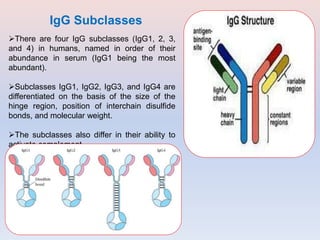
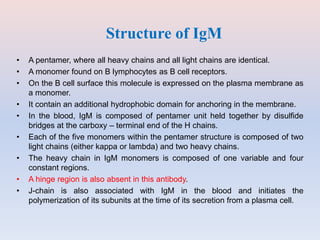
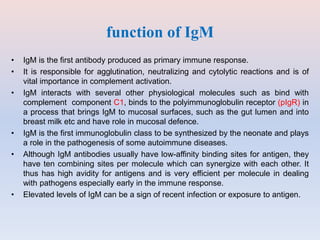
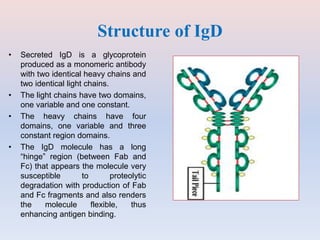
- Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are Y-shaped proteins that the immune system uses to identify and neutralize foreign objects like viruses and bacteria. They recognize and bind to a unique molecule on the pathogen called an antigen.
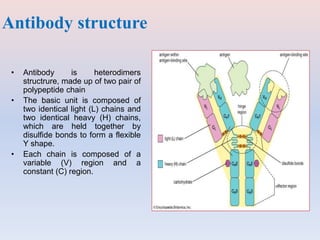
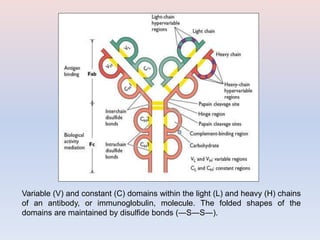
- Antibodies are made up of two pairs of polypeptide chains called light and heavy chains that form a flexible Y shape. The variable regions at the ends of the Y determine what antigen the antibody binds to.
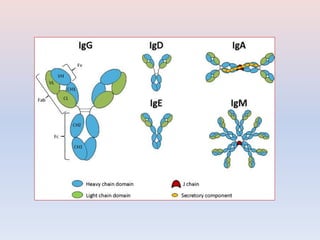
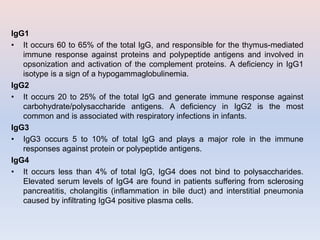
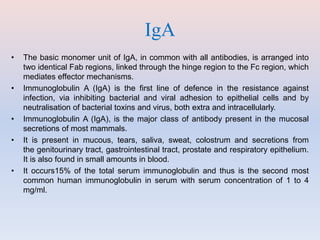
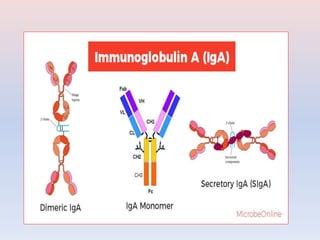
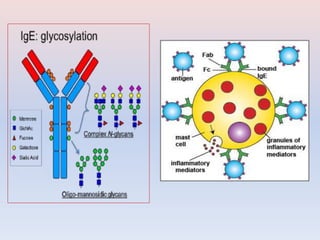
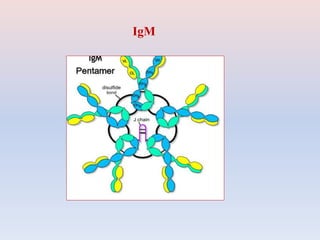
- There are five major classes of antibodies - IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE, and IgD - that have different structures and functions like defending against pathogens in the blood or mucous membranes. IgG is the most common antibody found in