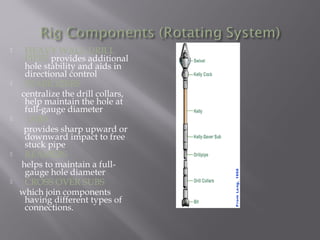
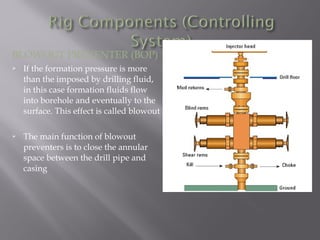
This document provides an overview of basic drilling engineering. It discusses the types of drilling including rotary, cable tool, and coil tubing drilling. It describes the historical development of drilling from the early 1800s to modern advances. It also outlines the key components of a conventional drilling rig including those used for hoisting, rotating, circulating, and controlling the drill string. Common drilling fluid types and their uses are also mentioned. Finally, it notes some factors that characterize a successful drilling operation.