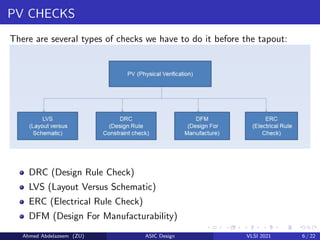
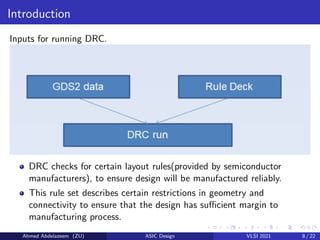
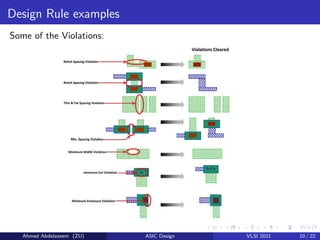
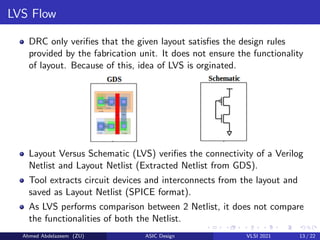
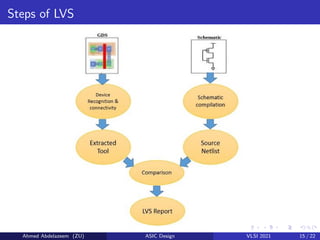
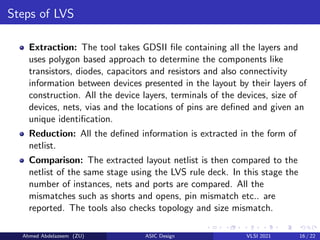
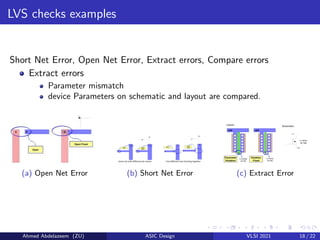
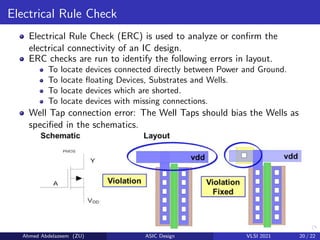
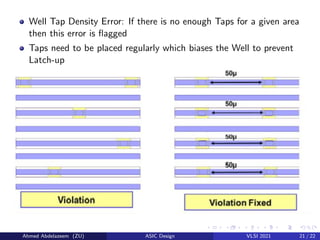
The document provides an overview of physical design verification in integrated circuit layout, emphasizing the importance of design rules checks (DRC), layout versus schematic (LVS), and electrical rule checks (ERC) to ensure manufacturability and correct functionality. It details the various inputs, checks, and tools used in the verification process, including examples of typical errors encountered. The content serves as a guide for ASIC design verification practices, including necessary steps for successful validation before production.