Directional Drilling
- 1. 1
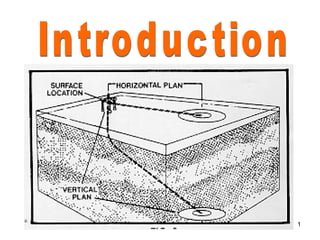
- 2. DIRECTIONAL DRILLING “Directional drilling is defined as an art and science involving deflection of a well bore in a specified direction in order to reach a predetermined object below the surface of the earth”. 2
- 3. APPLICATIONS OF DIRECTIONAL DRILLING 1. Multiple wells from single location. 2. Inaccessible locations. 3. Drilling to avoid geological problems. • Fault drilling. • Salt dome drilling. 4. Side tracking and straightening. 5. Relief well drilling. 6. Controlling straight holes. 7. Horizontal well. 8. ERD well. 9. Multilateral drilling. 3
- 4. NON PETROLEUM APPLICATIONS • Mining industry. • Construction industry. • Geo thermal engineering. 4
- 5. MULTIPLE WELLS FROM SINGLE LOCATION Optimum number of wells can be drilled from a single platform or artificial island. This greatly simplifies gathering systems and production techniques . 5
- 6. 6
- 7. INACCESSIBLE LOCATIONS If reservoir located under river beds, mountains, cities etc, this technique of directional drilling is used . 7
- 8. 8
- 9. DRILLING TO AVOID GEOLOGICAL PROBLEMS A. FAULT DRILLING: This eliminates the hazard of drilling a vertical well through steeply inclined fault plane which could slip and shear the casing. 9
- 10. 10
- 11. B. SALT DOME DRILLING To reach the producing formation which often lie underneath the over hanging cap of the dome, the well is first drilled at one side of the dome and is then deviated to producing zone to avoid drilling problems such as large washouts, lost circulation and corrosion . 11
- 13. SIDE TRACKING & STRAIGHTENING It is used as remedial operation either to side track obstruction by deviating the well bore away from obstruction by deviating the well bore back to vertical by straightening out crooked holes. 13
- 14. 14
- 15. RELIEF WELL DRILLING The technique is applied to the drilling of relief wells so that mud may be pumped into the reservoir of the uncontrolled well. 15
- 16. 16
- 17. ERD WELL Advantages: 1.Increased horizontal displacement from central platform. 2. Increased penetration length of reservoir. 3. Require less number of wells to develop a field. 4. Require less number of platforms to develop a field in offshore. 17
- 18. ERD WELL 18
- 19. 19
- 20. 20
- 21. HORIZONTAL WELL Advantages: 1.Increasing the drainage area. 2.Prevention of gas coning or water coning problems. 3.Increased penetration of the producing formation. 4.Increasing the efficiency of enhanced oil recovery ( EOR ). 5.Improving productivity in fractured reservoirs by intersecting a numbers of vertical fractures. 21
- 24. 24
- 25. Mutilateral. Drilling Multilateral well has been defined as a well that has more than one horizontal or near horizontal laterals drilled from single site and connected back to a single well bore. Applications . Greater reservoir exposure. · Drain more than one reservoir. · Exploit irregular reservoirs efficiently. · Speed up reservoir drainage. · 25
- 26. Mutilateral. Drilling · Reduction in drilling cost per unit length of the well bore contacting, the reservoir rock. · Ability to obtain a given length of horizontal well bore in reservoir where drag would perhaps limit the length of single horizontal well bore. · Reduction in number of slots and thus the number of production platforms. 26
- 28. NON PETROLEUM APPLICATIONS A. MINING INDUSTRY - Directional wells are used to produce methane gas that is contained in coal seams. - Methane presents a safety hazard and must be drained off before mining operations can begin. -In deep coal seams that are beyond the reach of conventional mining techniques, directional wells can be drilled for in situ gasification projects. 28
- 29. NON PETROLEUM APPLICATIONS A. MINING INDUSTRY 29
- 30. B. CONSTRUCTION INDUSTRY • A small diameter pilot hole is drilled in a smooth arc beneath the river until it immerges on the other side. This acts as a guide for the large diameter pipe forming the conduit. • The hole is drilled through soft sediments about 40’ below the river bed. This techniques has been used to cross rivers up to 200’ wide. 30
- 32. C.GEO THERMAL ENGINEERING High geothermal gradient found in some rocks( e.g. granite) can be harnessed to provide energy. Extracting the heat from this rocks requires the drilling of injection and production wells. 32
- 34. 34
- 35. 35
- 36. 36
- 37. 37
- 38. AZIMUTH 38
- 39. AZIMUTH 39
- 40. QUADRANTS 40
- 41. QUADRANTS 41
- 42. A radius of 100ft is commonly used as target zone depending on particular requirements e.g a relief well requires much smaller target in order to be effective. Smaller the target, greater number of correction runs. So longer drilling time , high drilling costs. So the target zone should be as large as the geologist/reservoir engineer can allow. DD’s job is then to place the wellbore within the target zone at minimum cost 42
- 43. 43
- 44. TYPES OF WELL PROFILES a. L- TYPE b. S- TYPE c. J- TYPE 44
- 45. TYPE I (BUILD AND HOLD OR ‘L’ TYPE) • This is the most common and simplest profile for a directional well. • The well is drilled down vertically to KOP, where the well is deviated to required inclination and further maintained to target. • Shallow KOP selected to reduce inclination. • This profile can be applied where large displacements are required at relatively shallow target depths. • Under normal condition inclination should be 15 to 55°. 45
