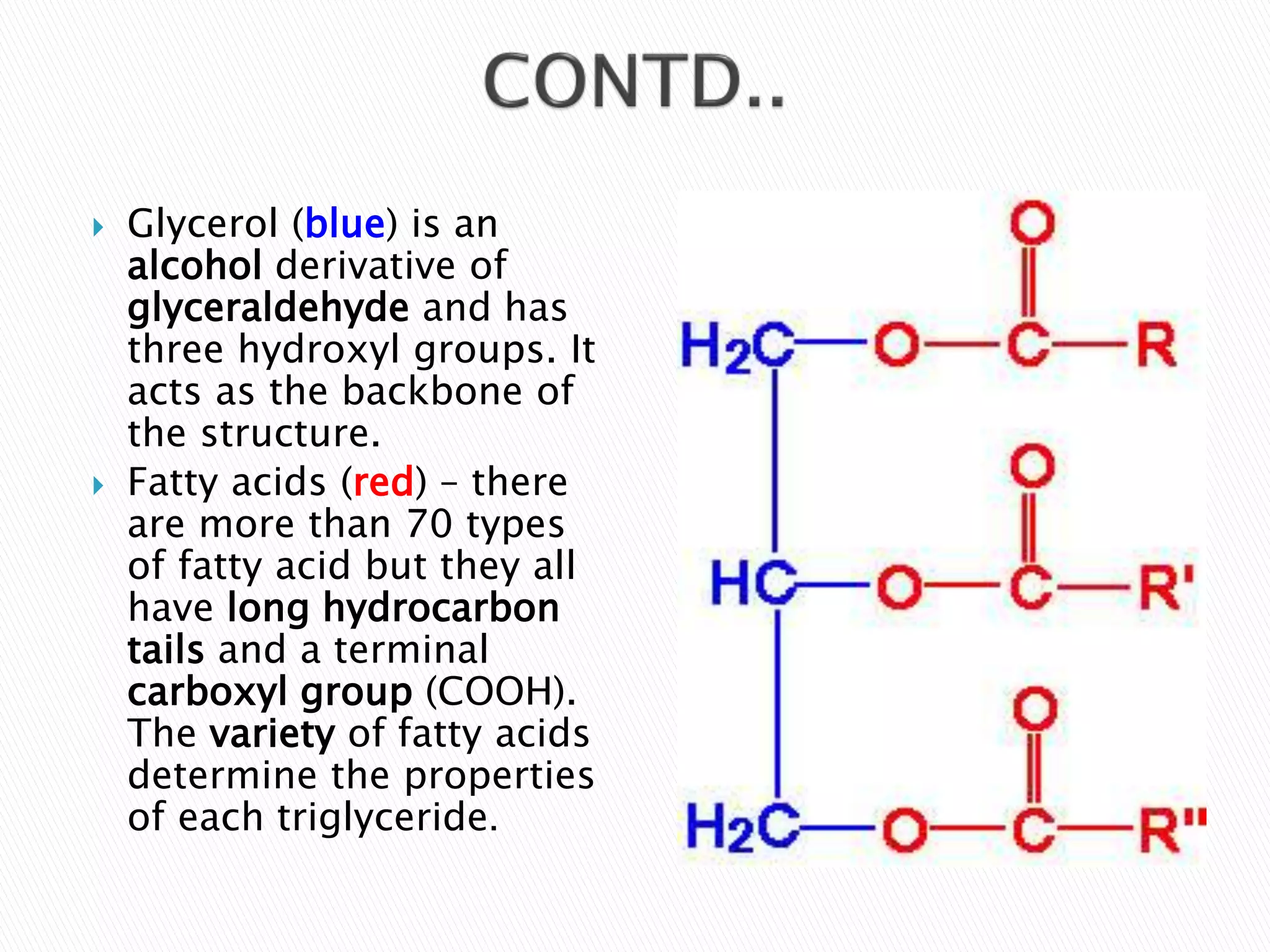
The document discusses lipids and triglycerides, explaining that triglycerides are composed of a glycerol molecule bonded to three fatty acids and serve as the main form of energy storage. It describes the processes of lipogenesis where triglycerides are synthesized from glucose, and lipolysis where triglycerides are broken down by hormones to release fatty acids. The summary also notes that triglycerides are stored in adipose tissue and mobilized from there to meet energy needs or deposited in the liver in conditions like fatty liver disease.