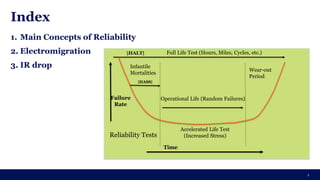
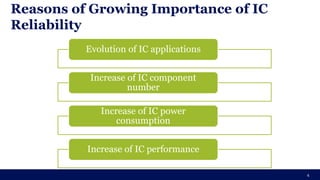
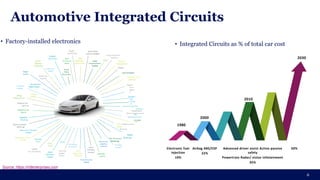
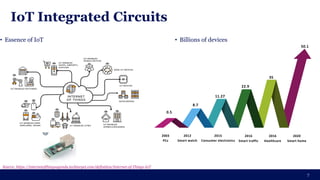
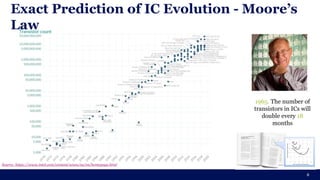
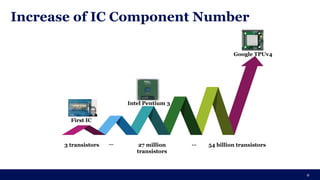
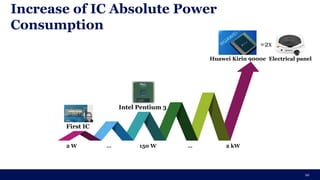
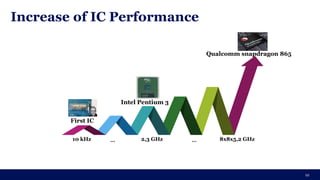
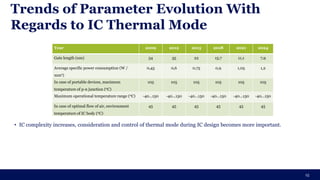
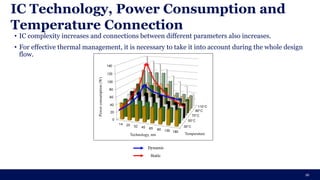
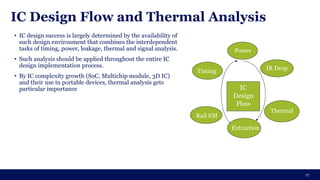
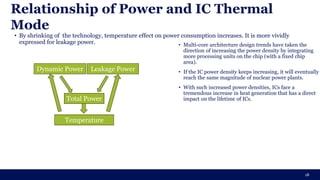
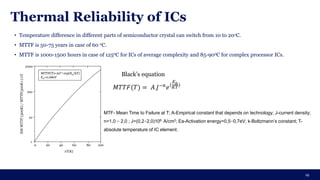
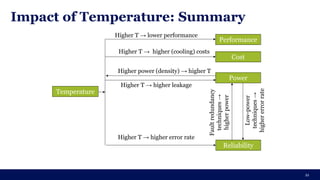
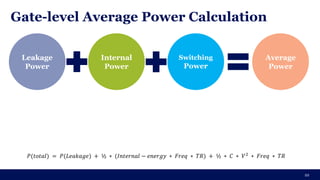
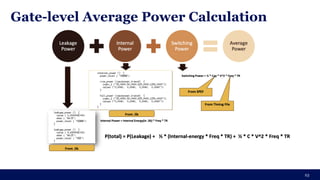
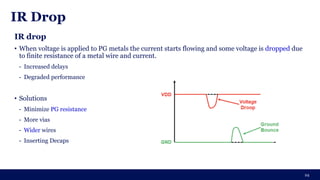
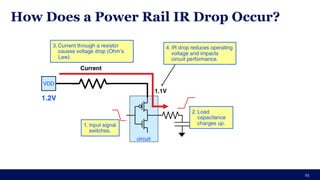
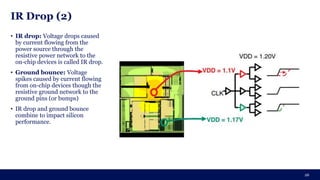
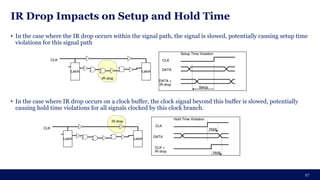
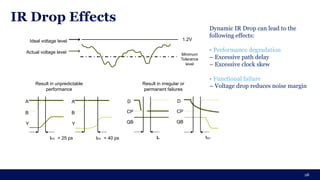
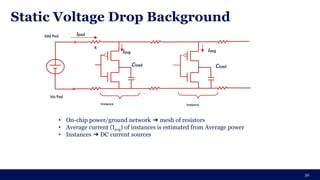
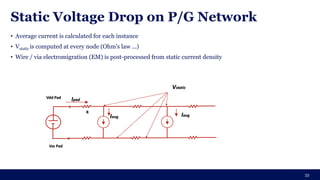
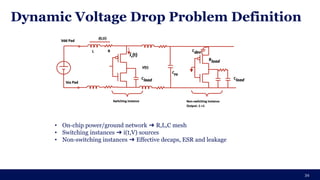
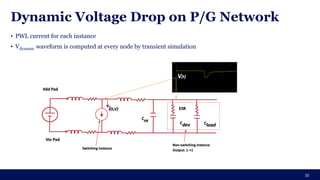
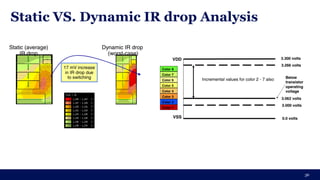
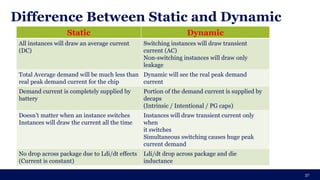
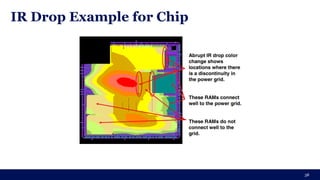
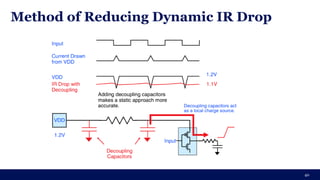
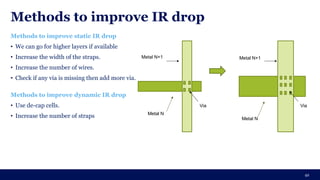
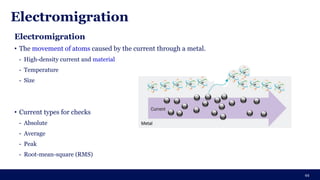
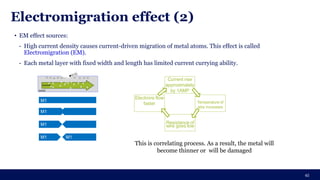
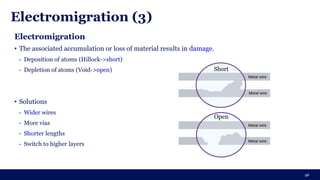
The document discusses the importance of Integrated Circuit (IC) reliability, detailing factors such as electromigration, IR drop, aging, and design complexity. It emphasizes the growing significance of IC reliability due to increased device complexity and performance, particularly in automotive and IoT applications. Additionally, it outlines various reliability tests and the impact of temperature on IC performance and lifespan.