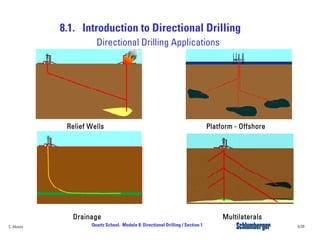
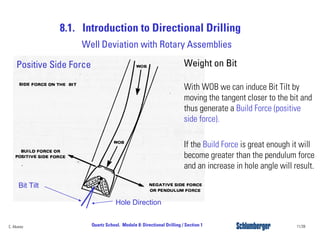
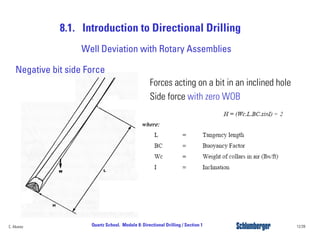
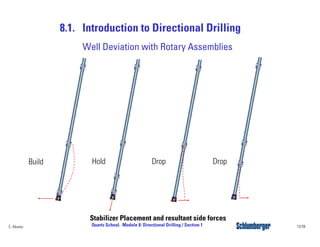
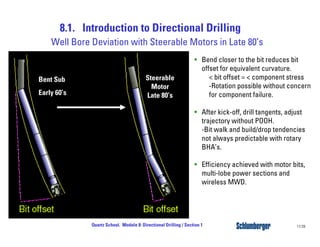
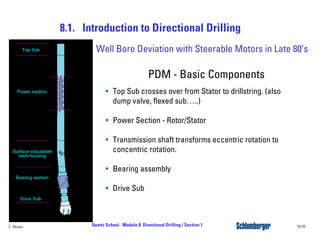
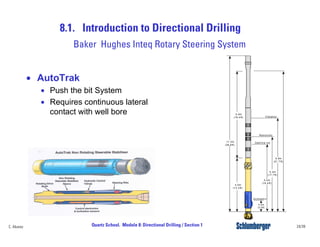
Directional drilling (DD) involves planning and drilling a wellbore along a planned path to a subsurface target location that is laterally and vertically offset from the surface entry point. DD is used in applications like reaching inaccessible locations, drilling around salt domes or faults, drilling relief wells, and creating multi-lateral wellbores. The evolution of DD technology over the decades has included early magnetic surveying tools, the introduction of mud motors in the 1960s for kick-offs, the development of steering tools in the 1970s, and more recent rotary steerable systems. Modern DD methods include using rotary assemblies, jetting, whipstocks, mud motors, and rotary steerable systems.