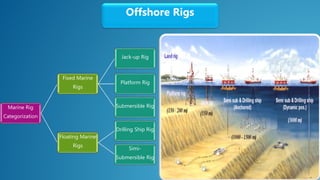
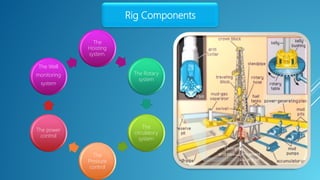
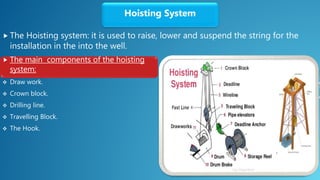
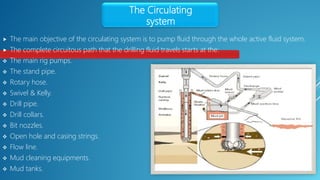
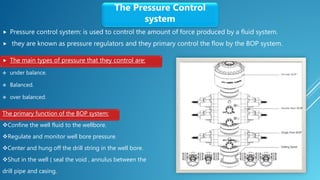
The document outlines rig design and selection, covering different types of rigs including onshore and offshore, and their respective depths and uses. It details rig components such as hoisting, rotary, circulating, pressure control, power control, and monitoring systems. Additionally, it describes various offshore rigs like jack-up rigs, platform rigs, and floating rigs, explaining their characteristics and operational depths.