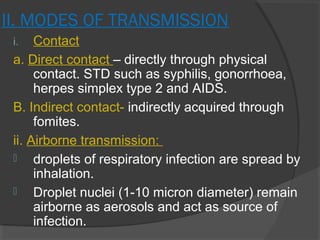
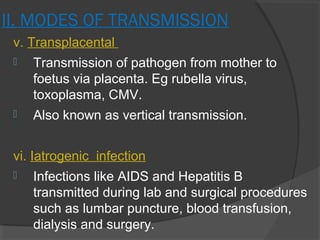
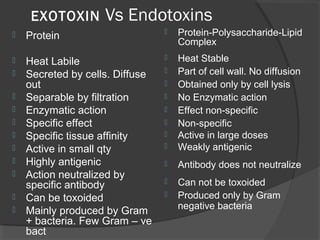
This document discusses various aspects of infectious diseases including definitions, classification, transmission, and pathogenic mechanisms. It defines infection as the lodgement and multiplication of an infectious agent in the body. Infections are classified as endogenous or exogenous depending on the source, and as acute, chronic, latent, or atypical depending on clinical manifestations. Microbes can be transmitted via contact, airborne droplets, ingestion, inoculation, transplacentally, or through iatrogenic means. Pathogenicity is determined by microbial adhesion, invasiveness, antiphagocytic factors, and toxins. Exotoxins are often heat-labile proteins that can be converted to toxoids.