- 46. 46
- 47. TYPE II (BUILD HOLD AND DROP OR ‘S’ TYPE) •This profile is similar to type-I up to tangential section. Here the profile enters a drop of section where inclination is reduced and in some cases becomes vertical as it reaches the target. •More torque and drag can be expected due to the additional bend. •Used where target is deep but horizontal displacement is relatively small. •It has also application when completing a well that intersect multiple producing zones. •Drilling of relief well where it is necessary to run parallel to wild well •Lease or target limitations. 47
- 48. 48
- 49. TYPE III (DEEP KICK OFF AND BUILD ‘J’ TYPE) • Initial deflection is started well below the surface and angle is built up to bottom. • It is used in particular situations like salt dome drilling, fault drilling and side- tracking or repositioning of target. • Disadvantages: • Formation may be harder & less responsive to deflection. • More tripping time to change BHA while deflecting. • BUR is more difficult to control. 49
- 50. 50
- 51. 51
- 52. 52
- 53. HORIZONTAL WELL PROFILES • HORIZONTAL WELLS ARE CATEGORIZED BY THE RADIUS OF CURVATURE ADOPTED TO MAKE THE WELL HORIZONTAL. THEY ARE ALSO CLASSIFIED BY BUILD UP RATES WHICH IS INVERSELY PROPORTIONAL TO THE RADIUS OF CURVATURE: – LONG RADIUS – MEDIUM RADIUS – SHORT RADIUS – ULTRA SHORT RADIUS 53
- 55. BUILDUP SECTION BETWEEN 1°- 6°/100’ OR RADIUS LENGTH BETWEEN 1000’-5000’ • ADVANTAGES:- – EASIER AS CONVENTIONAL DOWNHOLE HARDWARE IS USED – PDM MAY NOT BE REQUIRED – LOWER DOG - LEG SEVERITY GIVES LESS TORQUE AND DRAG – LONGER LATERAL SECTIONS(3500’ TO 5000’) (1000M TO 1500M) – EXTENDED REACH FROM SURFACE LOCATIONS – ACCOMMODATES FULL LOGGING ALL COMPLETION METHODS STIMULATION WORKOVER AND GASLIFT EQUIPMENT. • DISADVANTAGES:- – LONG RADIUS NECESSITATES BIGGER RIG, TOP DRIVE, LARGER PUMPS AND GREATER MUD MANAGEMENT CAPABILITIES – LONGER OPEN HOLE SECTIONS INCREASE RISK OF PIPE STICKING ,KICKS AND BOREHOLE DAMAGE – LESS PRECISE CONTROL OVER T.V.D – LITTLE USE IN SMALL LEASES BECAUSE OF LONG DISPLACEMENTS. Long Radius 55
- 57. • BUILDUP SECTION BETWEEN 8°-20°/100’ OR RADIUS LENGTH BETWEEN 716’ TO 286’(218M TO 87M) – ADVANTAGES:- • SUPERIOR IN PRECISION COMPARED TO LONG RADIUS • ACCOMMODATION OF NORMAL/SMALL SIZE M.W.D TOOLS • ABLE TO DRILL LONG HORIZONTAL SECTION UPTO 5000’ – DISADVANTAGES:- • TORQUE AND DRAG HIGHER THAN LONG RADIUS • LIMITATION IN COMPLETION AND WORKOVER OPERATIONS Medium Radius 57
- 59. • Buildup section between 1°-3.5°/1’ and radius length between 57’ to 16’ – Advantages:- • Precise vertical placement of horizontal drain • KOP below fluid contacts results less risk of poor isolation – Disadvantages:- • Requires customized drilling equipment • No control over bore hole azimuth (within 20°) • Limited to open hole completion • No coring and logging services Short Radius 59
- 61. 61
- 63. DROPPING ROTARY ASSEMBLY • Angle dropping principle is based on pendulum principle • Placing a stabilizer above the point of tangency causes a reverse action and the assembly becomes an angle dropping assembly. • The section of drill collars below the stabilizer bends and sags downwards due to pull of gravity, somewhat like the action of a pendulum. so this assembly is often called as pendulum assembly.
- 64. The stabilizer is normally placed 30’, 60’ or 90’ above the bit. As the distance increases, more bend occurs and more drill collar weight forces the bit to the lower side of the hole resulting in increase of angle dropping rate. Tentative guideline 30’: 0.25-.75°/100’ 60’: 0.5-1.25°/100’ 90’: 0.5-2.5°/100’ Variables for dropping rate • Stiffer the drill collar, less the bending rate. • More the drift angle in the well, greater the dropping rate • Higher the WOB, lesser the angle drop rate • All the variables equal (drift angle, WOB etc., increase in rotary speed will result in increase in angle drop. The exact position of stabilizer depends on drill collar size and weight, hole diameter, inclination and WOB The is adjusted with subs and pony drill collars to increase or decrease the rate of drop
- 65. HOLDING ASSEMBLY: • Packed hole assemblies are used when it is necessary to keep angle and direction change to a minimum • In directional wells, packed hole assemblies are used after the maximum drift angle is reached and it is desired to maintain the angle. • The stiff rigid assembly fits closely in the hole and is held in place by multiple stabilizers. • The stabilizers are normally placed at 0-10’-40’ or 0-10’-40-70’ above the bit. • The rigidity and stiffness force the bha to remain in the same relative position. • Its efficiency increases by increasing stiffness and rigidity
- 66. Given set of conditions determining hole size, d/collar size, inclination, WOB, to lesser degree RPM , these two stabilizer systems will have greater build tendency from 4 to 1.
- 67. Three stabilizer packed hole assemblies are designed to hold the bit on course. These assemblies may build or drop gradually due to local conditions and may be fine tuned by the use of under gauge stabilizers.
