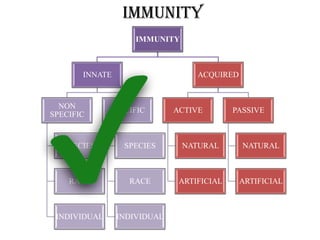
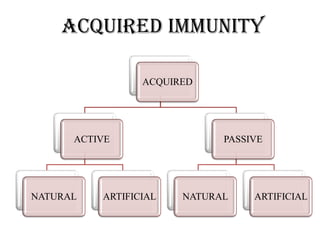
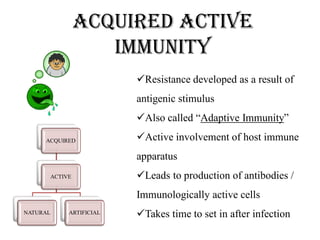
This document discusses different types of immunity, including innate immunity, acquired immunity, and the differences between active and passive immunity. It provides details on natural and artificial active immunity, as well as natural and artificial passive immunity. Various methods of conferring immunity are described, such as vaccination, administration of antibodies, and herd immunity. Measurement of immunity through antibody detection and cell-mediated immunity tests are also summarized.