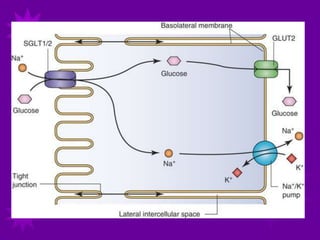
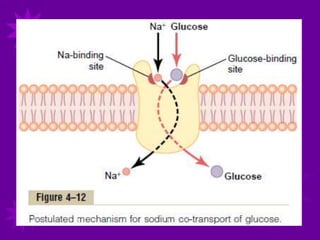
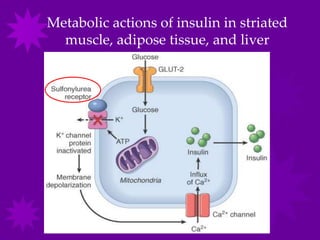
Glucose transport into cells is mediated by glucose transporter (GLUT) proteins. [1] There are five main GLUT transporters that are involved in glucose transport and each has a distinct tissue distribution and function. [2] GLUT transporters use a flip-flop mechanism to transport glucose across the cell membrane according to the concentration gradient. [3] Insulin regulates glucose transport by stimulating the translocation of GLUT4 and GLUT1 transporters from intracellular vesicles to the cell membrane, increasing the influx of glucose into cells.