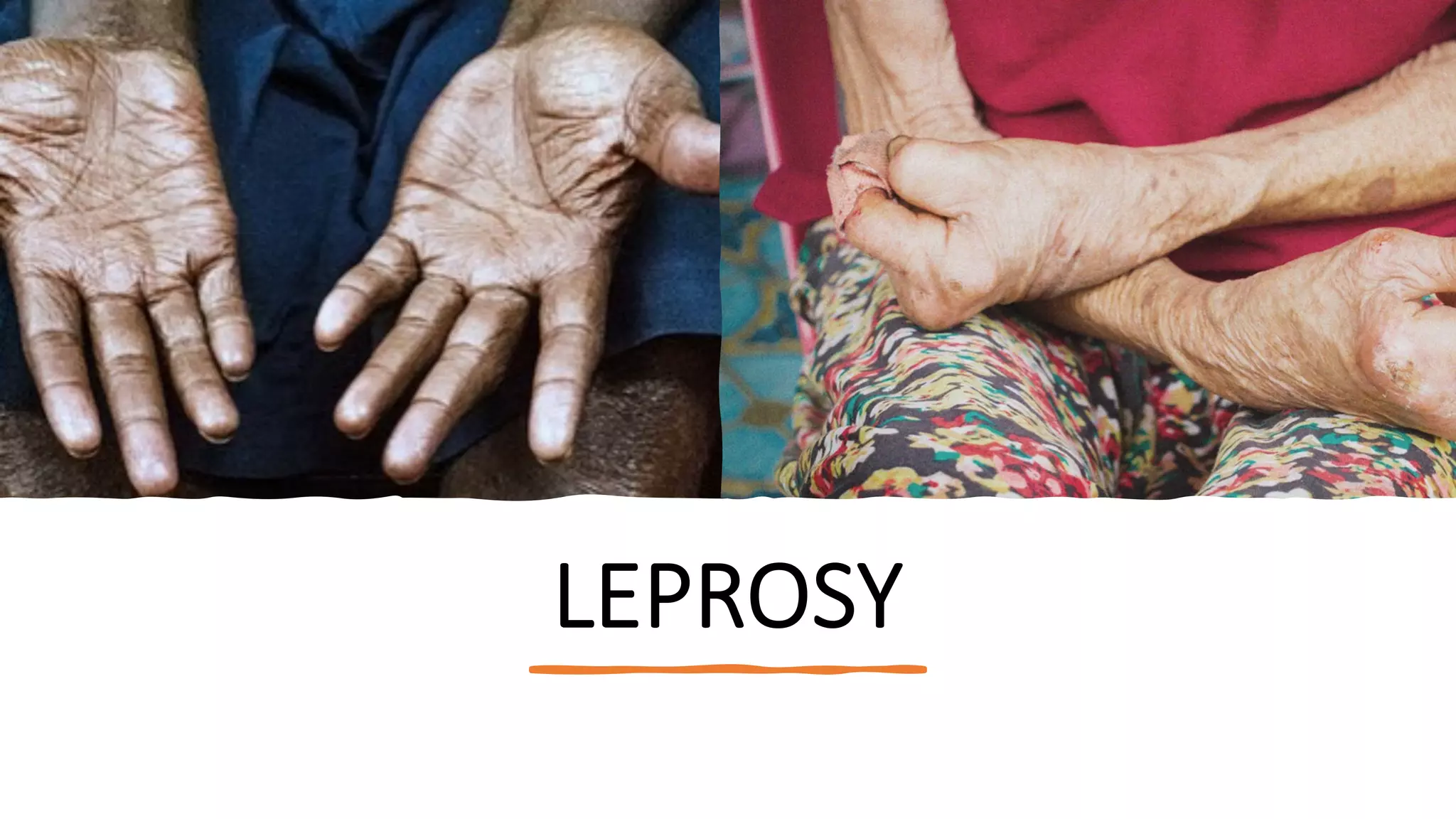
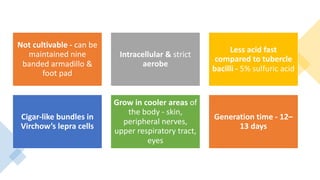
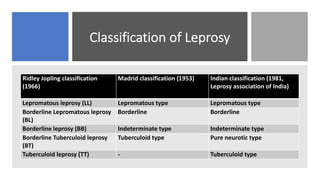
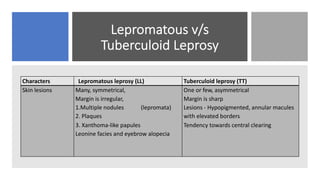
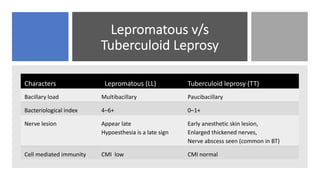
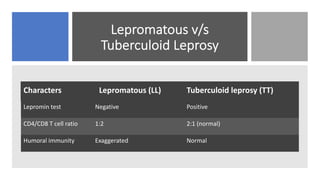
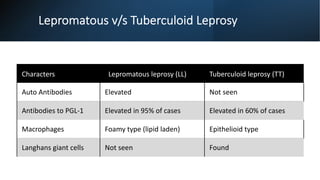
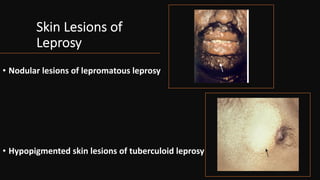
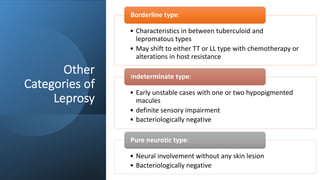
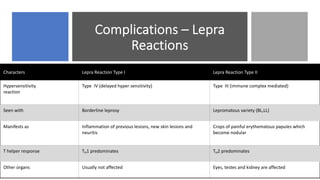
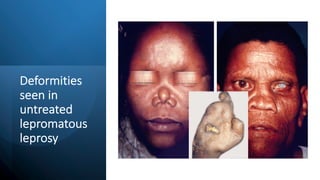
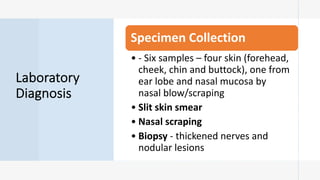
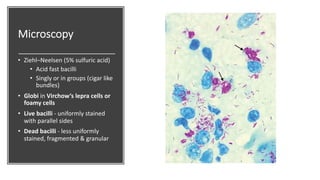
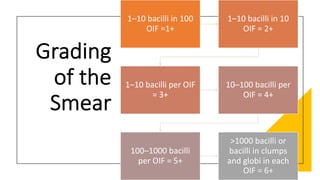
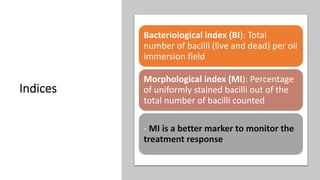
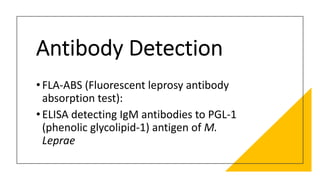
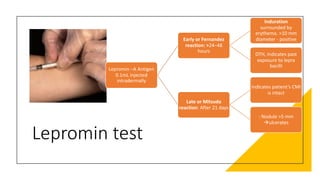
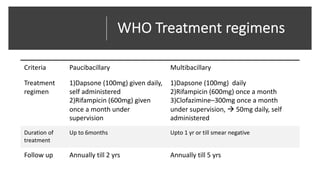
Leprosy, caused by Mycobacterium leprae, is a chronic bacterial disease recognized since ancient times, first identified by Hansen in 1873. It manifests in various forms, primarily lepromatous and tuberculoid, distinguished by skin lesions and immune response; treatment options vary based on bacillary load. Early diagnosis through laboratory techniques and careful management can prevent severe complications and deformities in affected individuals.