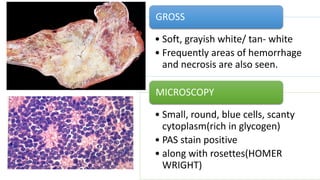
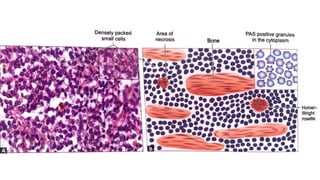
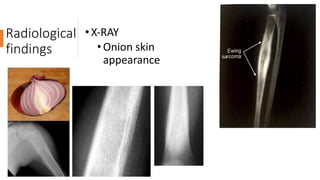
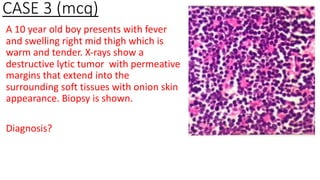
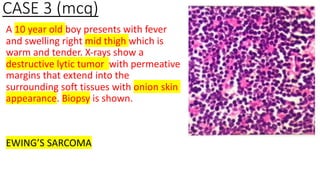
The document provides an overview of malignant bone tumors, focusing on classifications and specifics of various types such as osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, and Ewing sarcoma. It details clinical presentations, genetic mutations, histological features, and radiological findings associated with each tumor type. Additionally, the document includes multiple clinical case scenarios and questions related to the diagnosis of these bone tumors.