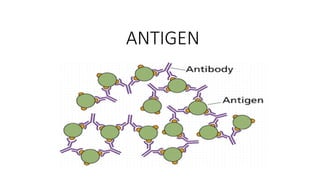
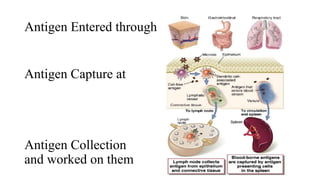
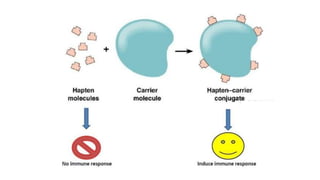
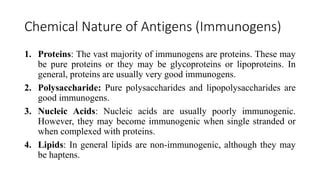
Antigen is a substance that induces an immune response through the formation of antibodies or activation of T cells. Antigens can be proteins, polysaccharides, nucleic acids, or lipids. Immunogens are antigens that are capable of inducing an immune response on their own due to their large size, while haptens require a carrier molecule. Antigenicity refers to the ability to bind antibodies, while immunogenicity is the ability to induce an immune response. Factors like molecular size, chemical composition, dose, and route of administration can influence a substance's immunogenicity. Adjuvants are substances that enhance the immune response to an immunogen when used together.