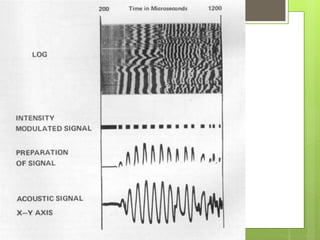
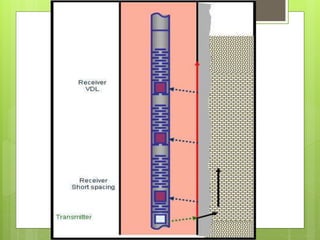
The document discusses variable density logs (VDL), which provide a color or grayscale representation of acoustic wave amplitude received during sonic or ultrasonic measurements. VDLs are commonly used alongside cement bond logs to provide better interpretation. It also discusses density logs, which measure formation density using gamma rays emitted from a borehole tool. Density is plotted on a bulk density scale and used to indicate porosity, derive total porosity, and identify lithology when used with neutron logs. Limitations include needing uniform mudcake/washouts less than 0.75 inches.