Embed presentation
Downloaded 38 times





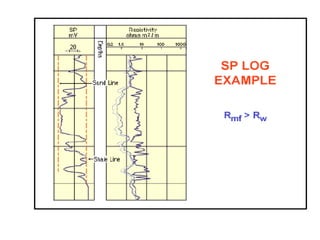
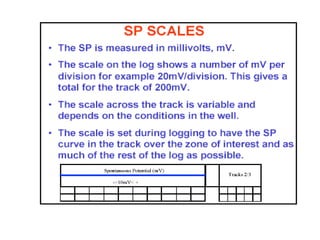


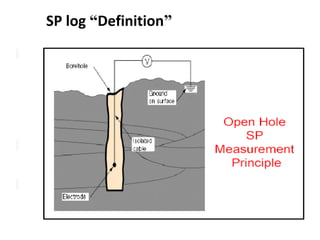



This document discusses electrical logs, including self potential (SP) logs. It defines the SP log as measuring the voltage difference between a downhole electrode and a surface electrode. The objectives are to understand the physical principles, interpretation for lithology and properties, and corrections needed. The SP log is used to identify impermeable zones like shale and permeable zones like sand, detect boundaries of permeable beds, and determine formation water resistivity and shale volume. It further explains the theory of measurement, factors affecting readings, and gives more details on the definition and general uses of SP logs.











