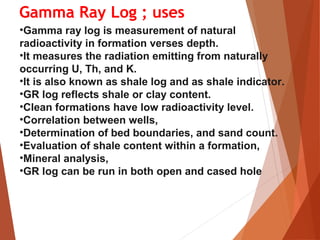
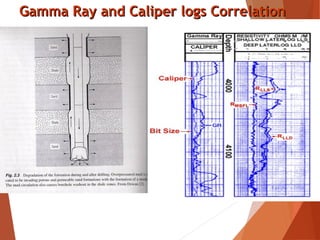
Gamma rays are high-energy electromagnetic waves emitted spontaneously by radioactive elements like potassium, uranium, and thorium found in rocks. A gamma ray log measures this natural radioactivity to indicate the presence of shale and clay in formations. The log uses a scintillation counter detector in the tool to measure gamma radiation from the formation. Radioactive elements tend to concentrate in shale and clay. Therefore, higher gamma ray readings indicate more shale, while clean formations like sandstone have lower readings. The log can be used to correlate between wells and evaluate shale content.