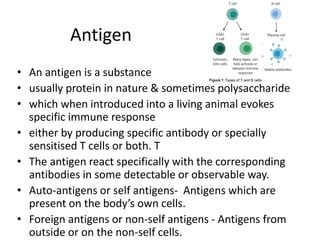
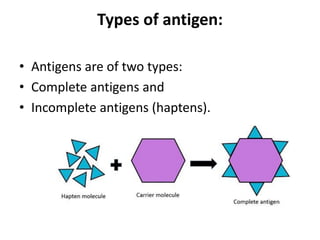
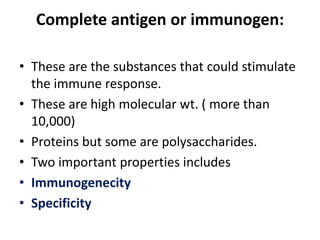
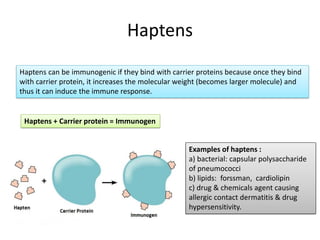
An antigen is a protein or polysaccharide that triggers a specific immune response in a living organism, leading to the production of antibodies or sensitized T cells. Antigens can be categorized into complete antigens, which induce an immune response, and incomplete antigens (haptens), which require binding to a carrier protein to become immunogenic. The document also discusses characteristics and determinants of antigenicity, including foreignness, size, chemical composition, and physical form.